| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 26(1); 2020 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
FOOTNOTES
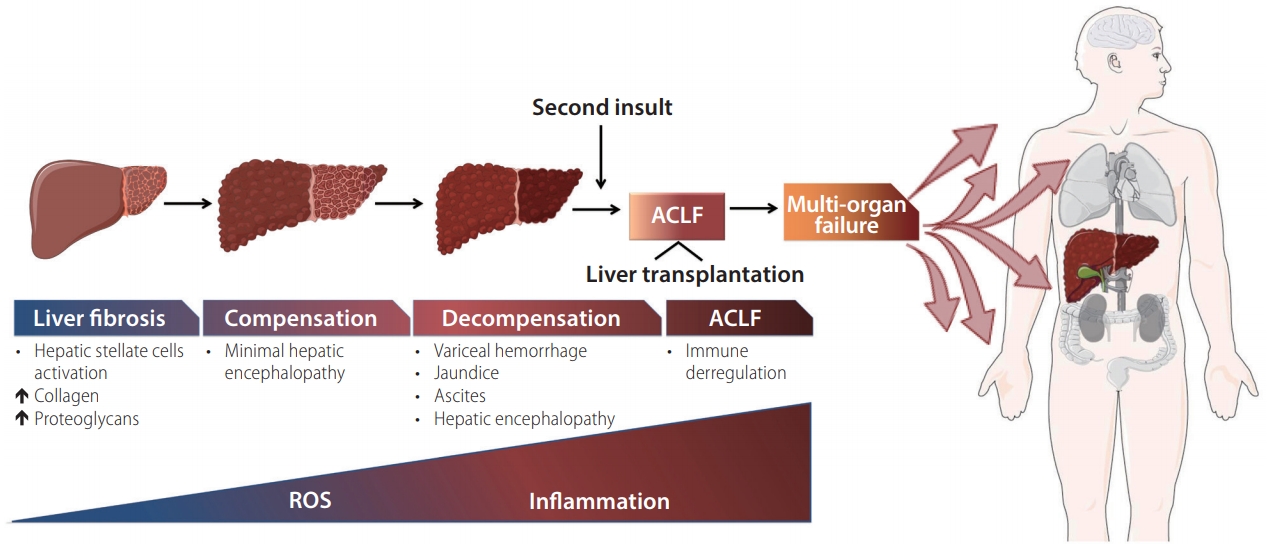
Figure┬Ā1.
Table┬Ā1.
This table was made by several articles as follows:
Definition: (APASL) Sarin et al. [16], (AASLD) Bajaj, et al. [17]; Duration betweem insult and ACLF: Bajaj[19]; Duration in which there is higher mortality: Bajaj[19]; Dignostic criteria: (APASL) Sarin et al. [16], (AASLD) Arroyo et al. [18]; What qualifies as precipitants: Bajaj[19]; Pedisposition: (APASL) Sarin et al. [16], (AASLD) Arroyo et al. [18]
APASL, the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver; AASLD, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; EASL, the European Association for the Study of the Liver; CLD, chronic liver disease; ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; TBil, total Bilirubin; INR, International Normalized Ratio; PTA, platelets.
Table┬Ā2.
| Gene | Relationship with ACLF | Gene information | Studies | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1846T, C1913A/G | Severity of liver disease and risk of ACLF | Mutation on HBV gene; encodes capsid protein; precapsid protein | 438 patients with liver diseases were retrospectively reviewed. A1846T was significantly associated with the mortality of ACLF patients within six months after the disease onset, while C1913A led to a significant decrease of core protein expression. | Zang et al. [44] |
| rs3129859 | Prognostic marker for the emergence, severity and survival of ACLF | A/C/G singlenucleotide variation on human chromosome 6 | 399 HBV-related ACLFs (cases) and 401 asymptomatic HBV carriers (AsCs, as controls). Clinical traits analysis in patients with ACLF showed that the risky rs3129859*C allele was associated with prolonged prothrombin time, faster progression to ascites development and higher 28-day mortality. | Tan et al. [41] |
| rs2910164 of miR-146a | Deficient immune response and high incidence of infection due to lower serum levels of TNF-╬▒ | C/G single-nucleotide variation on human chromosome 5 | Case-control study including 717 cases of HBV and 251 cases of ACLF-HBV and 466 cases of chronic hepatitis B. Results showed that the GG homozygote was a protective genotype in terms of susceptibility to ACLF-HBV, compared with CC+GC genotypes. | Jiang et al. [37] |
| TLR3 C1234T | Inactive response and low recognition response to viral pathogens | Toll-like receptor 3 polymorphism on human chromosome 4 | Case-control study including 452 chronic hepatitis B patients and 462 healthy controls. Data showed that subjects carrying 1234CT genotype and TT genotype had 1.42-fold and 2.31-fold increased risk of chronic HBV infection compared to those with CC genotype. | Rong et al. [46] |
| TLR3 L412F | Lower rejection rate of liver transplantation | Toll-like receptor 3 polymorphism on human chromosome 4 | Single-center study of 100 adult patients who received a first whole only liver graft from deceased donors. Homozygous mutant TT genotype for TLR3 L412F was associated with a lower rate of acute rejection compared with the homozygous wild-type genotype. | Citores et al. [48] |
Some of the gene polymorphisms that explain individual biological differences and how they affect humans to develop acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF).
HBV, hepatitis B virus; A/C/G, adenine/cytosine/guanine; AsCs, surface antigen carriers; C/G, cytosine/guanine; GG, guanine/guanine; CC, cytosine/cytosine; GC, guanine/cytosine; TNF-╬▒, tumor necrosis factor ╬▒; TT, thymine/thymine.
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Natalia Nu├▒o-L├Īmbarri

https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7616-2661 - Related articles



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



