| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 18(4); 2012 > Article |
ABSTRACT
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is an RNA virus that is unable to integrate into the host genome. However, its proteins interact with various host proteins and induce host responses. The oncogenic process of HCV infection is slow and insidious and probably requires multiple steps of genetic and epigenetic alterations, the activation of cellular oncogenes, the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, and dysregulation of multiple signal transduction pathways. Stellate cells may transdifferentiate into progenitor cells and possibly be linked to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Viral proteins also have been implicated in several cellular signal transduction pathways that affect cell survival, proliferation, migration and transformation. Current advances in gene expression profile and selective messenger RNA analysis have improved approach to the pathogenesis of HCC. The heterogeneity of genetic events observed in HCV-related HCCs has suggested that complex mechanisms underlie malignant transformation induced by HCV infection. Considering the complexity and heterogeneity of HCCs of both etiological and genetic aspects, further molecular classification is required and an understanding of these molecular complexities may provide the opportunity for effective chemoprevention and personalized therapy for HCV-related HCC patients in the future. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of the mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by HCV infection.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is an RNA virus that is unable to integrate into the host genome. However, its proteins interact with various host proteins and induce host responses that potentially contribute to the malignant transformation of cells. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development is usually a final consequence of sequential progression of chronic fibrosing liver diseases, and HCC usually occurs only after establishment of liver cirrhosis in HCV-infected individuals.1 In cirrhotic patients with HCV infection, the annual HCC development rates range between 1-7%.2
The incidence of HCV-related HCC continues to rise and is estimated to remain high in the next two decades.3 Although epidemiological evidence has suggested a clear, close relationship between HCV infection and HCC,4,5 the prevalence of HCV infection in HCC patients differs noticeably between geographical regions. HCV infection is found in 70-80% of HCC patients in Japan, 70% in Egypt, 40-50% in Italy and Spain, about 20% in the United States and Korea, and less than 10% in China.6-8 HCV increases the risk of HCC by promoting inflammation and fibrosis of the infected liver that eventually results in liver cirrhosis. Other factors including alcohol intake, diabetes, and obesity have also been reported to increase the risk of HCC development by about two- to fourfold, indicating a strong life-style effect on the process of hepatocarcinogenesis.9,10
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have suggested that the natural course of HCV infection might be modified by the genetic background of the host.11,12 Thus, both host and virus factors are considered to affect the process of hepatocarcinogenesis in a complex manner.
In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of the mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by HCV infection.
HCC is a highly heterogeneous tumor. Hepatocarcinogenesis is a complex multistep process involving a number of genetic and epigenetic alterations, the activation of cellular oncogenes and/or the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, and dysregulation of multiple signal transduction pathways. These pathways include Wnt/╬▓-catenin, p53, pRb, Ras, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt, Hedgehog and growth factors such as epidermal growth factor, and transforming growth factor-╬▓ (TGF-╬▓) pathways.13-15
The vast majority (80-90%) of HCCs develop in a cirrhotic liver.16 During the progression of liver injury, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) become activated, losing retinoid-containing lipid droplets and transforming into myofibroblast-like cells, which produce extracellular matrix, the first step in hepatic fibrosis.17 Unchecked progression of fibrosis ultimately eventuates in irreversible cirrhosis. The activated HSCs become responsive to both proliferative platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)18 and fibrogenic (TGF-╬▓) cytokines,19 which are upregulated in fibrogenesis and modulate inflammatory signaling from infiltrating immune cells.20 PDGF can activate both MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling cascades.20 In PDGF-C transgenic mice, activation and proliferation of HSCs precedes development of fibrosis, which in turn is followed by the occurrence of HCC. This progression is analogous to that seen in human HCC.21 The cirrhotic liver is also associated with telomere shortening, which may in turn lead to chromosomal instability and deletion of check points.22 Increased survival factors that prevented apoptosis of DNA-damaged hepatocytes and activated stellate cells (for example, Gas6215) and reduced tumor surveillance function due to decreased natural killer cell function are all possible factors related to HCC development in cirrhosis.23 Recent studies have found that stellate cells express stem cell markers such as CD133, nestin, c-kit and p75 neurotrophin receptor,24-27 and activated stellate cells appear to contribute to the stem cell niche.28 Hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways involved in stem cell differentiation and cancer formation are also found in stellate cells.29,30 These lines of evidences suggest that stellate cells may harbor the potential to transdifferentiate into progenitor cells and possibly be linked to the development of HCC.23
HCV belongs to the Flaviviridae family. It has a 9.6-kb positive-stranded linear RNA genome containing 5' and 3' untranslated regions including control elements required for translation and replication. The untranslated regions flank an uninterrupted open-reading frame encoding a single polyprotein of 3010 or 3011 amino acids, which is processed into three structural (core, E1, and E2) and seven non-structural (p7, NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B) proteins by host and viral proteases.31 HCV is an RNA virus unable to reverse transcribe its genome and thus to integrate it into the host genome. Instead, viral proteins and their evoked host responses contribute mostly to the viral oncogenic processes.
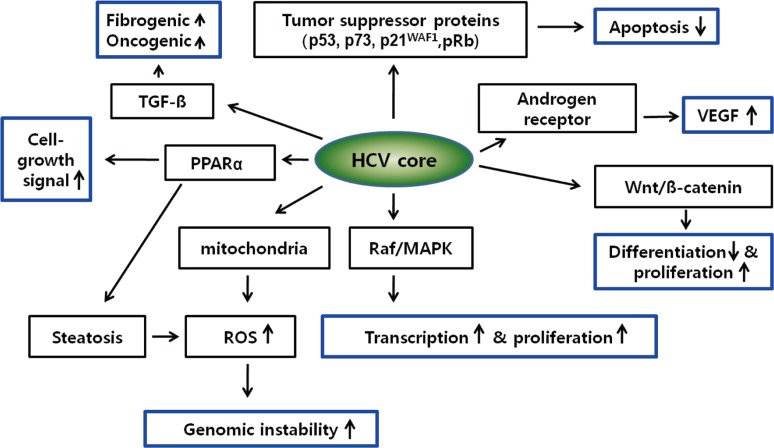
HCV core protein has been proposed to be involved in apoptosis, signal transduction, reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, lipid metabolism, transcriptional activation, transformation and immune modulation (Fig. 1).15,32
Several recent studies have indicated the statistically significant high frequency of mutations in the core gene in HCV-infected patients who developed HCC.33,34
HCV core protein binds to several tumor suppressor proteins, including p53, p73 and pRb.35,36 HCV core interacts with p73, causes nuclear translocation of core protein and prevents p73 ╬▒-dependent cell growth arrest in a p53-dependent manner.37 HCV core can also modulate the expression of the cyclin dependent inhibitor p21WAF1, which is a major target of p53 and regulates the activities of cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase complexes involved in cell-cycle control and tumor formation.38,39 Core protein may also influence the growth and proliferation of host cells through activation of signaling pathways such as Raf/MAPK,40 Wnt/╬▓-catenin,41 and TGF-╬▓.15,42 These pathways are known to be activated in HCC.43 However, the functional relevance of mutant core proteins on the malignant transformation of hepatocytes or the HCV life cycle has yet to be clarified.
NS3 inhibits the activity of the p21WAF1 promoter in a dose-dependent manner and is synergistic with core in this regard.46 NS3 inhibits the function of p53 in an NS3 sequence in an NS3 sequence-dependent manner.47 The expression of NS3 enhances cell growth, JNK activation and DNA-binding activities of the transcription factors AP-1 and ATF-2.48 NS3 also induces TNF-a production by activation of AP-1 and NF-kB.49
NS5A is essential for the replication of the HCV genome and is localized mainly in the cytoplasm of infected cells in association with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). NS5A is involved in a large number of cellular functions, including apoptosis, signal transduction, transcription, transformation and ROS production. High frequencies of wild-type NS5A genes were reported to be dominant in liver cirrhosis patients who finally developed HCC compared with those who did not,50 but the mechanistic significance of the NS5A wild/mutant genotypes in the process of HCV-related hepatocarcinogenesis remains uncertain. NS5A protein has been suggested to interact with various signaling pathways including cell cycle/apoptosis51 and lipid metabolism52-54 in host cells and shares some signaling targets with core protein. NS5A is recognized as a transcriptional activator for many target genes55 including p53 and its binding protein, TATA binding protein (TBP). Transcription factor IID activities were reported to be modified by NS5A in the suppression of p53-dependent transcriptional transactivation and apoptosis.56,57 NS5A may also interact with pathways such as Bcl2,58 PI3-K,59 Wnt/╬▓-catenin signaling,60 and mTOR61 to activate cell proliferation signaling and inhibit apoptosis. Taken together, intriguing data concerning the function of core and NS5A proteins on host cell signaling pathways, transcriptional activation, apoptosis, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism suggest a diverse role for HCV proteins in the pathophysiology of chronic HCV infection that leads to malignant transformation in infected hepatocytes.
It is now widely believed that tumors originate from normal cells as a result of accumulated genetic/epigenetic changes. These alterations affect the signaling pathways at transcriptional and posttranscriptional level that drive cells into uncontrolled cell division, growth, and migration. HCV proteins in infected cells can cause various host responses at transcriptional/translational/posttranslatonal levels, so genetic/genomic alterations and transcriptional/translational modifications can ultimately affect the cellular signaling pathway at the transcriptional level.
Recent advancement of molecular technologies have yielded comprehensive gene expression profiling techniques that have successfully provided candidate diagnostic and prognostic markers in human cancers.
Over the past decade, several methods (including differential display, serial analysis of gene expression [SAGE], and microarray) have been developed to allow comparative studies of gene expression between normal and cancer cells on a genome-wide scale,62 and the analysis of a set of all RNA molecules (mainly indicating messenger RNAs [mRNAs]) is termed as whole transcriptome analysis.
Early microarray and SAGE studies investigating the gene expression patterns of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and CHC indicated that many genes were differentially regulated between hepatitis B and C. In CHB, genes for induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and extracellular matrix degrading were up-regulated, whereas in hepatitis C, genes with antiapoptotic effects, cell cycle acceleration, and extracellular matrix storage were up-regulated.63,64
An early study comparing genes activated in HCV-related and HBV-related HCCs showed that expression of genes encoding CYP2E, AKR1C4, EPHX1, and FMO3 enzymes that convert several pro-carcinogens to activated metabolites increased exclusively in HCV-positive HCCs, which may suggest that their enhanced expression leads to a greater contribution of carcinogenic metabolites to the mechanisms of HCV-specific hepatocarcinogenesis. On the other hand, decreased expression of detoxification enzymes including UGT1A1, UGT2B10, and GPX2 was noted in HBV-positive HCCs. These results suggest that decreased expression of detoxification enzymes may be involved especially in the mechanisms of HBV-specific hepatocarcinogenesis.
The genes associated with xenobiotic metabolism were more abundantly expressed in HCV-related HCC, suggesting a detoxification role, which is potentially induced by chronic inflammation and generation of ROS resulting from HCV infection.65 In contrast, HBV-related HCC might closely correlate with the activation of imprint genes, including insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II), suggesting a role of de-differentiation or epigenetic alteration of the host genome in HBV-related HCC. The expression levels of many detoxification-related genes were increased in HCV-related HCC in comparison to HBV-related HCC. Markedly reduced levels of detoxification-related genes in HBV-related HCC suggests that HBV-infected liver could be more susceptible than HCV-infected liver to various xenobiotics or carcinogens.66 Activation of genes associated with interferon, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and lipid metabolism signaling was detected in HCV-related HCC and CHC specimens,64,67,68 consistent with numerous functional studies that have investigated the host response evoked by HCV structural and non-structural proteins.51
HCC risk predictors that identify the subset of cirrhotic patients with the highest risk of HCC are sorely needed. In addition, identification of molecular biomarkers may open new prospect toward the discovery of therapeutic targets.
Transcriptome analysis has also recently gave new understanding on the transcriptional alteration events occurring in early stages of HCV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. GPC3 (encoding Glypican 3) was suggested as one of the most activated transcripts in the early stage of hepatocarcinogenesis,64,69 also several recent studies have reported that gene signatures including GPC3 can successfully discriminate HCCs from pre-malignant dysplastic nodules and cirrhosis nodules.70,71
The genetic approach between each of the stages from normal, cirrhotic, and dysplastic to early and advanced HCV-related HCC identified gene signatures that accurately reflect the pathological progression of disease at each stage. In addition, pathway analysis revealed dysregulation of the Notch and Toll-like receptor pathways in cirrhosis, followed by deregulation of several components of the JAK/STAT pathway in early carcinogenesis, then upregulation of genes involved in DNA replication and repair and cell cycle in late cancerous stages.50,72 These findings provide a comprehensive molecular portrait of genomic changes in progressive HCV-related HCC. Aimed at identifying etiology-specific or independent genetic variants predictive of HCC risk, efforts have focused on the search for single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with the presence of HCC in candidate genes such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) based on certain biological hypothesis.73
Recent development of high-throughput genomics technology has enabled genome-wide scans of such loci in the setting of a GWAS. In HCC, the first GWAS was conducted on hepatitis B-related HCC patients and identified a SNP possibly associated with altered expression and function of several potential tumor suppressor genes in 1p36.22 namely KIF1B, UBE4B, and PGD.74
The first GWAS on HCV-related HCC has recently been reported by Kumar and colleagues.75 By analyzing 721 patients with HCV-related HCC and 2890 HCV-negative controls of Japanese origin for 432,703 autosomal SNPs, they identified eight possible HCC susceptibility loci with modest statistical significance. The following replication stage, involving 673 independent cases and 2596 HCV-negative controls, confirmed a novel SNP rs2596542 located in the 50 flanking region of MICA, the MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence A gene, on chromosome 6p21.33.
The authors further genotyped the locus in additional 1730 individuals with CHC who had not developed liver cirrhosis, and found that the association of the risk allele was observed in the comparison between CHC and HCC patients, but not in the comparison between CHC patients and HCV-negative controls, suggesting that the SNP is associated with progression from CHC to HCC rather than susceptibility to HCV infection.
However, the study by Kumar et al75 did not use HCV-related cirrhosis without HCC as the controls, it is possible that the risk allele in the MICA gene is actually responsible for increased progression of liver cirrhosis, which eventually contributes to development of HCC. That is, information from this allele may not be useful in distinguishing HCC high risk population among HCV related cirrhotic patients. In fact, the soluble MICA protein level was not different between CHC, cirrhosis, and HCC patients. This needs to be clarified in future studies for example by genotyping patients with HCV-related cirrhosis and following for HCC development to evaluate the risk allele's association with hazard of HCC occurrence within cirrhotic patients.76
Authors analyzed a large set of HCV Japanese carriers (n=3,312) using a case-control design, and they interrogated 467,538 germline SNPs and identified one, rs1012068, significantly associated with the risk of developing HCC. The SNP is located in chromosome 22, and by using fine mapping studies the authors identified DEPDC5 as the target gene harboring the different genotypes. Despite the function of this gene is unknown, there is some evidence of aberrations affecting its locus in human cancer (e.g., glioblastoma).
Recent advances in transcriptome analysis have also provided detailed information on the status of small noncoding RNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs) that regulate gene expression by targeting mRNAs through translational repression or RNA degradation. Many fundamental biological processes are modulated by miRNAs, and an important role for miRNAs in carcinogenesis is emerging.
Although the mechanisms of altered miRNA levels in human cancer are quite varied, including deletions, amplification or mutations involving miRNA genes, it is clear that miRNA-regulated expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes contribute to most - if not all - human cancers.1 Earlier studies noted specific changes in miRNA expression patterns in HCC as compared with adjacent normal liver tumor tissues, or liver cirrhosis that correlated with the disease outcome (Table 2).3,81-84
Since there is no HCV encoded oncoprotein, the question arises whether the deregulated miRNAs in HCC serve as "oncomiRs," that could function as an oncogene or a tumor suppressor, to regulate cell proliferation by targeting cell cycle check points and/or growth factors. Such oncomiRs in liver cancer would be expected to be involved through each step from normal liver to cirrhosis to HCC. The extant literature strongly supports the role of specific oncoMirs in the development and maintenance of HCC.
More recently, the investigators focused on miR-26a whose expression is most significantly perturbed in MYC-induced liver cancer model.87 MiR-26a targets expression of cyclins D2 and E2; and ectopic expression of miR-26a induced G1 arrest in HepG2 HCC cell line. Examination of paired biopsies from normal human liver tissues as compared with liver cancer showed consistent reduction of miR-26a in liver cancer, while miR-26a is expressed at high levels in normal liver as well as other tissues. Since miR-26a induces G1 arrest by targeting cyclins D2 and E2, the authors reasoned that forced expression of miR-26a in liver cancer cells might arrest tumor growth.
Indeed, the systemic administration of miR-26a in a mouse model of HCC using adeno-associated virus vector system, resulted in the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation by inducing tumor-specific apoptosis, with dramatic protection from disease progression without toxicity.87
Thus, the delivery of miR-26a, which is highly expressed and therefore tolerated in normal, but not in liver cancer cells, may be a useful strategy for miRNA-replacement therapy for HCC.89
Expression of miRNAs including miR-122 and -199a has been reported to modulate HCV replication,3,85,90 and miR-122 expression can be regulated by host interferon signaling and responses.52 HCV induced miR-155 expression promotes hepatocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis by activating Wnt signaling. The overexpression of miR-155 significantly inhibited hepatocyte apoptosis and promoted cell proliferation.91
HCV protein expression in turn could induce miRNAs and might affect the tumor suppressor DLC1 and the chemosensitivity of malignantly transformed cells.53,88 Several miRNAs were also differentially expressed between HCV-related and HBV-related HCCs as well as their corresponding non-cancerous liver tissues. The candidate signaling pathways potentially altered by miRNAs in HCV-related tissues were those associated with antigen presentation, cell cycle, and lipid metabolism,92 consistent with the mRNA microarray data described above. MiRNAs have also recently been reported to successfully discriminate between HCC and cirrhotic liver tissues,55 implicating their role in the early stages of malignant transformation. These data suggest that miRNAs may be good targets for the eradication of HCC as well as hepatocytes infected with HCV.
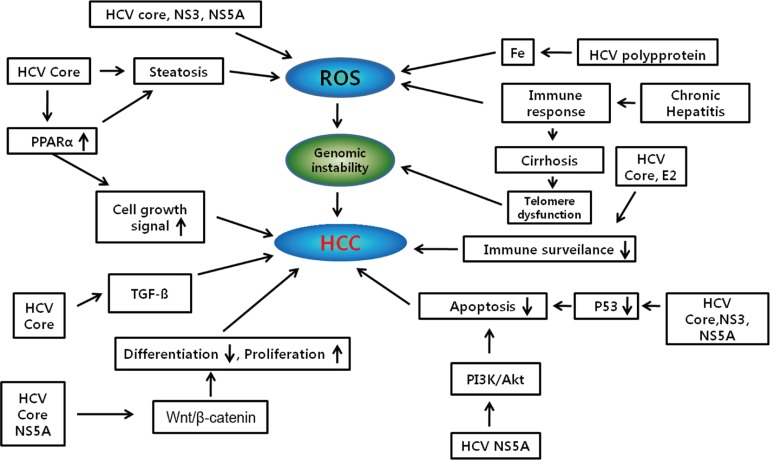
Hepatocarcinogenesis is a multistep process and involves multiple cellular signaling pathways. Although HCV is the major risk factors leading to the development of HCC, the precise pathogenetic mechanisms linking viral infection and HCC remain uncertain. Viral proteins also have been implicated in disrupting several cellular signal transduction pathways that affect cell survival, proliferation, migration and transformation (Fig. 2).15 Current advances in gene expression profile and selective mRNA analysis have improved approach to the pathogenesis of HCC. The heterogeneity of genetic events observed in HCV-related HCCs has suggested that complex mechanisms underlie malignant transformation induced by HCV infection. Considering the complexity and heterogeneity of HCCs of both etiological and genetic aspects, further molecular classification is required and an understanding of these molecular complexities may provide the opportunity for effective chemoprevention and personalized therapy for HCV-related HCC patients in the future.
Abbreviations
EGF
epidermal growth factor
ER
endoplasmic reticulum
GPC3
Glypican 3
GWAS
genome-wide association studies
HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
HCV
hepatitis C virus
HSCs
hepatic stellate cells
Jak/STAT
janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription
MAPK
mitogen-activated protein kinase
miRNAs
microRNAs
mRNAs
messenger RNAs
IGF-II
insulin-like growth factor-II
PDGF
platelet-derived growth factor
PI3-K
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
PI3K
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
ROS
reactive oxygen species
SAGE
serial analysis of gene expression
SNPs
single nucleotide polymorphisms
TBP
TATA binding protein
TGF-╬▓
transforming growth factor-╬▓
REFERENCES
1. Croce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2009;10:704-714. 19763153.




2. El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007;132:2557-2576. 17570226.


3. Murakami Y, Aly HH, Tajima A, Inoue I, Shimotohno K. Regulation of the hepatitis C virus genome replication by miR-199a. J Hepatol 2009;50:453-460. 19144437.


4. Bruix J, Barrera JM, Calvet X, Ercilla G, Costa J, Sanchez-Tapias JM, et al. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in Spanish patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic cirrhosis. Lancet 1989;2:1004-1006. 2572739.


5. Colombo M, Kuo G, Choo QL, Donato MF, Del Ninno E, Tommasini MA, et al. Prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in Italian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 1989;2:1006-1008. 2572740.


6. Liang TJ, Heller T. Pathogenesis of hepatitis C-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004;127:S62-S71. 15508105.


7. Yoshizawa H. Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis C virus infection in Japan: projection to other countries in the foreseeable future. Oncology 2002;62(Suppl 1):8-17. 11868791.


8. Yuen MF, Hou JL, Chutaputti A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;24:346-353. 19220670.


9. Yu MC, Yuan JM. Environmental factors and risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004;127:S72-S78. 15508106.


10. Kawaguchi T, Sata M. Importance of hepatitis C virus-associated insulin resistance: therapeutic strategies for insulin sensitization. World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:1943-1952. 20419831.



11. Thomas DL, Thio CL, Martin MP, Qi Y, Ge D, O'Huigin C, et al. Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nature 2009;461:798-801. 19759533.



12. Tillmann HL, Thompson AJ, Patel K, Wiese M, Tenckhoff H, Nischalke HD, et al. A polymorphism near IL28B is associated with spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus and jaundice. Gastroenterology 2010;139:1586-1592. 1592.e1. 20637200.


13. Branda M, Wands JR. Signal transduction cascades and hepatitis B and C related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2006;43:891-902. 16628664.


14. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008;48:1312-1327. 18821591.



16. Caldwell S, Park SH. The epidemiology of hepatocellular cancer: from the perspectives of public health problem to tumor biology. J Gastroenterol 2009;44(Suppl 19):96-101. 19148801.


17. Okuda M, Li K, Beard MR, Showalter LA, Scholle F, Lemon SM, et al. Mitochondrial injury, oxidative stress, and antioxidant gene expression are induced by hepatitis C virus core protein. Gastroenterology 2002;122:366-375. 11832451.


18. Friedman SL, Arthur MJ. Activation of cultured rat hepatic lipocytes by Kupffer cell conditioned medium. Direct enhancement of matrix synthesis and stimulation of cell proliferation via induction of platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Clin Invest 1989;84:1780-1785. 2556445.



19. Matsuzaki K. Modulation of TGF-beta signaling during progression of chronic liver diseases. Front Biosci 2009;14:2923-2934. 19273245.

20. Parsons CJ, Takashima M, Rippe RA. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;22(Suppl 1):S79-S84. 17567474.


21. Campbell JS, Hughes SD, Gilbertson DG, Palmer TE, Holdren MS, Haran AC, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor C induces liver fibrosis, steatosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:3389-3394. 15728360.



22. Satyanarayana A, Manns MP, Rudolph KL. Telomeres and telomerase: a dual role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2004;40:276-283. 15368430.


24. Fujio K, Evarts RP, Hu Z, Marsden ER, Thorgeirsson SS. Expression of stem cell factor and its receptor, c-kit, during liver regeneration from putative stem cells in adult rat. Lab Invest 1994;70:511-516. 7513770.

25. Niki T, Pekny M, Hellemans K, Bleser PD, Berg KV, Vaeyens F, et al. Class VI intermediate filament protein nestin is induced during activation of rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 1999;29:520-527. 9918930.


26. Cassiman D, Denef C, Desmet VJ, Roskams T. Human and rat hepatic stellate cells express neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors. Hepatology 2001;33:148-158. 11124831.


27. Kordes C, Sawitza I, Muller-Marbach A, Ale-Agha N, Keitel V, Klonowski-Stumpe H, et al. CD133+ hepatic stellate cells are progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007;352:410-417. 17118341.


28. Roskams T. Different types of liver progenitor cells and their niches. J Hepatol 2006;45:1-4. 16723168.


29. Myung SJ, Yoon JH, Gwak GY, Kim W, Lee JH, Kim KM, et al. Wnt signaling enhances the activation and survival of human hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett 2007;581:2954-2958. 17544413.


30. Yang HI, Yeh SH, Chen PJ, Iloeje UH, Jen CL, Su J, et al. Associations between hepatitis B virus genotype and mutants and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008;100:1134-1143. 18695135.




31. Chisari FV. Unscrambling hepatitis C virus-host interactions. Nature 2005;436:930-932. 16107831.



32. Anzola M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: role of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses proteins in hepatocarcinogenesis. J Viral Hepat 2004;11:383-393. 15357643.


33. Akuta N, Suzuki F, Kawamura Y, Yatsuji H, Sezaki H, Suzuki Y, et al. Amino acid substitutions in the hepatitis C virus core region are the important predictor of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2007;46:1357-1364. 17657816.


34. Fishman SL, Factor SH, Balestrieri C, Fan X, Dibisceglie AM, Desai SM, et al. Mutations in the hepatitis C virus core gene are associated with advanced liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:3205-3213. 19383824.



35. Ray RB, Steele R, Meyer K, Ray R. Transcriptional repression of p53 promoter by hepatitis C virus core protein. J Biol Chem 1997;272:10983-10986. 9110985.


36. Cho J, Baek W, Yang S, Chang J, Sung YC, Suh M. HCV core protein modulates Rb pathway through pRb down-regulation and E2F-1 up-regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001;1538:59-66. 11341983.


37. Alisi A, Giambartolomei S, Cupelli F, Merlo P, Fontemaggi G, Spaziani A, et al. Physical and functional interaction between HCV core protein and the different p73 isoforms. Oncogene 2003;22:2573-2580. 12730672.



38. Yamanaka T, Kodama T, Doi T. Subcellular localization of HCV core protein regulates its ability for p53 activation and p21 suppression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;294:528-534. 12056798.


39. Kwun HJ, Jang KL. Dual effects of hepatitis C virus Core protein on the transcription of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 gene. J Viral Hepat 2003;10:249-255. 12823590.


40. Tsutsumi T, Suzuki T, Moriya K, Shintani Y, Fujie H, Miyoshi H, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein activates ERK and p38 MAPK in cooperation with ethanol in transgenic mice. Hepatology 2003;38:820-828. 14512869.


41. Levrero M. Viral hepatitis and liver cancer: the case of hepatitis C. Oncogene 2006;25:3834-3847. 16799625.



42. Matsuzaki K, Murata M, Yoshida K, Sekimoto G, Uemura Y, Sakaida N, et al. Chronic inflammation associated with hepatitis C virus infection perturbs hepatic transforming growth factor beta signaling, promoting cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2007;46:48-57. 17596875.


43. Wang XW, Hussain SP, Huo TI, Wu CG, Forgues M, Hofseth LJ, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Toxicology 2002;181-182:43-47. 12505283.


44. Sakamuro D, Furukawa T, Takegami T. Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein NS3 transforms NIH 3T3 cells. J Virol 1995;69:3893-3896. 7745741.



45. Zemel R, Gerechet S, Greif H, Bachmatove L, Birk Y, Golan-Goldhirsh A, et al. Cell transformation induced by hepatitis C virus NS3 serine protease. J Viral Hepat 2001;8:96-102. 11264729.


46. Kwun HJ, Jung EY, Ahn JY, Lee MN, Jang KL. p53-dependent transcriptional repression of p21(waf1) by hepatitis C virus NS3. J Gen Virol 2001;82:2235-2241. 11514734.


47. Deng L, Nagano-Fujii M, Tanaka M, Nomura-Takigawa Y, Ikeda M, Kato N, et al. NS3 protein of Hepatitis C virus associates with the tumour suppressor p53 and inhibits its function in an NS3 sequence-dependent manner. J Gen Virol 2006;87:1703-1713. 16690937.


48. Hassan M, Ghozlan H, Abdel-Kader O. Activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway is essential for the stimulation of hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 3 (NS3)-mediated cell growth. Virology 2005;333:324-336. 15721365.


49. Hassan M, Selimovic D, Ghozlan H, Abdel-Kader O. Induction of high-molecular-weight (HMW) tumor necrosis factor(TNF) alpha by hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 3 (NS3) in liver cells is AP-1 and NF-kappaB-dependent activation. Cell Signal 2007;19:301-311. 16916598.


50. De Mitri MS, Cassini R, Bagaglio S, Morsica G, Andreone P, Marino N, et al. Evolution of hepatitis C virus non-structural 5A gene in the progression of liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2007;27:1126-1133. 17845542.


51. Kasprzak A, Adamek A. Role of hepatitis C virus proteins (C, NS3, NS5A) in hepatic oncogenesis. Hepatol Res 2008;38:1-26. 17894800.


52. Dharancy S, Malapel M, Perlemuter G, Roskams T, Cheng Y, Dubuquoy L, et al. Impaired expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha during hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology 2005;128:334-342. 15685545.


53. Benga WJ, Krieger SE, Dimitrova M, Zeisel MB, Parnot M, Lupberger J, et al. Apolipoprotein E interacts with hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A and determines assembly of infectious particles. Hepatology 2010;51:43-53. 20014138.


54. Kim K, Kim KH, Ha E, Park JY, Sakamoto N, Cheong J. Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein increases hepatic lipid accumulation via induction of activation and expression of PPARgamma. FEBS Lett 2009;583:2720-2726. 19631645.


55. Kato N, Lan KH, Ono-Nita SK, Shiratori Y, Omata M. Hepatitis C virus nonstructural region 5A protein is a potent transcriptional activator. J Virol 1997;71:8856-8859. 9343247.



56. Lan KH, Sheu ML, Hwang SJ, Yen SH, Chen SY, Wu JC, et al. HCV NS5A interacts with p53 and inhibits p53-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 2002;21:4801-4811. 12101418.



57. Majumder M, Ghosh AK, Steele R, Ray R, Ray RB. Hepatitis C virus NS5A physically associates with p53 and regulates p21/waf1 gene expression in a p53-dependent manner. J Virol 2001;75:1401-1407. 11152513.



58. Chung YL, Sheu ML, Yen SH. Hepatitis C virus NS5A as a potential viral Bcl-2 homologue interacts with Bax and inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2003;107:65-73. 12925958.


59. He Y, Nakao H, Tan SL, Polyak SJ, Neddermann P, Vijaysri S, et al. Subversion of cell signaling pathways by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein via interaction with Grb2 and P85 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Virol 2002;76:9207-9217. 12186904.



60. Park CY, Choi SH, Kang SM, Kang JI, Ahn BY, Kim H, et al. Nonstructural 5A protein activates beta-catenin signaling cascades: implication of hepatitis C virus-induced liver pathogenesis. J Hepatol 2009;51:853-864. 19726098.


61. Peng L, Liang D, Tong W, Li J, Yuan Z. Hepatitis C virus NS5A activates the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, contributing to cell survival by disrupting the interaction between FK506-binding protein 38 (FKBP38) and mTOR. J Biol Chem 2010;285:20870-20881. 20439463.



62. Yamashita T, Honda M, Kaneko S. Application of Serial Analysis of Gene Expression in cancer research. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2008;9:375-382. 18855690.


63. Honda M, Kaneko S, Kawai H, Shirota Y, Kobayashi K. Differential gene expression between chronic hepatitis B and C hepatic lesion. Gastroenterology 2001;120:955-966. 11231949.


64. Yamashita T, Kaneko S, Hashimoto S, Sato T, Nagai S, Toyoda N, et al. Serial analysis of gene expression in chronic hepatitis C and hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001;282:647-654. 11401510.


65. Okabe H, Satoh S, Kato T, Kitahara O, Yanagawa R, Yamaoka Y, et al. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in human hepatocellular carcinomas using cDNA microarray: identification of genes involved in viral carcinogenesis and tumor progression. Cancer Res 2001;61:2129-2137. 11280777.

66. Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, Mori N, Tamesa T, Okada T, et al. Comparison of gene expression profiles between hepatitis B virus- and hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocellular carcinoma by oligonucleotide microarray data on the basis of a supervised learning method. Cancer Res 2002;62:3939-3944. 12124323.

67. Yamashita T, Honda M, Takatori H, Nishino R, Minato H, Takamura H, et al. Activation of lipogenic pathway correlates with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2009;50:100-110. 19008011.


68. Honda M, Yamashita T, Ueda T, Takatori H, Nishino R, Kaneko S. Different signaling pathways in the livers of patients with chronic hepatitis B or chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2006;44:1122-1138. 17058214.


69. Capurro M, Wanless IR, Sherman M, Deboer G, Shi W, Miyoshi E, et al. Glypican-3: a novel serum and histochemical marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2003;125:89-97. 12851874.


70. Jia HL, Ye QH, Qin LX, Budhu A, Forgues M, Chen Y, et al. Gene expression profiling reveals potential biomarkers of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:1133-1139. 17317821.


71. Llovet JM, Chen Y, Wurmbach E, Roayaie S, Fiel MI, Schwartz M, et al. A molecular signature to discriminate dysplastic nodules from early hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2006;131:1758-1767. 17087938.


72. Wurmbach E, Chen YB, Khitrov G, Zhang W, Roayaie S, Schwartz M, et al. Genome-wide molecular profiles of HCV-induced dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2007;45:938-947. 17393520.


73. Ji J, Yamashita T, Budhu A, Forgues M, Jia HL, Li C, et al. Identification of microRNA-181 by genome-wide screening as a critical player in EpCAM-positive hepatic cancer stem cells. Hepatology 2009;50:472-480. 19585654.



74. Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Calin GA, et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008;27:5651-5661. 18521080.



75. Kumar V, Kato N, Urabe Y, Takahashi A, Muroyama R, Hosono N, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for HCV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 2011;43:455-458. 21499248.



76. Abu Dayyeh BK, Yang M, Fuchs BC, Karl DL, Yamada S, Sninsky JJ, et al. A functional polymorphism in the epidermal growth factor gene is associated with risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2011;141:141-149. 21440548.



77. Miki D, Ochi H, Hayes CN, Abe H, Yoshima T, Aikata H, et al. Variation in the DEPDC5 locus is associated with progression to hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C virus carriers. Nat Genet 2011;43:797-800. 21725309.



78. Villanueva A, Forns X, Llovet JM. Molecular epidemiology in HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: first steps. J Hepatol 2012;57:213-214. 22282033.


79. Zhang H, Zhai Y, Hu Z, Wu C, Qian J, Jia W, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 1p36.22 as a new susceptibility locus for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. Nat Genet 2010;42:755-758. 20676096.



80. Clifford RJ, Zhang J, Meerzaman DM, Lyu MS, Hu Y, Cultraro CM, et al. Genetic variations at loci involved in the immune response are risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010;52:2034-2043. 21105107.


81. Varnholt H, Drebber U, Schulze F, Wedemeyer I, Schirmacher P, Dienes HP, et al. MicroRNA gene expression profile of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008;47:1223-1232. 18307259.


82. Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T, et al. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2006;25:2537-2545. 16331254.



83. Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA, Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ, et al. Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:419-427. 18223217.



84. Kumar A. MicroRNA in HCV infection and liver cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011;1809:694-699. 21821155.


85. Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, Lemon SM, Sarnow P. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific MicroRNA. Science 2005;309:1577-1581. 16141076.


86. Jopling CL, Schutz S, Sarnow P. Position-dependent function for a tandem microRNA miR-122-binding site located in the hepatitis C virus RNA genome. Cell Host Microbe 2008;4:77-85. 18621012.



87. Kota J, Chivukula RR, O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang HW, et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 2009;137:1005-1017. 19524505.



88. Banaudha K, Kaliszewski M, Korolnek T, Florea L, Yeung ML, Jeang KT, et al. MicroRNA silencing of tumor suppressor DLC-1 promotes efficient hepatitis C virus replication in primary human hepatocytes. Hepatology 2011;53:53-61. 20967756.


90. Sarasin-Filipowicz M, Krol J, Markiewicz I, Heim MH, Filipowicz W. Decreased levels of microRNA miR-122 in individuals with hepatitis C responding poorly to interferon therapy. Nat Med 2009;15:31-33. 19122656.



91. Zhang Y, Wei W, Cheng N, Wang K, Li B, Jiang X, et al. Hepatitis C Virus-induced upregulation of miR-155 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by activating Wnt signaling. Hepatology 2012.
Figure┬Ā1
Cellular signaling pathways implicated in hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein-related hepatocarcinogenesis.
Blue boxes indicate key driving forces for carciniogenesis.
Table┬Ā1.
Published GWAS in hepatocellular carcinoma (Adapted from Villanueva A, et al. J Hepatol 2012;57:213-214)78
| Article |
Sample analyzed |
Etiology of liver disease | DNA regions identified | Candidate genes | Effect size/Odds ratio (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC (validation) | Controls (validation) | Total | |||||
| Miki D [70] | 212 (710) | 765 (1625) | 3312 | HCV | Chr 22q12.2 | DEPDC5 | 1.75 (1.51-2.03) |
| Kumar V [71] | 721 (673) | 2890 (2596) | 6880 | HCV | Chr 6p21.33 | MICA | 1.39 (1.27-1.63) |
| Zhang H [77] | 348 (1962) | 359 (1430) | 4099 | HBV | Chr 1p36.22 | UBE4B- KIF1B-PDG | 0.61 (0.55-0.67) |
| Clifford RJ [78] | 180 (337) | 206 (336) | 1059 | HBV, HCV | Chr 13q12.11 | TPTE2 | 0.27 (0.19-0.39) |
| Chr 2q14.1 | Non-coding | 3.38 (2.07-5.52) | |||||
Table┬Ā2.
Selected examples of reported alterations in miRNA expression in HCV infection and their proposed role in Hepatocellular carcinoma (Adapted from Kumar A, et al. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2011;1809:694-699).84
|
Selected examples of microRNAs in HCV infection and Hepatocellular carcinoma |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| MicroRNA | Target | Phenotype | References |
| MiR-122 | HCV 5ŌĆÖ-UTR | Viral RNA amplification | [85,86] |
| MicroRNA alterations | Not validated | HCC/normal tissue HCV Inf.HCC | [81] |
| Mir-199a | HCV 5ŌĆÖ-UTR | Suppression of HCV replication | [3] |
| MiR-181 | Transcription regulation | Up regulated in HCC | [73] |
| Mir-221 | CDK inhibitor | Up regulated in HCC | [74] |
| Mir-199a | Predicted cell | Increased expression in HCC | [83] |
| Mir-21, Mir-301 | Cycle genes | ||
| Mir-26a | Cyclin D2/E2 | Reduced expression in HCC | [87] |
| Mir-141 | DLC-1 | Up regulated HCV infection | [88] |



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print




