| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 29(Suppl); 2023 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are common health problems related to aging. Despite the differences in their diagnostic methods, several cross-sectional and longitudinal studies have revealed the close link between sarcopenia and NAFLD. Sarcopenia and NAFLD are linked by several shared pathogenetic mechanisms, including insulin resistance, hormonal imbalance, systemic inflammation, myostatin and adiponectin dysregulation, nutritional deficiencies, and physical inactivity, thus implicating a bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD. However, there is not sufficient data to support a direct causal relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD. Moreover, it is currently difficult to conclude whether sarcopenia is a risk factor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or is a consequence of NASH. Therefore, this review intends to touch on the shared common mechanisms and the bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD.
The global epidemic of obesity and metabolic syndrome in an aging population has led to growing health problems including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and sarcopenia. Sarcopenia is defined as the progressive and generalized loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and/or function with a risk of adverse outcomes such as physical disability, hospitalization, and mortality [1,2]. Despite the differences in their diagnostic methods, several studies have revealed the close link between sarcopenia and NAFLD [3-16]. This review focuses on the shared mechanisms and a bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD.
Sarcopenia, previously considered an aging-related syndrome, is now recognized as a progressive disease associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), metabolic syndrome, liver disease, and cardiovascular disease [17-20]. It is primarily associated with aging and secondarily with diseases mediated by systemic inflammation and insulin resistance (IR) [21]. In 2018, the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People defined sarcopenia by low levels across three parameters: muscle strength, muscle quantity/quality, and physical performance. The presence of low muscle strength is the primary parameter to suspect sarcopenia, while the presence of low muscle mass (quantity) and quality are confirmatory. The coexistence of these factors represents severe sarcopenia [2]. Therefore, all these parameters enable improved understanding and awareness of sarcopenia.
Sarcopenia and NAFLD share common underlying mechanisms, including IR, hormonal imbalance, systemic inflammation, myostatin and adiponectin dysregulation, nutritional deficiencies, and physical inactivity (Fig. 1) [22].
IR is the main pathologic mechanism causing both sarcopenia and NAFLD. IR results from the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It causes increased lipolysis with the consequent release of free fatty acids (FFA) from adipose tissue. IR also inhibits growth hormone (GH)/insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) axis that normally plays a protective role in muscle regeneration and age-related muscle loss [17,23,24]. It causes compensatory hyperinsulinemia, which leads to promotion of gluconeogenesis, upregulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c, inhibition of β-oxidation, increased FFA delivery, and altered triglyceride (TG) transport. These events leads to accumulation of TGs in skeletal muscle and the liver, often referred to as ectopic fat [25,26].
Impaired suppression of gluconeogenesis promotes proteolysis and reduces protein synthesis [7], which results in age-related muscle depletion and sarcopenia [27-29]. Insulin activates the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), 4E-binding protein 1, and ribosomal S6 kinase 1. These are involved in protein synthesis, maintenance of muscle mass, and skeletal muscle anabolism [30]. Skeletal muscle IR leads to increased muscle degradation with decreased mitochondrial content, function, and oxidative capacity [31]. A study demonstrated that T2DM was independently associated with sarcopenia, leading to metabolic disorders and physical disability in older adults with T2DM [32]. Furthermore, sarcopenia aggravates IR, since skeletal muscle is a primary insulin-responsive organ [33]. Likewise, myosteatosis, defined as fatty infiltration of muscle, is associated with reduced muscle function, IR, and a high risk of mortality in cirrhotic patients [34,35]. Both sarcopenia and obesity simultaneously induce more severe IR and glycemic dysregulation [33].
Inflammation and oxidative stress have been linked to the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Intramuscular lipid accumulation induces the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines from adipose tissue and generates oxygen-free radicals in the liver by inhibiting mitochondrial function for β-oxidation, leading to lipid peroxidation. Cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) induce chronic low-grade inflammation [36,37]. Compared to healthy subjects, patients with isolated steatosis and steatohepatitis had increased TNF-α levels [38]. TNF-α causes lipid accumulation in the liver through activation of de novo lipogenesis (DNL) [39]. It also stimulates nuclear factor κB, the main transcriptional factor for proinflammatory cytokines that contribute to the development of NAFLD and muscle catabolism [36,39,40]. Catabolic inflammation further worsens sarcopenia among older patients because of the release of numerous inflammatory mediators from immune cells and adipocytes that contribute to the development of IR [41]. Patients with sarcopenia demonstrate chronic inflammation, increased levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and proinflammatory cytokines, and decreased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines [3]. IL-6 and CRP levels are also positively associated with total body fat mass and inversely associated with appendicular lean body mass [4,42].
Vitamin D is involved in the modulation of IR, NAFLD, metabolic syndrome, and sarcopenia [43]. It plays an essential role in myogenesis, myoblast proliferation and differentiation, production and growth of skeletal muscle cells, and skeletal muscle inflammation [44-47]. It exerts its effects through the nuclear vitamin D receptor (VDR), which is expressed in the liver and skeletal muscle [48,49]. Downregulation of VDR expression by vitamin D deficiency and aging may lead to sarcopenia [36]. Studies shows that subjects with sarcopenia have significantly lower vitamin D levels [6,50]. Decreased levels of vitamin D are associated with decreased muscle strength, poor muscle function, and an increased risk of sarcopenia among older adults [51]. However, vitamin D supplementation increases VDR expression in skeletal muscle, preventing the development of sarcopenia [52].
The relationship between vitamin D and NAFLD has been already acknowledged. A meta-analysis including 17 cross-sectional and case-control studies showed that patients with NAFLD had decreased levels of serum vitamin D [43]. Hypovitaminosis D was strongly associated with the presence of NAFLD independent of metabolic syndrome, T2DM, and IR [50].
Furthermore, vitamin D downregulates the expression of SREBP-1c, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase, and fatty acid synthase that modulate DNL, while peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor α and carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 that mediate hepatic fatty acid oxidation are upregulated by vitamin D [53]. An animal study demonstrated that vitamin D deficiency worsened NAFLD by activating the inflammationmediated pathway [43]. Vitamin D deficiency also causes IR via upregulation of hepatic IR, inflammatory, and oxidative stress genes [54,55]. Moreover, VDR-knockout mice spontaneously developed hepatic steatosis [55]. Most studies, to date, have shown that vitamin D plays a pivotal role in the development of sarcopenia and NAFLD. On the contrary, other studies demonstrated no significant relationship between vitamin D level and NAFLD/sarcopenia [56,57].
Skeletal muscle is an endocrine organ that releases myokines [58,59] after muscle contraction or strength training [60]. Myokines are involved in the autocrine regulation of muscle metabolism and the paracrine/endocrine regulation of other tissues and organs including the liver, adipose tissue, and brain [61-63].
Myostatin, a member of the TGF-β family, is predominantly expressed in skeletal muscles [64,65]. It is an inhibitor of muscle mass and a key regulator of adipogenesis [65-68]. It mediates Smad 2/3 activation, inhibiting myogenesis and protein synthesis by suppressing the Akt-mediated mTOR signaling pathway [69]. This causes muscle atrophy. Muscle proteolysis is stimulated through FoxO-dependent activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and autophagy [69]. Myostatin also increases adipose tissue mass and inhibits adiponectin secretion [22,70,71]. Animal studies have demonstrated that blockage of myostatin significantly increases muscle mass, improves insulin sensitivity, and protects against liver steatosis [72,73]. Animal models have demonstrated increased expression of activin type IIB, a myostatin receptor expressed in stellate cells, in liver fibrosis [74,75]. Stellate cell cultures exposed to myostatin increase the expression of profibrotic proteins [76]. Therefore, myostatin, IR, and liver fibrogenesis are interconnected.
Irisin, an exercise-induced myokine, is inversely associated with the degree of fatty liver in obese patients and is a potential cause of sarcopenia and NAFLD. It increases energy expenditure through peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor α-dependent downstream signaling and improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis by upregulating fibroblast growth factor-21; these effects were independent of reduction in body weight and adiposity in a mouse model [77,78]. It increases glucose uptake by enhancing glucose transporter type 4 translocation and β-oxidation of FFA through AMP-activated protein kinase activation in muscle cells [79]. Irisin expression in muscle and serum irisin level are reduced in obese subjects [80].
IL-6 has a dual metabolic effect. Muscle contrations stimulate acute IL-6 release from muscles [81,82], with the levels increasing as the duration and intensity of muscle contraction increase [83,84]. IL-6 improves hepatic glucogenesis, lipolysis in adipose tissue, pancreatic β-cell viability, and insulin secretion [81,85,86]. It also enhances glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation through adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling processes [87,88]. However, IL-6 acts as a pro-inflmmatory cytokine in chronic inflammatory states such as obesity, infection, and cancer [89]. A study have demonstrated that increased IL-6 levels are associated with NASH, hepatic fibrosis, and IR [90].
The lack of physical activity causes loss of muscle mass and reduces energy consumption, resulting in obesity and hepatic steatosis [91]. Both sarcopenia and NAFLD are worsened by chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and IR [92]. During exercise, production of pro-inflammatory cytokines is decreased while anti-inflammatory cytokine production, muscle protein synthesis, regeneration, and glucose uptake are increased. Physical activity mitigates the risk of sarcopenia progression [93]. Exercise can improve metabolic health status even without significant weight loss [94].
Adiponectin, a hormone secreted from adipose tissue, mediates glucose and lipid metabolism in insulin-sensitive tissues such as liver and muscle. In the liver, adiponectin promotes glucose use and enhances fatty acid oxidation by improvement of insulin action via activation of AMPK [95,96]. In addition, adiponectin has an anti-inflammatory effect by neutralizing TNF-α, and improves hepatic steatosis and inflammation [97].
Anabolic hormones, such as GH and IGF-1, decline with aging process, which affects the progressive loss of muscle mass [98]. Fat accumulation and aging impair the GH/IGF-1 signaling pathway, leading to deterioration of muscle mass synthesis [99,100]. In an experiental mouse model of NAFLD, NAFLD was associated with decreased muscle mass and strength, and reduced IGF-1 level, implicating that IGF-1 reduction might play a role in the development of NAFLD-related sarcopenia [101].
Numerous studies have reported a relationship between NAFLD and sarcopenia (Tables 1, 2). Sarcopenia is a risk factor for the presence and severity of NAFLD (Table 1) [7,22,102,103]. The prevalence of sarcopenia is significantly increased in NAFLD and NASH compared to that in non-NAFLD (17.9% and 35.0% vs. 8.7%, respectively) [3]. NAFLD patients with sarcopenia had a 2-fold higher risk of developing NASH and significant fibrosis independent of obesity and IR [3]. However, most studies were cross-sectional in design and the causal relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD remains unclear. A recent study demonstrated that NAFLD was developed in 14.8% of its participants during a 7-year follow-up, with an increased incidence in participants with the lowest tertile of skeletal muscle mass at baseline. Baseline skeletal muscle mass was also positively associated with the resolution of existing NAFLD, regardless of metabolic risk factors [10]. Sarcopenia was associated with poor clinical outcomes, including severe hepatic fibrosis and increased mortality, in NAFLD patients [104-106]. Hence, low skeletal muscle mass may cause the development of NAFLD. In a multicenter prospective study, hepatic steatosis at baseline was significantly associated with the risk of sarcopenia in older adults. Lower muscle mass and strength were more common in NAFLD patients [16]. In another study, the loss of skeletal muscle mass was faster in subjects with NAFLD compared to those without NAFLD. When stratified by fibrosis severity, skeletal muscle mass loss was faster in NAFLD subjects with an intermediate-to-high probability of advanced fibrosis than in those without (Table 2) [107].
Muscle quality also plays a critical role in the development of NASH. Myosteatosis determines muscle strength and function, and metabolic and liver-related clinical outcomes [108-110]. It is a prognosticator for NASH development [108,111,112]. Studies have suggested that myosteatosis is a clinically useful surrogate marker for NASH [108] by demonstrating that severe myosteatosis, but not sarcopenia, predicts NASH development and fibrosis progression [111]. The prevalence of myosteatosis is increased in obese subjects with NASH; hence, myosteatosis could reflect the histological features of NASH [110]. Muscle alterations are linked with fibrosis severity in subjects with NAFLD [3-5,9,22,113-117]. These suggest that the role of sarcopenia in NASH development is unclear. Both sarcopenia and myosteatosis have been linked to advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis [22,34,118-121]. However, the relatively low skeletal muscle mass observed in NAFLD patients may derive from increased body fat percentage [15,110]. Muscle wasting is often seen in patients with advanced fibrosis, implicating reverse causality between low skeletal muscle mass and NAFLD severity [9,14]. Patients with liver cirrhosis had concomitant sarcopenia (43%), sarcopenic obesity (low muscle mass with obesity) (26%), and myosteatosis (52%) [34]. Hence, advanced fibrosis is more likely to cause sarcopenia rather than sarcopenia causing fibrosis progression.
It is currently difficult to conclude whether sarcopenia is a risk factor or a consequence of NASH. However, sarcopenia and NAFLD are linked by several shared pathogenetic mechanisms, implicating a bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD. Therefore, further studies are needed to investigate the effects of low muscle function and performance on NAFLD progression. In addition, prospective standardized trials with accurate diagnoses of sarcopenia and NAFLD are warranted to elucidate the cause-and-effect relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MEST) (2021R1A2C2005820 and 2021M3A9E4021818), the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI21C0538), and the Research Program funded by the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2022ER090200).
FOOTNOTES
Figure 1.
Bidirectional relationship between sarcopenia and NAFLD. NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
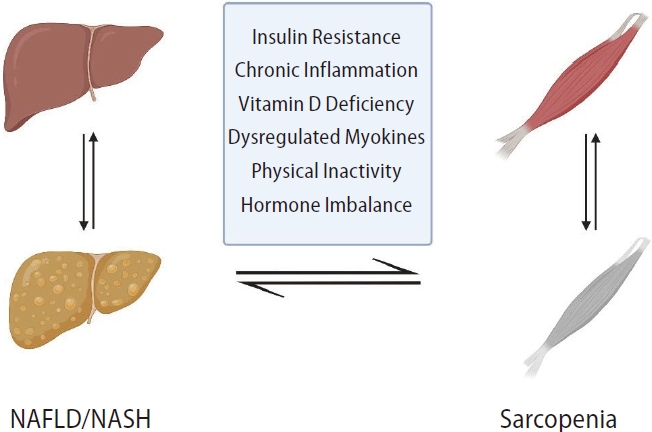
Table 1.
Studies of sarcopenia as a risk factor for NAFLD
| Study (yr) | Study design | Study size | Study population | Sarcopenia assessment | NAFLD assessment | Study conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hong et al. (2014) [4] | Cross-sectional | 526 | Korean | DXA | CT | 5-fold increased risk of NAFLD |
| Lee et al. (2015) [6] | Cross-sectional | 15,132 | Korean | DXA | Noninvasive models | 2.3- to 3.3-fold increased risk of NAFLD in patients with sarcopenia |
| Lee et al. (2016) [7] | Cross-sectional | 2,761 | Korean | DXA | Noninvasive models | 2-fold increased risk of fibrosis in patients with sarcopenia |
| Kim et al. (2016) [8] | Cross-sectional | 3,739 | Korean | DXA | Noninvasive models | Low SMI is associated with NAFLD according to age group and menopause status |
| Koo et al. (2017) [3] | Cross-sectional | 309 | Korean | BIA | Liver biopsy | Increased prevalence of sarcopenia with NAFLD severity |
| 2.5-fold increased risk of NASH and significant fibrosis in patients with sarcopenia | ||||||
| Petta et al. (2017) [9] | Cross-sectional | 225 | Italian | BIA | Liver biopsy | 2-fold increased risk of fibrosis in NAFLD in patients with sarcopenia |
| Zhai et al. (2018) [12] | Cross-sectional | 494 | Chinese | DXA | US | NAFLD is not independently associated with sarcopenia. |
| Kim et al. (2018) [10] | Longitudinal | 10,534 | Korean | BIA | Noninvasive models | Increased incidence of NAFLD in patients with sarcopenia |
| Increased resolution of baseline NAFLD with higher muscle mass | ||||||
| Wijarnpreecha et al. (2019) [13] | Cross-sectional | 11,325 | American | BIA | US | 2.3-fold increased risk of NAFLD in patients with sarcopenia |
| 1.8-fold increased advanced fibrosis in patients with sarcopenia | ||||||
| Hsieh et al. (2021) [104] | Cross-sectional | 521 | Korean | CT | Liver biopsy | Increased risk of significant fibrosis in NAFLD |
| Hsieh et al. (2022) [111] | Longitudinal | 338 | Korean | CT | Liver biopsy | Severe myosteatosis is significantly associated with early NASH and fibrosis progression in early stage NAFLD |
Table 2.
Studies of NAFLD as a risk factor for sarcopenia
| Study (yr) | Study design | Study size | Study population | Sarcopenia assessment | NAFLD assessment | Study conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Issa et al. (2014) [5] | Cross-sectional | 75 | American | CT | Liver biopsy | Increased risk of sarcopenia in NASH and NASH cirrhosis |
| Sinn et al. (2022) [107] | Longitudinal | 52,815 | Korean | BIA | US | Faster loss of skeletal muscle mass in NAFLD |
| Much faster loss of skeletal muscle mass in NAFLD according to fibrosis severity | ||||||
| Roh et al. (2022) [16] | Longitudinal | 1,595 | Korean | DXA | Noninvasive models | Increased risk of developing LMM (1.65-fold) and LMS (2.29-fold) in NAFLD |
Abbreviations
CRP
C-reactive protein
FFA
free fatty acid
GH
growth hormone
IGF-1
insulin growth factor-1
IL-6
interleukin-6
IR
insulin resistance
NAFLD
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
NASH
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
TG
triglyceride
T2DM
type 2 diabetes mellitus
TGF-β
transforming growth factor-β
TNF-α
tumor necrosis factor-α
VDR
vitamin D receptor
REFERENCES
2. Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. 2019;48:16-31 Erratum in: Age Ageing 2019;48:601. 601.



3. Koo BK, Kim D, Joo SK, Kim JH, Chang MS, Kim BG, et al. Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and significant fibrosis. J Hepatol 2017;66:123-131.


4. Hong HC, Hwang SY, Choi HY, Yoo HJ, Seo JA, Kim SG, et al. Relationship between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study. Hepatology 2014;59:1772-1778.


5. Issa D, Alkhouri N, Tsien C, Shah S, Lopez R, McCullough A, et al. Presence of sarcopenia (muscle wasting) in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2014;60:428-429 Erratum in: Hepatology 2015;62:1330.



6. Lee YH, Jung KS, Kim SU, Yoon HJ, Yun YJ, Lee BW, et al. Sarcopaenia is associated with NAFLD independently of obesity and insulin resistance: nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008-2011). J Hepatol 2015;63:486-493.


7. Lee YH, Kim SU, Song K, Park JY, Kim DY, Ahn SH, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with significant liver fibrosis independently of obesity and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008-2011). Hepatology 2016;63:776-786.



8. Kim HY, Kim CW, Park CH, Choi JY, Han K, Merchant AT, et al. Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2016;15:39-47.


9. Petta S, Ciminnisi S, Di Marco V, Cabibi D, Cammà C, Licata A, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with severe liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017;45:510-518.



10. Kim G, Lee SE, Lee YB, Jun JE, Ahn J, Bae JC, et al. Relationship between relative skeletal muscle mass and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 7-year longitudinal study. Hepatology 2018;68:1755-1768.



11. Lee MJ, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Kim GA, Park SW, Choe J, et al. Agerelated decrease in skeletal muscle mass is an independent risk factor for incident nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 10-year retrospective cohort study. Gut Liver 2019;13:67-76.



12. Zhai Y, Xiao Q, Miao J. The relationship between NAFLD and sarcopenia in elderly patients. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;2018:5016091.




13. Wijarnpreecha K, Kim D, Raymond P, Scribani M, Ahmed A. Associations between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and advanced fibrosis in the USA. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;31:1121-1128.


14. Kang MK, Park JG, Lee HJ, Kim MC. Association of low skeletal muscle mass with advanced liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;34:1633-1640.



15. Peng TC, Wu LW, Chen WL, Liaw FY, Chang YW, Kao TW. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia in a Western population (NHANES III): the importance of sarcopenia definition. Clin Nutr 2019;38:422-428.


16. Roh E, Hwang SY, Yoo HJ, Baik SH, Lee JH, Son SJ, et al. Impact of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on the risk of sarcopenia: a nationwide multicenter prospective study. Hepatol Int 2022;16:545-554.



17. Kalyani RR, Corriere M, Ferrucci L. Age-related and diseaserelated muscle loss: the effect of diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:819-829.



18. Wong E, Backholer K, Gearon E, Harding J, Freak-Poli R, Stevenson C, et al. Diabetes and risk of physical disability in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2013;1:106-114.


19. Zhang H, Lin S, Gao T, Zhong F, Cai J, Sun Y, et al. Association between sarcopenia and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged and older non-obese adults: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Nutrients 2018;10:364.



20. Hsu CS, Kao JH. Sarcopenia and chronic liver diseases. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;12:1229-1244.


21. Bauer J, Morley JE, Schols AMWJ, Ferrucci L, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Dent E, et al. Sarcopenia: a time for action. An SCWD position paper. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019;10:956-961.




22. Bhanji RA, Narayanan P, Allen AM, Malhi H, Watt KD. Sarcopenia in hiding: the risk and consequence of underestimating muscle dysfunction in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2017;66:2055-2065.



23. DeFronzo RA, Tripathy D. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32 Suppl 2:S157-S163.




24. Reaven GM. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988;37:1595-1607.


25. Postic C, Girard J. Contribution of de novo fatty acid synthesis to hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: lessons from genetically engineered mice. J Clin Invest 2008;118:829-838.



26. Martín-Domínguez V, González-Casas R, Mendoza-JiménezRidruejo J, García-Buey L, Moreno-Otero R. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2013;105:409-420.


27. Guillet C, Boirie Y. Insulin resistance: a contributing factor to age-related muscle mass loss? Diabetes Metab 2005;31 Spec No 2:5S20-5S26.


28. Bonaldo P, Sandri M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis Model Mech 2013;6:25-39.




29. Fujita S, Glynn EL, Timmerman KL, Rasmussen BB, Volpi E. Supraphysiological hyperinsulinaemia is necessary to stimulate skeletal muscle protein anabolism in older adults: evidence of a true age-related insulin resistance of muscle protein metabolism. Diabetologia 2009;52:1889-1898.




30. Fujita S, Rasmussen BB, Cadenas JG, Drummond MJ, Glynn EL, Sattler FR, et al. Aerobic exercise overcomes the age-related insulin resistance of muscle protein metabolism by improving endothelial function and Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. Diabetes 2007;56:1615-1622.




31. Turcotte LP, Fisher JS. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance: roles of fatty acid metabolism and exercise. Phys Ther 2008;88:1279-1296.




32. Kim TN, Park MS, Yang SJ, Yoo HJ, Kang HJ, Song W, et al. Prevalence and determinant factors of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Care 2010;33:1497-1499. Erratum in: Diabetes Care 2010;33:2294.
33. Srikanthan P, Hevener AL, Karlamangla AS. Sarcopenia exacerbates obesity-associated insulin resistance and dysglycemia: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III. PLoS One 2010;5:e10805.



34. Montano-Loza AJ, Angulo P, Meza-Junco J, Prado CM, Sawyer MB, Beaumont C, et al. Sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis are associated with higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016;7:126-135.



35. Stephen WC, Janssen I. Sarcopenic-obesity and cardiovascular disease risk in the elderly. J Nutr Health Aging 2009;13:460-466.



36. Beyer I, Mets T, Bautmans I. Chronic low-grade inflammation and age-related sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2012;15:12-22.


37. Han JW, Kim DI, Nam HC, Chang UI, Yang JM, Song DS. Association between serum tumor necrosis factor-α and sarcopenia in liver cirrhosis. Clin Mol Hepatol 2022;28:219-231.




38. Hui JM, Hodge A, Farrell GC, Kench JG, Kriketos A, George J. Beyond insulin resistance in NASH: TNF-alpha or adiponectin? Hepatology 2004;40:46-54.


39. Wree A, Kahraman A, Gerken G, Canbay A. Obesity affects the liver - the link between adipocytes and hepatocytes. Digestion 2011;83:124-133.



40. Kawaguchi T, Torimura T. Leaky gut-derived tumor necrosis factor-α causes sarcopenia in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Mol Hepatol 2022;28:177-180.




41. Tilg H, Moschen AR. Insulin resistance, inflammation, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2008;19:371-379.


42. Cesari M, Pedone C, Incalzi RA, Pahor M. ACE-inhibition and physical function: results from the Trial of AngiotensinConverting Enzyme Inhibition and Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factors (TRAIN) study. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2010;11:26-32.



43. Eliades M, Spyrou E, Agrawal N, Lazo M, Brancati FL, Potter JJ, et al. Meta-analysis: vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013;38:246-254.


44. Pang Q, Qu K, Liu C, Zhang JY, Liu SS. Sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: new evidence for low vitamin D status contributing to the link. Hepatology 2016;63:675.



46. Bouillon R, Bischoff-Ferrari H, Willett W. Vitamin D and health: perspectives from mice and man. J Bone Miner Res 2008;23:974-979.


47. Garcia LA, King KK, Ferrini MG, Norris KC, Artaza JN. 1,25(OH)2vitamin D3 stimulates myogenic differentiation by inhibiting cell proliferation and modulating the expression of promyogenic growth factors and myostatin in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology 2011;152:2976-2986.




48. Han S, Chiang JY. Mechanism of vitamin D receptor inhibition of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene transcription in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 2009;37:469-478.



49. Girgis CM, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Hamrick MW, Holick MF, Gunton JE. The roles of vitamin D in skeletal muscle: form, function, and metabolism. Endocr Rev 2013;34:33-83.



50. Barchetta I, Angelico F, Del Ben M, Baroni MG, Pozzilli P, Morini S, et al. Strong association between non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and low 25(OH) vitamin D levels in an adult population with normal serum liver enzymes. BMC Med 2011;9:85.



51. Visser M, Deeg DJ, Lips P; Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. Low vitamin D and high parathyroid hormone levels as determinants of loss of muscle strength and muscle mass (sarcopenia): the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:5766-5772.



52. Tanaka K, Kanazawa I, Yamaguchi T, Yano S, Kaji H, Sugimoto T. Active vitamin D possesses beneficial effects on the interaction between muscle and bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014;450:482-487.


53. Yin Y, Yu Z, Xia M, Luo X, Lu X, Ling W. Vitamin D attenuates high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in rats by modulating lipid metabolism. Eur J Clin Invest 2012;42:1189-1196.


54. Dunlop TW, Väisänen S, Frank C, Molnár F, Sinkkonen L, Carlberg C. The human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta gene is a primary target of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its nuclear receptor. J Mol Biol 2005;349:248-260.

55. Roth CL, Elfers CT, Figlewicz DP, Melhorn SJ, Morton GJ, Hoofnagle A, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in obese rats exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and increases hepatic resistin and Toll-like receptor activation. Hepatology 2012;55:1103-1111.


56. Nelson JE, Roth CL, Wilson LA, Yates KP, Aouizerat B, MorganStevenson V, et al. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased risk of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: possible role for MAPK and NF-κB? Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:852-863.




57. Patel YA, Henao R, Moylan CA, Guy CD, Piercy DL, Diehl AM, et al. Vitamin D is not associated with severity in NAFLD: results of a paired clinical and gene expression profile analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:1591-1598.




59. Hartwig S, Raschke S, Knebel B, Scheler M, Irmler M, Passlack W, et al. Secretome profiling of primary human skeletal muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014;1844:1011-1017.


60. Raschke S, Eckardt K, Bjørklund Holven K, Jensen J, Eckel J. Identification and validation of novel contraction-regulated myokines released from primary human skeletal muscle cells. PLoS One 2013;8:e62008.



61. Carson BP. The potential role of contraction-induced myokines in the regulation of metabolic function for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2017;8:97.



62. Koo BK, Um SH, Seo DS, Joo SK, Bae JM, Park JH, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 predicts advanced fibrosis in biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 2018;38:695-705.



63. Oh S, Lee J. Sarcopenia and blood myokine levels as prognostic biomarkers in patients with liver cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol 2020;26:476-479.



64. Ji S, Losinski RL, Cornelius SG, Frank GR, Willis GM, Gerrard DE, et al. Myostatin expression in porcine tissues: tissue specificity and developmental and postnatal regulation. Am J Physiol 1998;275:R1265-R1273.


65. McPherron AC, Lawler AM, Lee SJ. Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta superfamily member. Nature 1997;387:83-90.



66. Lee SJ, McPherron AC. Myostatin and the control of skeletal muscle mass. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1999;9:604-607.


67. Rebbapragada A, Benchabane H, Wrana JL, Celeste AJ, Attisano L. Myostatin signals through a transforming growth factor beta-like signaling pathway to block adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2003;23:7230-7242.




68. Artaza JN, Bhasin S, Magee TR, Reisz-Porszasz S, Shen R, Groome NP, et al. Myostatin inhibits myogenesis and promotes adipogenesis in C3H 10T(1/2) mesenchymal multipotent cells. Endocrinology 2005;146:3547-3557. Erratum in: Endocrinology 2006;147:4679.
69. Han HQ, Zhou X, Mitch WE, Goldberg AL. Myostatin/activin pathway antagonism: molecular basis and therapeutic potential. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2013;45:2333-2347.


70. Suzuki ST, Zhao B, Yang J. Enhanced muscle by myostatin propeptide increases adipose tissue adiponectin, PPAR-alpha, and PPAR-gamma expressions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008;369:767-773.

71. Dasarathy S. Is the adiponectin-AMPK-mitochondrial axis involved in progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? Hepatology 2014;60:22-25.



72. Wilkes JJ, Lloyd DJ, Gekakis N. Loss-of-function mutation in myostatin reduces tumor necrosis factor alpha production and protects liver against obesity-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2009;58:1133-1143.


73. Zhang C, McFarlane C, Lokireddy S, Bonala S, Ge X, Masuda S, et al. Myostatin-deficient mice exhibit reduced insulin resistance through activating the AMP-activated protein kinase signalling pathway. Diabetologia 2011;54:1491-1501. Erratum in: Diabetologia 2015;58:643.
74. Pistilli EE, Bogdanovich S, Goncalves MD, Ahima RS, Lachey J, Seehra J, et al. Targeting the activin type IIB receptor to improve muscle mass and function in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am J Pathol 2011;178:1287-1297.



75. Amthor H, Hoogaars WM. Interference with myostatin/ActRIIB signaling as a therapeutic strategy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Curr Gene Ther 2012;12:245-259.


76. Delogu W, Caligiuri A, Provenzano A, Rosso C, Bugianesi E, Coratti A, et al. Myostatin regulates the fibrogenic phenotype of hepatic stellate cells via c-jun N-terminal kinase activation. Dig Liver Dis 2019;51:1400-1408.


77. Zhang HJ, Zhang XF, Ma ZM, Pan LL, Chen Z, Han HW, et al. Irisin is inversely associated with intrahepatic triglyceride contents in obese adults. J Hepatol 2013;59:557-562.


78. Xu J, Lloyd DJ, Hale C, Stanislaus S, Chen M, Sivits G, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in dietinduced obese mice. Diabetes 2009;58:250-259.




79. Lee HJ, Lee JO, Kim N, Kim JK, Kim HI, Lee YW, et al. Irisin, a novel myokine, regulates glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells via AMPK. Mol Endocrinol 2015;29:873-881.



80. Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Serrano M, Guerra E, Pardo G, Tinahones F, et al. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013;98:E769-E778.



81. Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscle as an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiol Rev 2008;88:1379-1406.


82. Pedersen BK, Steensberg A, Fischer C, Keller C, Keller P, Plomgaard P, et al. Searching for the exercise factor: is IL-6 a candidate? J Muscle Res Cell Motil 2003;24:113-119.

83. Helge JW, Stallknecht B, Pedersen BK, Galbo H, Kiens B, Richter EA. The effect of graded exercise on IL-6 release and glucose uptake in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 2003;546(Pt 1):299-305.




84. Steensberg A, van Hall G, Osada T, Sacchetti M, Saltin B, Klarlund Pedersen B. Production of interleukin-6 in contracting human skeletal muscles can account for the exercise-induced increase in plasma interleukin-6. J Physiol 2000;529(Pt 1):237-242.




85. Ellingsgaard H, Hauselmann I, Schuler B, Habib AM, Baggio LL, Meier DT, et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat Med 2011;17:1481-1489.




86. Paula FM, Leite NC, Vanzela EC, Kurauti MA, Freitas-Dias R, Carneiro EM, et al. Exercise increases pancreatic β-cell viability in a model of type 1 diabetes through IL-6 signaling. FASEB J 2015;29:1805-1816.



87. Al-Khalili L, Bouzakri K, Glund S, Lönnqvist F, Koistinen HA, Krook A. Signaling specificity of interleukin-6 action on glucose and lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle. Mol Endocrinol 2006;20:3364-3375.



88. Carey AL, Steinberg GR, Macaulay SL, Thomas WG, Holmes AG, Ramm G, et al. Interleukin-6 increases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in humans and glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in vitro via AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes 2006;55:2688-2697.



89. Choi K, Jang HY, Ahn JM, Hwang SH, Chung JW, Choi YS, et al. The association of the serum levels of myostatin, follistatin, and interleukin-6 with sarcopenia, and their impacts on survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol 2020;26:492-505.




90. Wieckowska A, Papouchado BG, Li Z, Lopez R, Zein NN, Feldstein AE. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:1372-1379.


91. Biolo G, Cederholm T, Muscaritoli M. Muscle contractile and metabolic dysfunction is a common feature of sarcopenia of aging and chronic diseases: from sarcopenic obesity to cachexia. Clin Nutr 2014;33:737-748.


92. Lang T, Streeper T, Cawthon P, Baldwin K, Taaffe DR, Harris TB. Sarcopenia: etiology, clinical consequences, intervention, and assessment. Osteoporos Int 2010;21:543-559.



93. Steffl M, Bohannon RW, Sontakova L, Tufano JJ, Shiells K, Holmerova I. Relationship between sarcopenia and physical activity in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Interv Aging 2017;12:835-845.




94. Johnson NA, Sachinwalla T, Walton DW, Smith K, Armstrong A, Thompson MW, et al. Aerobic exercise training reduces hepatic and visceral lipids in obese individuals without weight loss. Hepatology 2009;50:1105-1112.


95. Kob R, Bollheimer LC, Bertsch T, Fellner C, Djukic M, Sieber CC, et al. Sarcopenic obesity: molecular clues to a better understanding of its pathogenesis? Biogerontology 2015;16:15-29.



96. Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 2002;8:1288-1295.



97. Tilg H, Hotamisligil GS. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: cytokine-adipokine interplay and regulation of insulin resistance. Gastroenterology 2006;131:934-945.


98. Ryall JG, Schertzer JD, Lynch GS. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and weakness. Biogerontology 2008;9:213-228.



99. Egerman MA, Glass DJ. Signaling pathways controlling skeletal muscle mass. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2014;49:59-68.



100. Berryman DE, Glad CA, List EO, Johannsson G. The GH/IGF-1 axis in obesity: pathophysiology and therapeutic considerations. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2013;9:346-356.



101. Cabrera D, Ruiz A, Cabello-Verrugio C, Brandan E, Estrada L, Pizarro M, et al. Diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with sarcopenia and decreased serum insulin-like growth factor-1. Dig Dis Sci 2016;61:3190-3198.



102. Pan X, Han Y, Zou T, Zhu G, Xu K, Zheng J, et al. Sarcopenia contributes to the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseaserelated fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis 2018;36:427-436.



103. Yu R, Shi Q, Liu L, Chen L. Relationship of sarcopenia with steatohepatitis and advanced liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol 2018;18:51.




104. Hsieh YC, Joo SK, Koo BK, Lin HC, Kim W. Muscle alterations are independently associated with significant fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 2021;41:494-504.



105. Golabi P, Gerber L, Paik JM, Deshpande R, de Avila L, Younossi ZM. Contribution of sarcopenia and physical inactivity to mortality in people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JHEP Rep 2020;2:100171.



106. Moon JH, Koo BK, Kim W. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia additively increase mortality: a Korean nationwide survey. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021;12:964-972.




107. Sinn DH, Kang D, Kang M, Guallar E, Hong YS, Lee KH, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and accelerated loss of skeletal muscle mass: a longitudinal cohort study. Hepatology 2022;76:1746-1754.



108. Nachit M, De Rudder M, Thissen JP, Schakman O, Bouzin C, Horsmans Y, et al. Myosteatosis rather than sarcopenia associates with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease preclinical models. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021;12:144-158.




109. Montano-Loza AJ, Meza-Junco J, Baracos VE, Prado CM, Ma M, Meeberg G, et al. Severe muscle depletion predicts postoperative length of stay but is not associated with survival after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2014;20:640-648.


110. Nachit M, Kwanten WJ, Thissen JP, Op De Beeck B, Van Gaal L, Vonghia L, et al. Muscle fat content is strongly associated with NASH: a longitudinal study in patients with morbid obesity. J Hepatol 2021;75:292-301.


111. Hsieh YC, Joo SK, Koo BK, Lin HC, Lee DH, Chang MS, et al. Myosteatosis, but not sarcopenia, predisposes NAFLD subjects to early steatohepatitis and fibrosis progression. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022 Jan 31;doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.01.020.


112. Nachit M, Lanthier N, Rodriguez J, Neyrinck AM, Cani PD, Bindels LB, et al. A dynamic association between myosteatosis and liver stiffness: results from a prospective interventional study in obese patients. JHEP Rep 2021;3:100323.



113. Gan D, Wang L, Jia M, Ru Y, Ma Y, Zheng W, et al. Low muscle mass and low muscle strength associate with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Nutr 2020;39:1124-1130.


114. Kitajima Y, Hyogo H, Sumida Y, Eguchi Y, Ono N, Kuwashiro T, et al. Severity of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with substitution of adipose tissue in skeletal muscle. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;28:1507-1514.



115. Nachit M, Leclercq IA. Emerging awareness on the importance of skeletal muscle in liver diseases: time to dig deeper into mechanisms! Clin Sci (Lond) 2019;133:465-481.



116. Tanaka M, Okada H, Hashimoto Y, Kumagai M, Nishimura H, Oda Y, et al. Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and muscle quality as well as quantity evaluated by computed tomography. Liver Int 2020;40:120-130.



117. Kang S, Moon MK, Kim W, Koo BK. Association between muscle strength and advanced fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a Korean nationwide survey. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020;11:1232-1241.




118. Ebadi M, Montano-Loza AJ. Clinical relevance of skeletal muscle abnormalities in patients with cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis 2019;51:1493-1499.


119. Bhanji RA, Narayanan P, Moynagh MR, Takahashi N, Angirekula M, Kennedy CC, et al. Differing impact of sarcopenia and frailty in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and alcoholic liver disease. Liver Transpl 2019;25:14-24.




120. Kim TH, Jung YK, Yim HJ, Baik JW, Yim SY, Lee YS, et al. Impacts of muscle mass dynamics on prognosis of outpatients with cirrhosis. Clin Mol Hepatol 2022;28:876-889.




121. Song DS, Chang UI, Yang JM. Sarcopenia: multiple factors need to be considered in cirrhosis. Clin Mol Hepatol 2022 Oct 31;doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0339.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





