| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 28(1); 2022 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
FOOTNOTES
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā1.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā4.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā5.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā6.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā1.
Figure┬Ā1.
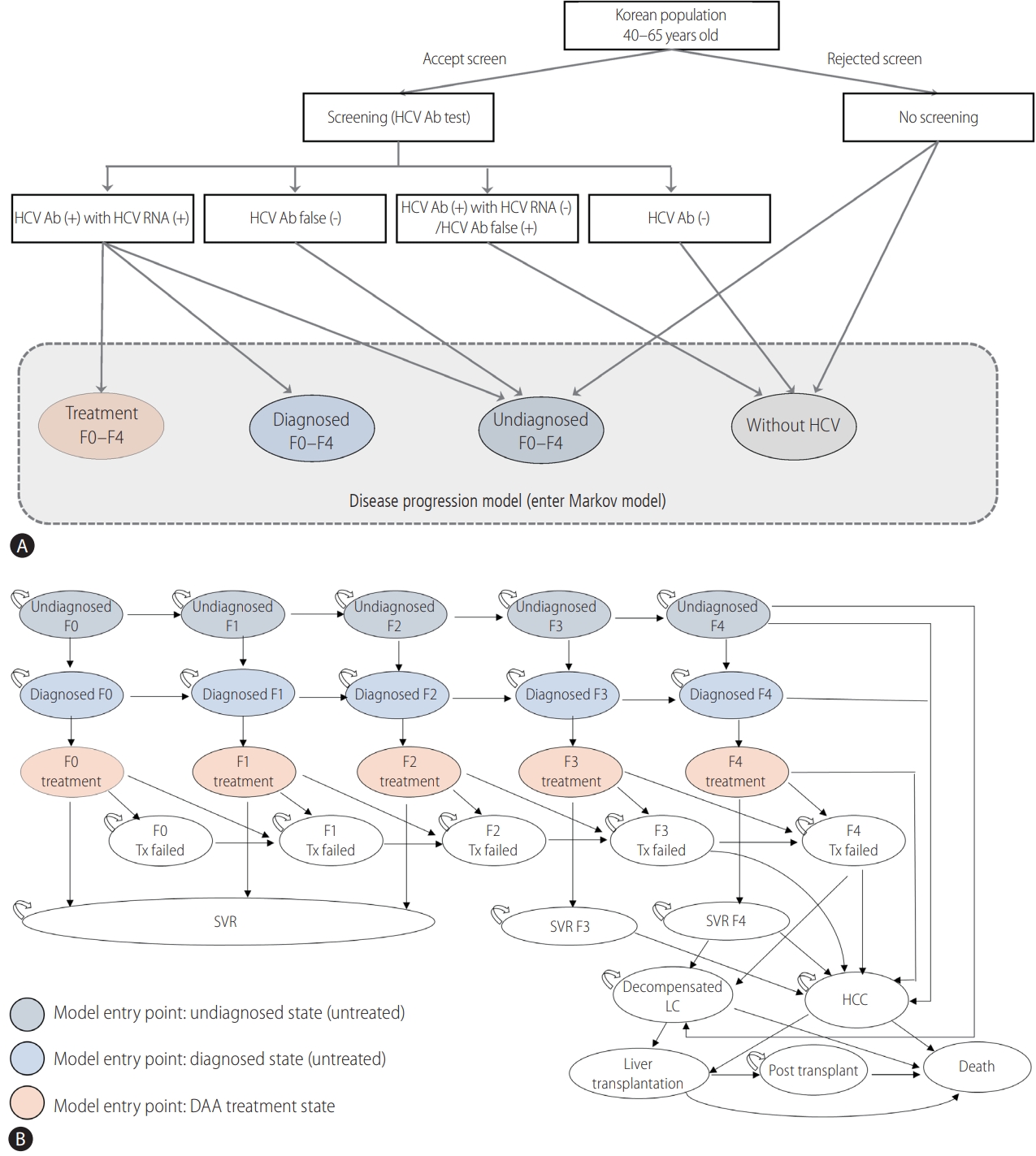
Figure┬Ā2.

Figure┬Ā3.
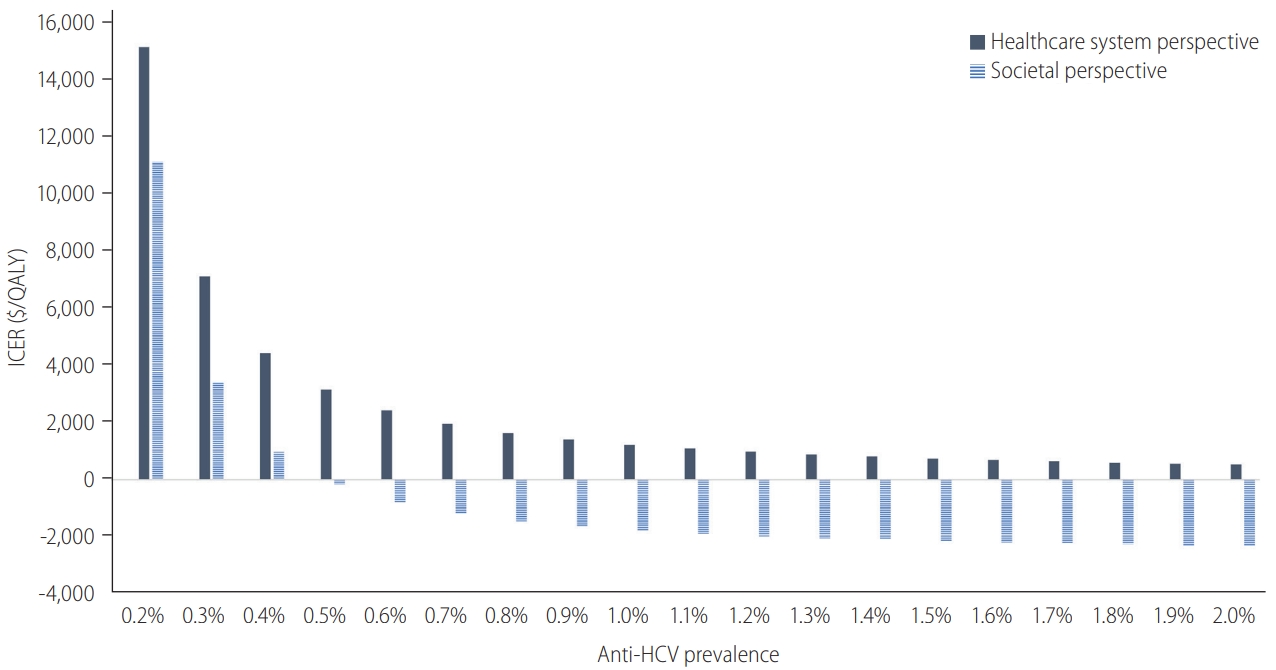
Figure┬Ā4.
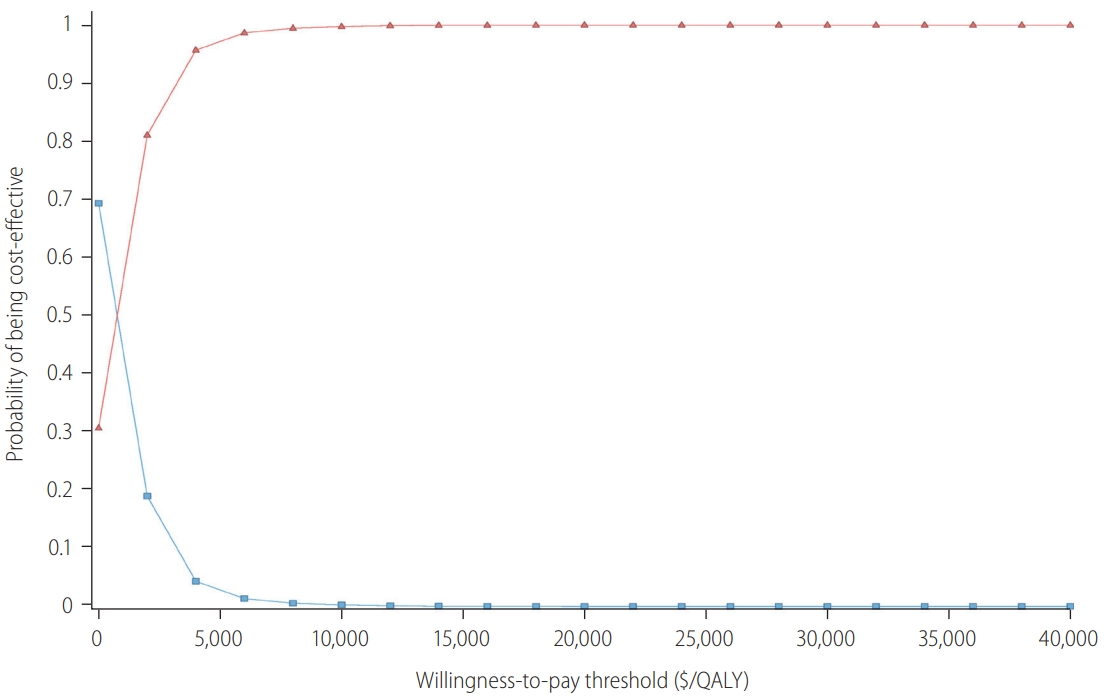
Table┬Ā1.
| Parameter | Value | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population characteristics & analysis conditions | ||||
| ŌĆā | Population structure by age | [16] | ||
| ŌĆā | Age 40ŌĆō49 years | 39.68% | ||
| Age 50ŌĆō59 years | 40.55% | |||
| Age 60ŌĆō65 years | 19.78% | |||
| Anti-HCV prevalence by age group | [6] | |||
| In 40s | 0.38% (0.28ŌĆō1.00%) | |||
| In 50s | 0.61% (0.60ŌĆō1.30%) | |||
| In 60s | 1.06% (0.88ŌĆō1.80%) | |||
| Acceptability of screening | 77.35% | KNHIS claim data | ||
| Referral rate | 70.0% (60.0ŌĆō80.0%) | Assumption | ||
| Acceptability of treatment | 72.8% | [6] | ||
| Treatment efficacy (SVR rate)* | 96.3% | [17,19-22] | ||
| Awareness of HCV infection | 20.0% | [43] | ||
| Detection rate without screeningŌĆĀ | [6,18] | |||
| In 40s | 5.26% | |||
| In 50s | 5.57% | |||
| In 60s | 3.77% | |||
| HCV screening test | [44] | |||
| Sensitivity | 98.1% (92.6ŌĆō99.7%) | |||
| Specificity | 99.8% (99.2ŌĆō99.9%) | |||
| HCV RNA positivity in people with anti-HCV | 46.5% (30.0ŌĆō50.0%) | [9,15] | ||
| Distribution of fibrosis stage by age | [45] | |||
| Age 40ŌĆō49 years | ||||
| ŌĆāStage F0 | 6.67% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F1 | 45.33% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F2 | 26.67% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F3 | 13.33% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F4 | 8.00% | |||
| Age 50ŌĆō59 years | ||||
| ŌĆāStage F0 | 10.28% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F1 | 27.10% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F2 | 38.32% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F3 | 14.95% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F4 | 9.35% | |||
| Age 60ŌĆō65 years | ||||
| ŌĆāStage F0 | 4.31% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F1 | 34.44% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F2 | 24.44% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F3 | 16.80% | |||
| ŌĆāStage F4 | 20.00% | |||
| Transition probability | ||||
| Annual probability of fibrosis progression | [25] | |||
| F0 to F1 | 0.107 (0.097ŌĆō0.118) | |||
| F1 to F2 | 0.082 (0.074ŌĆō0.091) | |||
| F2 to F3 | 0.117 (0.107ŌĆō0.129) | |||
| F3 to F4 | 0.116 (0.104ŌĆō0.131) | |||
| Annual probability of disease progression | ||||
| F3 to HCC | 0.0073 (0.0000ŌĆō0.0087) | [23,24] | ||
| F4 to DC | 0.048 (0.030ŌĆō0.067) | [24,26,27] | ||
| F4 to HCC | 0.053 (0.024ŌĆō0.077) | [24,27,30] | ||
| DC to HCC | 0.075 (0.014ŌĆō0.082) | [23,26,30] | ||
| DC to LT | 0.023 (0.010ŌĆō0.062) | [31] | ||
| DC to death | 0.118 (0.103ŌĆō0.216) | [23,26,30] | ||
| HCC to LT | 0.04 (0.00ŌĆō0.14) | [31] | ||
| HCC to death | 0.32 (0.19ŌĆō0.43) | [23,32,33] | ||
| LT to death | 0.21 (0.14ŌĆō0.21) | [28] | ||
| Post-LT to death | 0.014 (0.011ŌĆō0.034) | [28] | ||
| Annual probability of disease progression after SVR | ||||
| SVR(F3) ŌåÆ HCC | 0.00475 (0.00000ŌĆō0.00577) | [31] | ||
| SVR(F4) ŌåÆ DC | 0.0033 | [29] | ||
| SVR(F4) ŌåÆ HCC | 0.0034 | [29] | ||
Values are presented as number (range).
HCV, hepatitis C virus; KNHIS, Korean National Health Insurance Service; SVR, sustained virologic response; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; DC, decompensated cirrhosis; LT, liver transplantation.
* Weighted average value by the distribution of direct acting antiviral use (2019 data from Korean HCV cohort study).
ŌĆĀ Number of notification of hepatitis C infection/antibodies to HCV prevalence (data from the infectious disease portal [http://www.kdca.go.kr/npt/biz/npp/ist/bass/bassSexdstnAgeStatsMain.do]).
Table┬Ā2.
Table┬Ā3.
| Scenario (applied value at base-case) |
ICER ($/QALY) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare perspective | Societal perspective | ||
| Base-case | 2,666 | 431 | |
| Anti-HCV prevalence (40s: 0.23%, 50s: 0.38%, 60s: 1.06%) | |||
| ŌĆā | 0.4% | 4,429 | 962 |
| 0.6% | 2,422 | Dominant* | |
| 0.8% | 1,634 | Dominant* | |
| 1.0% | 1,223 | Dominant* | |
| 1.2% | 973 | Dominant* | |
| 1.4% | 806 | Dominant* | |
| Detection rate without HCV screening (40s: 5.26%, 50s: 5.57%, 60s: 3.77%) | |||
| 2% | 1,841 | Dominant* | |
| 12% | 5,174 | 3,731 | |
| Age group (40ŌĆō65 years) | |||
| 40s | 3,561 | Dominant* | |
| 50s | 2,808 | 1,446 | |
| 60s | 1,728 | 1,352 | |
| Acceptability of DAA treatment (72.8%) | |||
| 60% | 3,788 | 2143 | |
| 80% | 2,084 | Dominant* | |
| SVR rate (96.3%) | |||
| -5%: 91.5% | 3,186 | 1,025 | |
| +3%: 99.2% | 2,378 | 101 | |
| Cost | |||
| Excluding genotype test ($127.32): $0 | 2,313 | 254 | |
| Screening test ($3.91): D7026, $13.61 | 8,199 | 5,964 | |
| HCC state ($10,972.06): from other source8, $6,160 | 3,433 | 1,197 | |
| DC state ($8,487.37): from other source8, $6,258 | 3,019 | 783 | |
| Discount rate (4.5%) | |||
| 0% | Dominant* | Dominant* | |
| 3% | 992 | Dominant* | |
| Utility | |||
| SVR (0.894): lower value, 0.83 | 3,936 | 636 | |
| SVR (0.894): upper value, 0.92 | 2,357 | 381 | |
| F0ŌĆōF3 (0.854): lower value, 0.79 | 2,193 | 354 | |
| F0ŌĆōF3 (0.854): upper value, 0.88 | 2,922 | 472 | |
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Sook-Hyang Jeong

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4916-7990 - Related articles
-
Current status of and strategies for hepatitis C control in South Korea2017 September;23(3)




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print



