| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 27(1); 2021 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
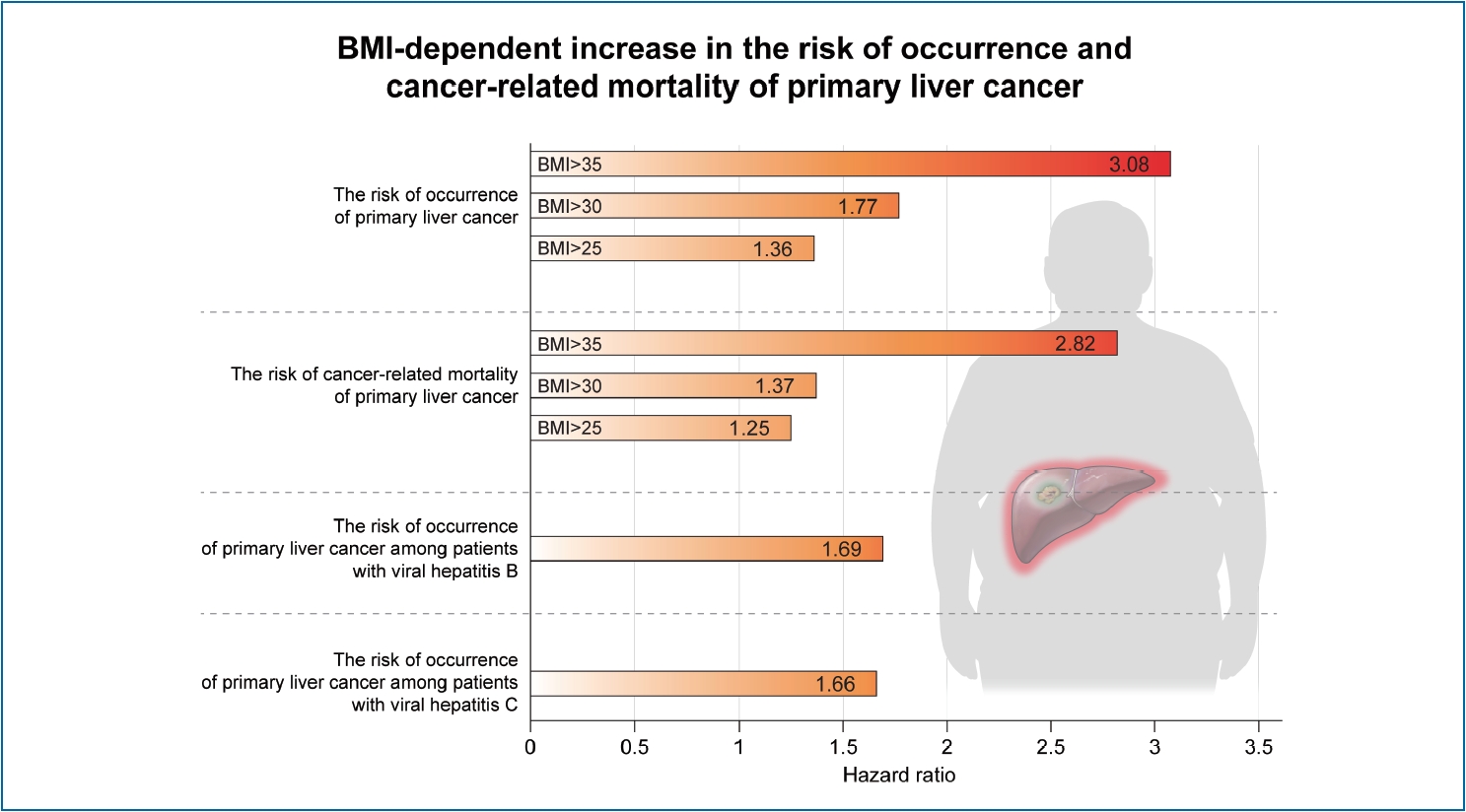
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
FOOTNOTES
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 4.
Supplementary Figure 5.
Figure 2.
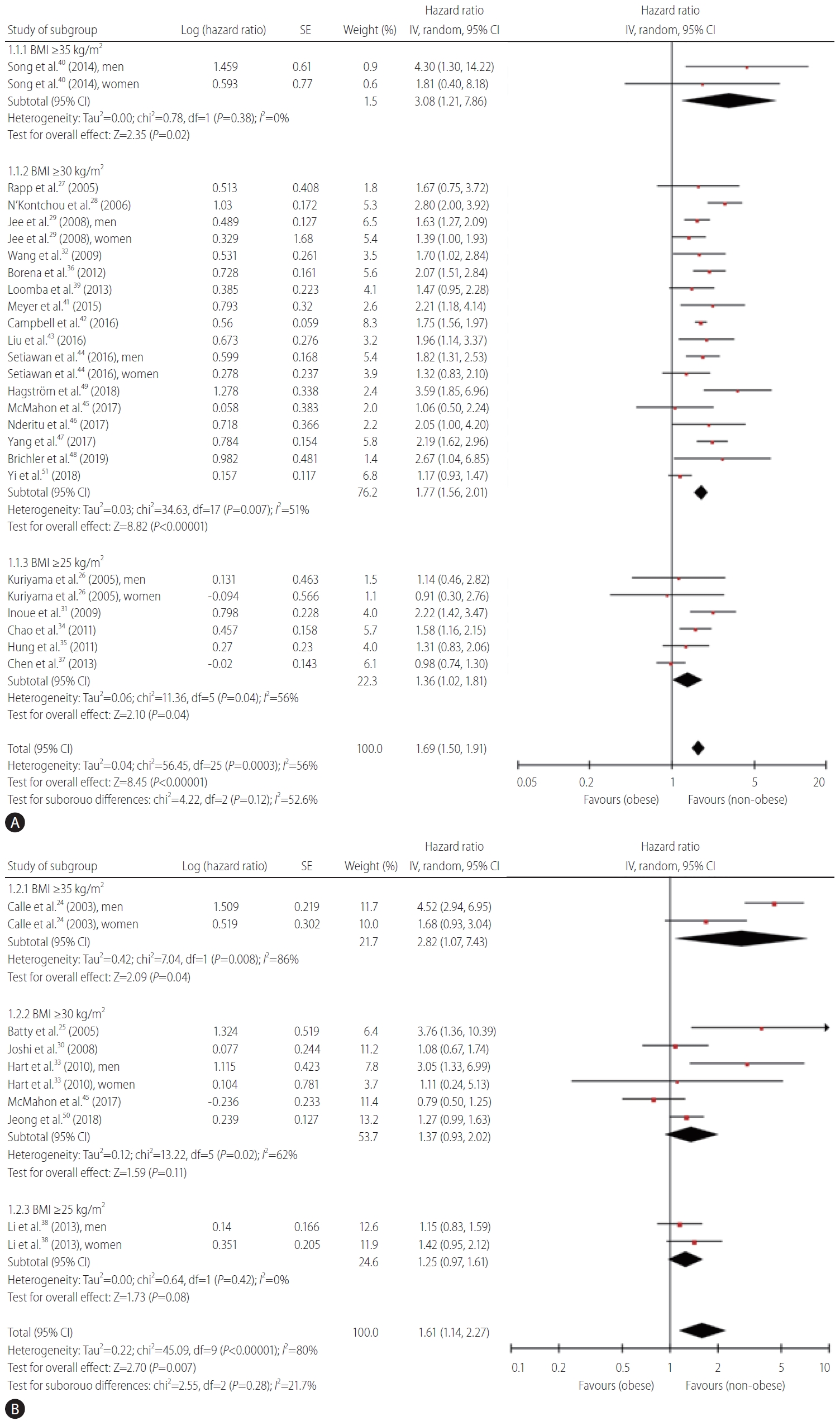
Figure 3.
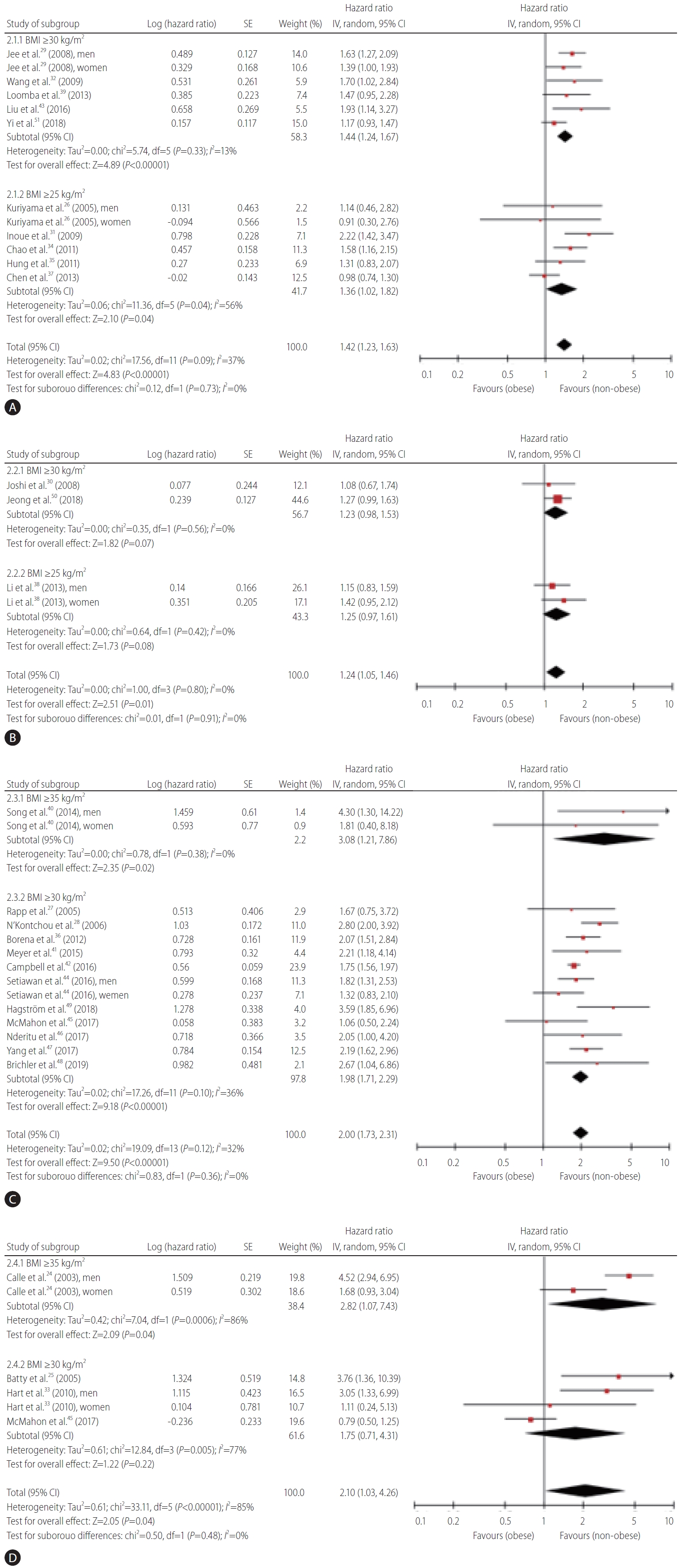
Table 1.
| Study | Region | Study period | Number of subjects | Male (%) |
Newcastle-Ottawa scale |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection | Comparability | Outcome | |||||
| Calle et al. [24] (2003) | USA | 1982–1988 | 900,053 | 45.0 | **** | * | *** |
| Batty et al. [25] (2005) | UK | 1967–2002 | 18,403 | 100.0 | *** | * | ** |
| Kuriyama et al. [26] (2005) | Japan | 1984–1992 | 27,539 | 45.3 | *** | * | ** |
| Rapp et al. [27] (2005) | Austria | 1985–2002 | 145,931 | 46.2 | *** | * | ** |
| N’Kontchou et al. [28] (2006) | France | 1994–2004 | 771 | 64.3 | **** | ** | * |
| Jee et al. [29] (2008) | Korea | 1992–2006 | 1,213,829 | 63.5 | *** | * | * |
| Joshi et al. [30] (2008) | Korea | 1998–2004 | 548,530 | 100.0 | *** | ** | ** |
| Inoue et al. [31] (2009) | Japan | 1993–2006 | 17,590 | 34.6 | **** | ** | ** |
| Wang et al. [32] (2009) | Taiwan | 1997–2004 | 5,929 | 43.5 | *** | ** | ** |
| Hart et al. [33] (2010) | Scotland | 1965–2007 | 26,738 | 61.8 | **** | * | *** |
| Chao et al. [34] (2011) | Taiwan | 1989–2006 | 1,142 | 100.0 | **** | ** | *** |
| Hung et al. [35] (2011) | Taiwan | 1999–2009 | 1,470 | 52.1 | **** | ** | *** |
| Borena et al. [36] (2012) | Europe | 1972–2006 | 578,700 | 50.1 | **** | * | *** |
| Chen et al. [37] (2013) | Taiwan | 2004–2007 | 56,231 | 30.9 | **** | ** | ** |
| Li et al. [38] (2013) | Japan | 1988–2009 | 72,473 | 42.8 | **** | * | *** |
| Loomba et al. [39] (2013) | Taiwan | 1991–2004 | 23,712 | 50.3 | **** | ** | *** |
| Song et al. [40] (2014) | Europe | 1972–2008 | 54,725 | 48.7 | **** | * | *** |
| Meyer et al. [41] (2015) | Europe | 1977–2008 | 35,784 | 47.2 | **** | * | ** |
| Campbell et al. [42] (2016) | USA | 1980–2011 | 1,570,023 | 40.8 | *** | * | ** |
| Liu et al. [43] (2016) | China | 1996–2013 | 68,253 | 0.0 | **** | * | ** |
| Setiawan et al. [44] (2016) | USA | 1993–2010 | 168,476 | 46.3 | **** | * | *** |
| McMahon et al. [45] (2017) | USA | 1995–2012 | 1,080 | 49.3 | **** | ** | ** |
| Nderitu et al. [46] (2017) | Sweden | 1985–2011 | 65,224 | 57.2 | **** | * | ** |
| Yang et al. [47] (2017) | USA | 1995–2011 | 297,928 | 58.5 | *** | * | ** |
| Brichler et al. [48] (2019) | France | 2006–2012 | 317 | 82.3 | **** | ** | ** |
| Hagström et al. [49] (2018) | Sweden | 1969–2012 | 1,220,261 | 100.0 | **** | * | ** |
| Jeong et al. [50] (2018) | Korea | 2002–2013 | 510,148 | 54.3 | **** | * | *** |
| Yi et al. [51] (2018) | Korea | 2002–2013 | 504,646 | 54.3 | **** | ** | ** |
Table 2.
| Study | Viral hepatitis | Use of alcohol (%) | DM (%) | Obesity group (N, definition) | Control group (N, definition) | HR for occurrence of PLC (95% CI) | HR for cancerrelated mortality (95% CI) | Adjustment variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calle et al. [24] (2003) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A; BMI ≥35 kg/m2 | N/A; BMI <25 kg/m2 | N/A | 4.52 (2.94–6.94) | Age, education, smoking status and number of cigarettes smoked, physical activity, alcohol use, marital status, race, aspirin use, fat consumption, and vegetable consumption |
| Calle et al. [24] (2003), women | N/A | N/A | NA | N/A; BMI ≥35 kg/m2 | N/A; BMI <25 kg/m2 | N/A | 1.68 (0.93–3.05) | Age, education, smoking status and number of cigarettes smoked, physical activity, alcohol use, marital status, race, aspirin use, fat consumption, and vegetable consumption |
| Batty et al. [25] (2005) | N/A | N/A | 1.6 | 717; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 9,288; BMI <25 kg/m2 | N/A | 3.76 (1.36–10.40) | Age, employment grade, physical activity, smoking habit, marital status, disease at entry, weight loss in the last year, blood pressure-lowering medication, height adjusted FEV1, triceps skinfold thickness, systolic blood pressure, plasma cholesterol, glucose intolerance and diabetes status |
| Kuriyama et al. [26] (2005) | N/A | 45.8 | N/A | 620; BMI ≥27.5 kg/m2 | 9,497; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.14 (0.46–2.87) | N/A | Age, smoking status, alcohol drinking status, consumption of meat, consumption of fish, consumption of fruits, consumption of green or yellow vegetables, consumption of bean-paste soup, type of health insurance, menopausal status, parity, age at menarche, and age at end of first pregnancy |
| Kuriyama et al. [26] (2005), women | N/A | 3.4 | N/A | 1,172; BMI ≥27.5 kg/m2 | 10,514; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 0.91 (0.30–2.80) | N/A | Age, smoking status, alcohol drinking status, consumption of meat, consumption of fish, consumption of fruits, consumption of green or yellow vegetables, consumption of bean-paste soup, type of health insurance, menopausal status, parity, age at menarche, and age at end of first pregnancy |
| Rapp et al. [27] (2005) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 5,551; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 34,041; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.67 (0.75–3.72) | N/A | Age, smoking status, and occupational group |
| N’Kontchou et al. [28] (2006) | HCV: 71.0% | 38.0 | 30.0 | 112; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 410; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 2.80 (2.00–4.00) | N/A | Age, sex, cause of cirrhosis, and diabetes |
| Jee et al. [29] (2008) | N/A | 76.8 | N/A | N/A; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | N/A; 23 kg/m2 ≤BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.63 (1.27–2.10) | N/A | Age, and smoking status |
| Jee et al. [29] (2008), women | N/A | 16.6 | N/A | N/A; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | N/A; 23 kg/m2 ≤BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.39 (1.00–1.94) | N/A | Age, and smoking status |
| Joshi et al. [30] (2008) | HBV: 6.6% | 36.4 | 4.1 | 8,508; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 360,879; BMI <18.5 kg/m2 | N/A | 1.08 (0.67–1.72) | Fasting serum glucose, body mass index, alcohol intake and tobacco smoking, and HBsAg |
| Inoue et al. [31] (2009) | N/A | 30.1 | N/A | 5,410; BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 12,180; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 2.22 (1.42–3.48) | N/A | Gender, age, area, smoking status, weekly ethanol intake, coffee intake, total cholesterol, HCV, HBV, metabolic syndrome, high blood pressure, high glucose, low HDL-cholesterol, and high triglycerides |
| Wang et al. [32] (2009) | HBV: 11.7% | 5.0 | 9.2 | 810; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 5,119; BMI <30 kg/m2 | 1.70 (1.02–2.80) | N/A | Gender, age, HBsAg, anti-HCV Ab, diabetes, smoking, and alcohol |
| HCV: 16.6% | ||||||||
| Hart et al. [33] (2010) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1,275; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 7,858; BMI <18.5 kg/m2 | N/A | 3.05 (1.33–7.00) | Age, study, social class, smoking, systolic blood pressure, height, ischemia on ECG, bronchitis, FEV1, angina and diabetes |
| Hart et al. [33] (2010), women | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1,405; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 5,176; BMI <18.5 kg/m2 | N/A | 1.11 (0.24–5.27) | Age, study, social class, smoking, systolic blood pressure, height, ischemia on ECG, bronchitis, FEV1, angina and diabetes |
| Chao et al. [34] (2011) | HBV: 100.0% | 8.3 | N/A | 351; BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 791; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.58 (1.16–2.17) | N/A | Age, smoking, alcohol consumption, family history of HCC, HBV, and number of visits |
| Hung et al. [35] (2011) | HCV: 100.0% | N/A | 17.2 | 585; BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 727; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.31 (0.83–2.05) | N/A | Age, gender, diabetes, cirrhosis, HCV genotype, SVR, platelet count, and AFP |
| Borena et al. [36] (2012) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 66,283; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 kg/m2 | 301,702; BMI <30 kg/m2 | 2.07 (1.51–2.83) | N/A | Age at baseline, stratified by cohort, f birth year, sex, and smoking status |
| Chen et al. [37] (2013) | HBV: 10.0% | N/A | 9.6 | 13,538; BMI ≥27 | 50,856; BMI <27 kg/m2 | 0.98 (0.74–1.30) | N/A | Age, sex, cause of liver disease, ALT, platelet count, albumin globulin ratio, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome |
| HCV: 9.2% | ||||||||
| Li et al. [38] (2013) | N/A | N/A | 7.1 | 5,758; BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 8,892; 21 kg/m2 ≤BMI <23 kg/m2 | N/A | 1.15 (0.83–1.60) | Age, smoking status, ethanol consumption, hours of walking, hours of exercise, frequencies of coffee and fish intake, education level, area of residence, histories of diabetes mellitus, gallbladder disease, blood transfusion, and history of liver disease |
| Li et al. [38] (2013), women | N/A | N/A | 7.1 | 9,676; BMI ≥25 kg/m2 | 11,094; 21 kg/m2 ≤BMI <23 kg/m2 | N/A | 1.42 (0.95–2.13) | Age, smoking status, ethanol consumption, hours of walking, hours of exercise, frequencies of coffee and fish intake, education level, area of residence, histories of diabetes mellitus, gallbladder disease, blood transfusion, and history of liver disease |
| Loomba et al. [39] (2013) | HBV: 17.5% | 10.6 | 2.5 | 1,147; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 22,565; BMI <30 kg/m2 | 1.47 (0.95–2.30) | N/A | Age, sex, alcohol consumption, smoking, HBsAg, ALT, HCV antibody, and diabetes |
| HCV: 5.5% | ||||||||
| Song et al. [40] (2014), men | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A; BMI ≥35 kg/m2 | N/A; BMI <18.5 kg/m2 | 4.30 (1.30–12.65) | N/A | Age, living area, smoking status, leisure-time physical activity, and education |
| Song et al. [40] (2014), women | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A; BMI ≥35 kg/m2 | N/A; BMI <18.5 kg/m2 | 1.81 (0.40–8.21) | N/A | Age, living area, smoking status, leisure-time physical activity, and education |
| Meyer et al. [41] (2015) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2,821; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 21,99; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 2.21 (1.18–4.15) | N/A | Age, sex, survey, alcohol consumption, frequency of PA, civil status, years of education, nationality, and healthy diet |
| Campbell et al. [42] (2016) | N/A | N/A | 6.5 | 320,285; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | N/A; 18.5 kg/m2 ≤BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.75 (1.56–1.98) | N/A | Age, sex, study, alcohol, cigarette smoking, race, and diabetes |
| Liu et al. [43] (2016) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3,534; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 64,719; BMI <30 kg/m2 | 1.93 (1.14–3.27) | N/A | Education, total energy intake, total vegetable and fruit intake, total meat intake, leisure-time physical activity, and alcohol consumption, hormone replacement treatment, menopausal status, spouse smoking exposure, parity, and family history of cancer |
| Setiawan et al. [44] (2016), men | N/A | 19.0 | 12.3 | 13,627; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 27,964; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.82 (1.31–2.52) | N/A | Age, race/ethnicity, education, alcohol intake, smoking status, and diabetes |
| Setiawan et al. [44] (2016), women | N/A | 5.1 | 10.7 | 20,112; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 41,628; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.32 (0.83–2.11) | N/A | Age, race/ethnicity, education, alcohol intake, smoking status, and diabetes |
| McMahon et al. [45] (2017) | HCV: 100.0% | 29.0 | 10.0 | N/A; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | N/A; BMI <30 kg/m2 | 1.06 (0.50–2.10) | 0.79 (0.50–1.20) | Age, sex, and HCV genotype |
| Nderitu et al. [46] (2017) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4,973; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 40,066; BMI <25 kg/m2 | 2.05 (1.00–4.22) | N/A | Age, gender, social economic status, BMI, triglycerides, cholesterol, raised glucose, diabetic status, and history of liver disease |
| Yang et al. [47] (2017) | N/A | N/A | 8.4 | 62,704; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 106,966; 18.5 kg/m2 ≤BMI <25 kg/m2 | 2.19 (1.62–2.95) | N/A | Age, sex, physical activity, cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, history of diabetes, and red meat consumption |
| Brichler et al. [48] (2019) | HBV: 100.0% | 5.5 | 11.0 | 34; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 137; BMI <30 kg/m2 | 2.67 (1.04–6.84) | N/A | Age, varix, hypertension, GGT, bilirubin, platelet count, and AFP |
| Hagström et al. [49] (2018) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 19,658; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 744,131; 18.5 kg/m2 ≤BMI <22.5 kg/m2 | 3.59 (1.85–6.99) | N/A | Age, location of conscription, own and parental education, parental socioeconomic status, scores on intelligence test, cardiovascular capacity, muscular strength tests, systolic and diastolic blood pressures |
| Jeong et al. [50] (2018) | N/A | 11.3 | N/A | 14,621; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 65,329; 18.5 kg/m2 ≤BMI <25 kg/m2 | N/A | 1.27 (0.99–1.62) | Age, sex, smoking, alcohol intake, household income, and physical activity |
| Yi et al. [51] (2018) | HBV: 0.5% | 22.4 | 10.3 | 14,527; BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 315741; 18.5 kg/m2 ≤BMI <25 kg/m2 | 1.17 (0.93–1.46) | N/A | Age, sex, smoking status, alcohol use, physical activity, income status, BMI, diabetes status, cirrhosis, HBV, and HCV |
| HCV: 0.1% |
DM, diabetes mellitus; N, number; HR, hazard ratio; PLC, primary liver cancer; CI, confidence interval; N/A, not available; BMI, body mass index; FEV1, forced expiratory volume-one second; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; HDL, high density lipoprotein; ECG, electrocardiogram; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; SVR, sustained virological response; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; ALT, alanine transaminase; PA, physical activity; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase.
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Seung Kew Yoon

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4476-4868 - Related articles
-
Drug induced liver injury: East versus West – a systematic review and meta-analysis2020 April;26(2)
Radiomics and radiogenomics of primary liver cancers2019 March;25(1)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print



