| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 26(2); 2020 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
FOOTNOTES
Figure 1.
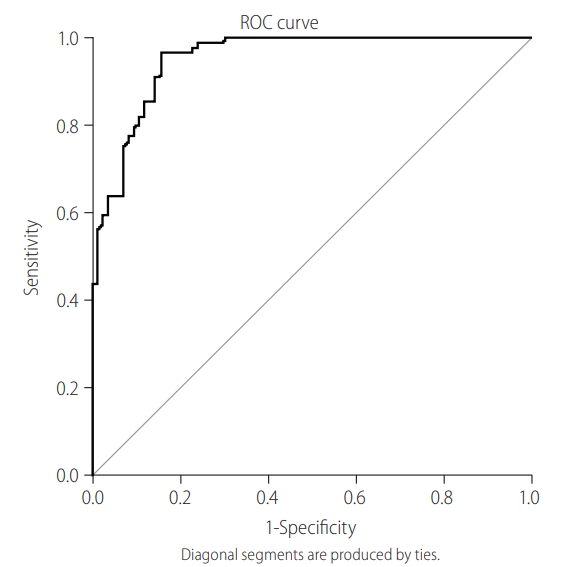
Figure 2.
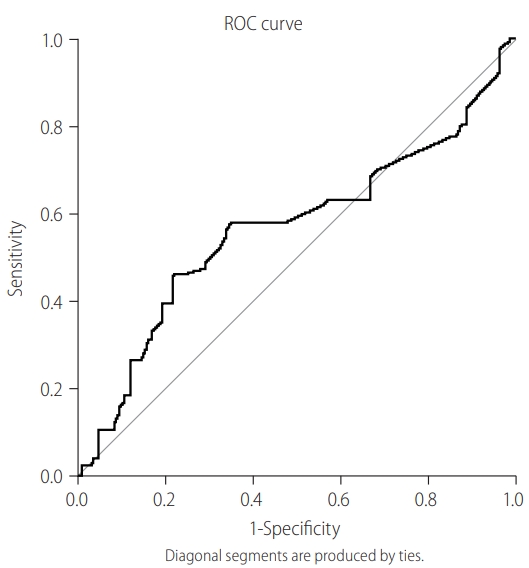
Figure 3.
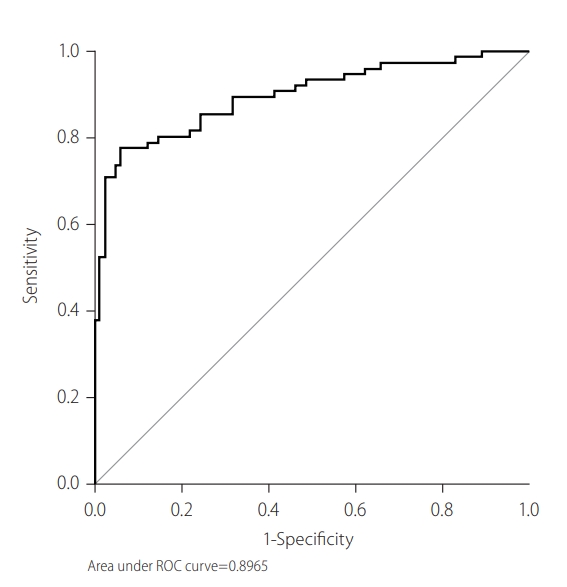
Table 1.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or median (IQ range).
AHB, acute hepatitis B; CHB-AE, chronic hepatitis B with acute exacerbation; NR, normal range; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international normalized ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; APRI, AST platelet ratio index; IQ, interquartile range from the 25th (Q1) to the 75th (Q3) percentile.
Table 2.
Values are presented as median (IQ range) or mean±standard deviation. Values of qHBsAg and HBV DNA were log-transformed for analysis.
AHB, acute hepatitis B; CHB-AE, chronic hepatitis B with acute exacerbation; HBeAg, hepatitis B e antigen; S/Co, signal cut-off; qHBsAg, quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV, hepatitis B virus; IgM anti-HBc, immunoglobulin M antibody to hepatitis B core antigen; IQ range, interquartile range.
Table 3.
| Significant variable | P-value | Odds ratio | 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| IgM anti HBc, S/Co | <0.001 | 0.9 | 0.8–0.9 |
| INR | 0.01 | 1.8 | 1.1–2.2 |
Table 4.
| S/Co | AHB | CHB-AE | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| <10 | 2 | 49 | <0.001 |
| 10–20 | 12 | 17 | 0.23 |
| 20–30 | 27 | 8 | 0.14 |
| >30 | 48 | 9 | <0.001 |
| Total | 89 | 83 | 172 |
Table 5.
| Study | Year/location | Technique | IgM anti HBc | HBV DNA | Other relevant findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rodella et al. [16] | 2006/Italy | Chemilluminiscent immunoassay | S/Co=10, avidity index=0.7 diagnostic for AHB | Not done | HBsAg levels differed significantly AHB > CHB-AE |
| Huang et al. [17] | 2006/Taiwan | Serology: MEIA | Mean index value 2.9 AHB vs. 1.5 CHB-AE | Comparable in both groups | Cut-off for IgM anti-HBc 2.4–2.5 showed sensitivity and specificity 90% |
| HBV DNA-qPCR | |||||
| Han et al. [18] | 2008/Shanghai | Serology: enzyme immunoassay | At 1:10,000 titer high sensitivity and specificity of 96.2% and 93% | No significant difference | Combining HBV DNA + HBeAg increases diagnostic power |
| HBV DNA: qPCR | Low HBeAg level more useful than negative HBeAg | ||||
| Kumar et al. [19] | 2006/India | Enzyme immunoassay | Titer >1:1,000 seen in 80% people of AHB | <0.5 pg/mL | |
| Seen in CHB-AE | |||||
| Dao et al. [20] | 2012 | Enzyme immunoassay | S/N higher in AHB=88.2 | 3.9 log10 IU/mL vs. 5.2 log10 IU/mL for AHB vs. CHB-AE | Cut point S/N ratio of 5.0 for IgM |
| Park et al. [21] | 2015 | Chemilluminiscent immunoassay | S/Co ratio of IgM | HBV DNA level was significantly higher in CHB-AE group | The optimal cut-off values of IgM anti-HBc and HBV DNA levels for differentiating the two conditions were 8 S/Co ratio and 5.5 log10 IU/mL, respectively |
| Anti-HBc was significantly higher in AHB group |
AHB, acute hepatitis B; CHB-AE, chronic hepatitis B with acute exacerbation; IgM anti-HBc, immunoglobulin M antibody to hepatitis B core antigen; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBeAg, hepatitis B e antigen; S/Co, signal cut-off; qPCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; MEIA, microparticle enzyme immunoassay; S/N, signal by noise ratio; qHBsAg, quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen.
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Ekta Gupta

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5237-216X - Related articles




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



