| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 26(4); 2020 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
FOOTNOTES
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā1.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā2.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā1.
Supplementary┬ĀTable┬Ā2.
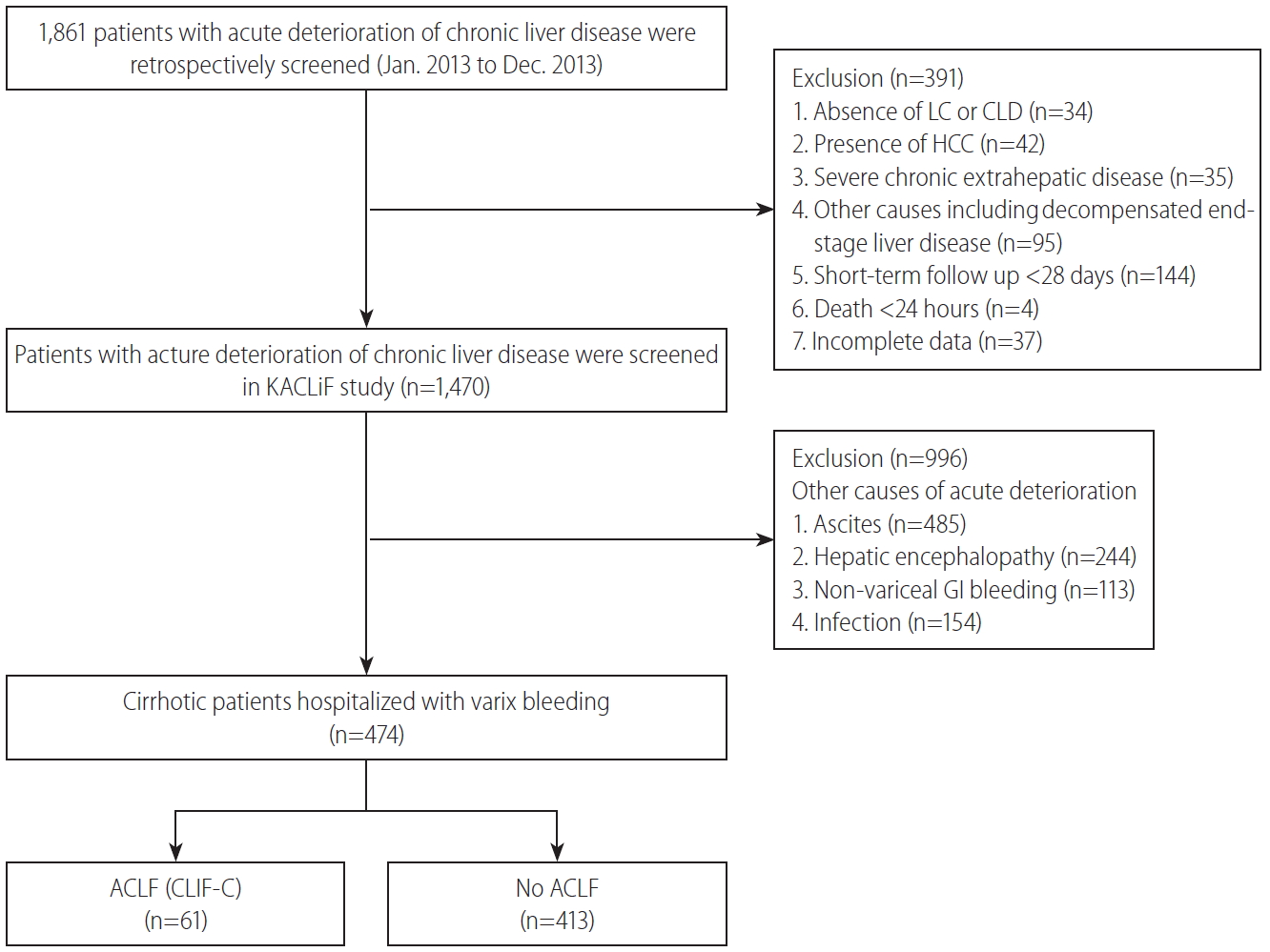
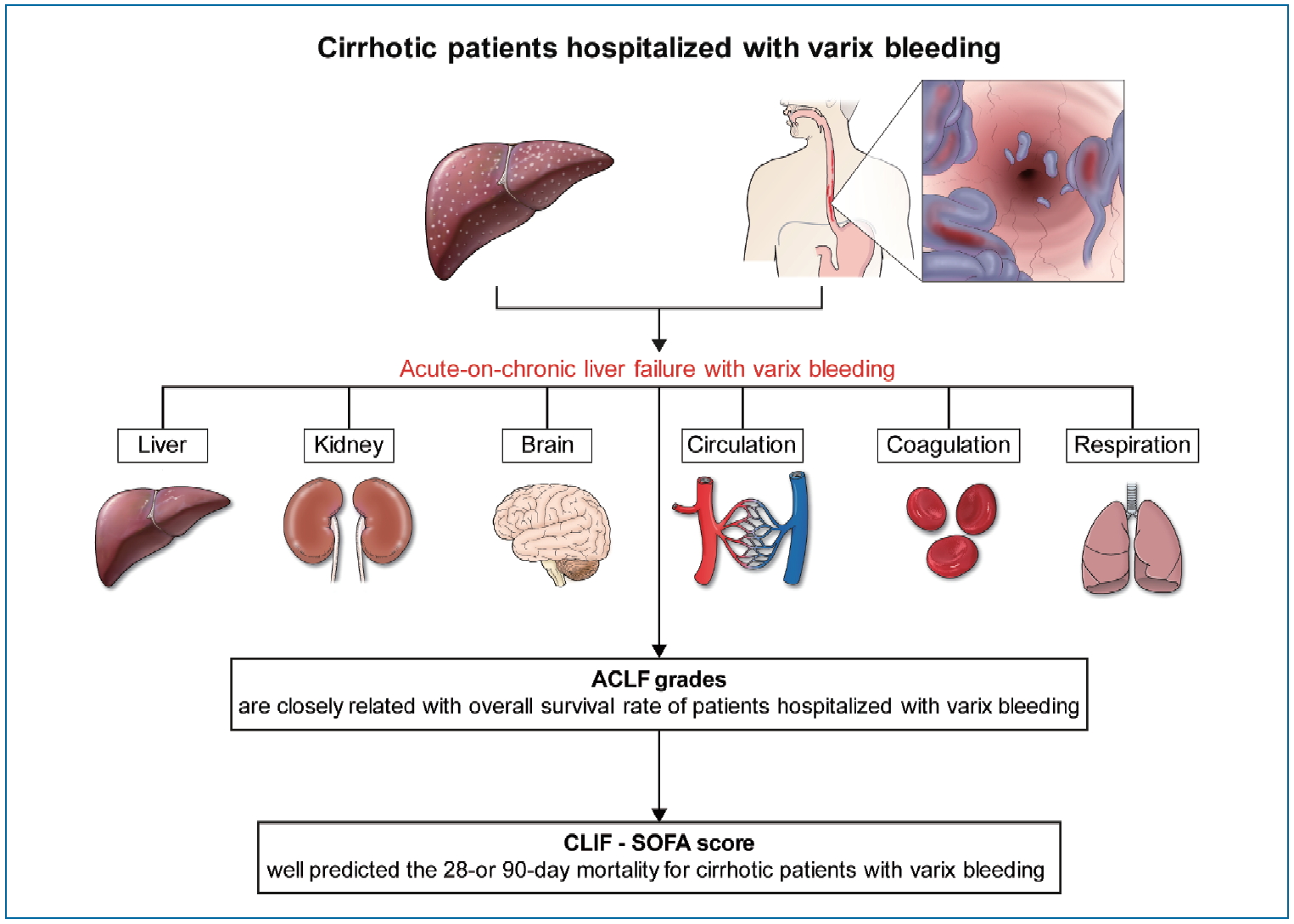
Figure┬Ā1.
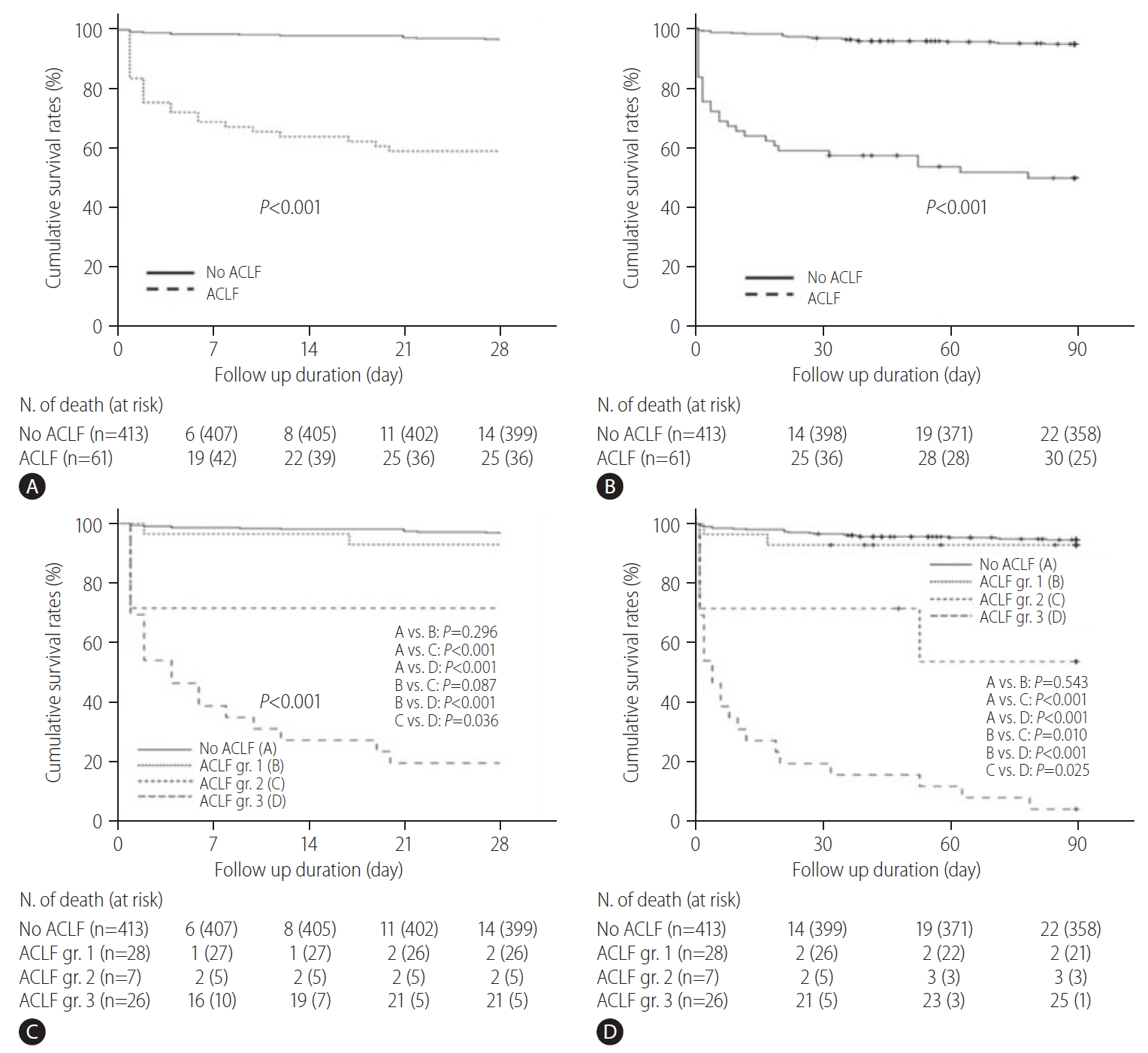
Figure┬Ā2.
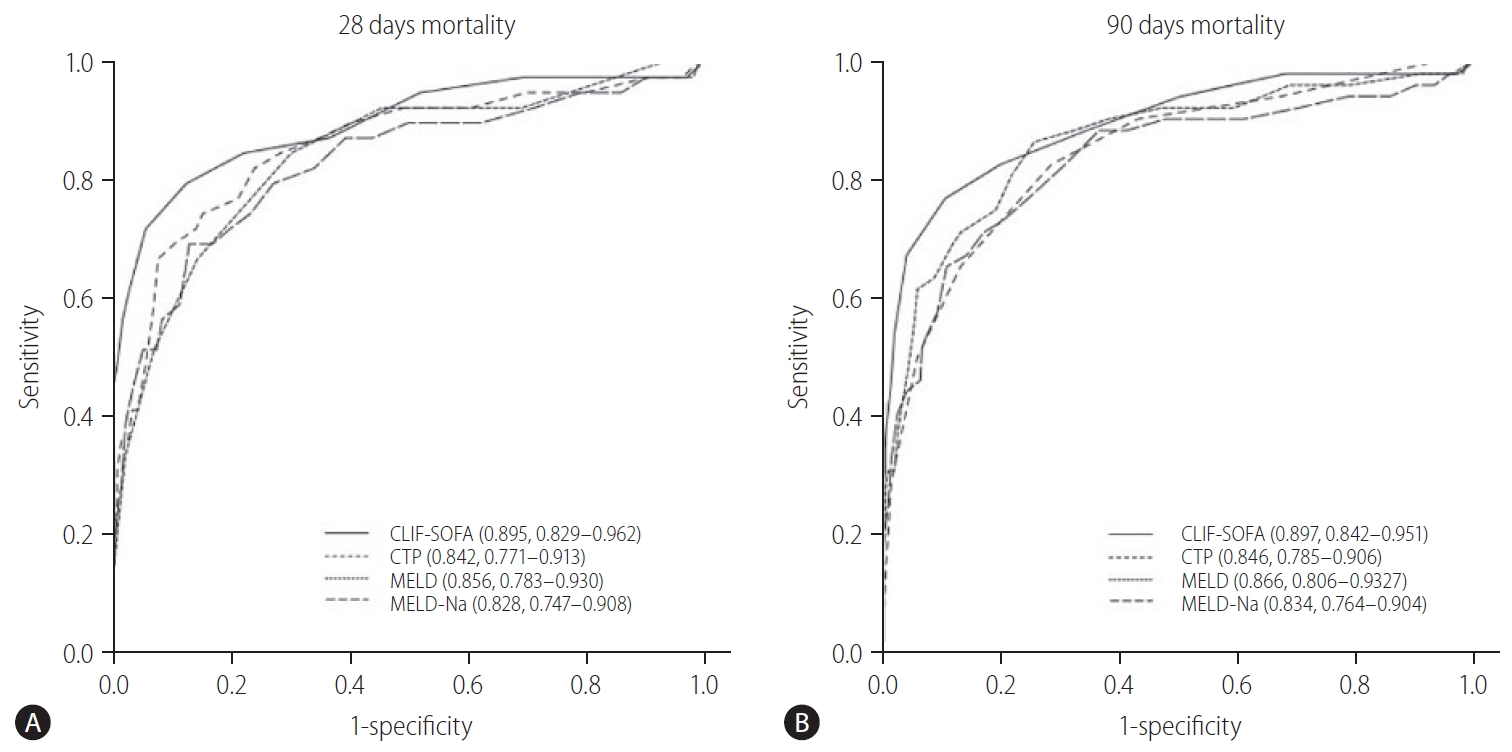
Figure┬Ā3.
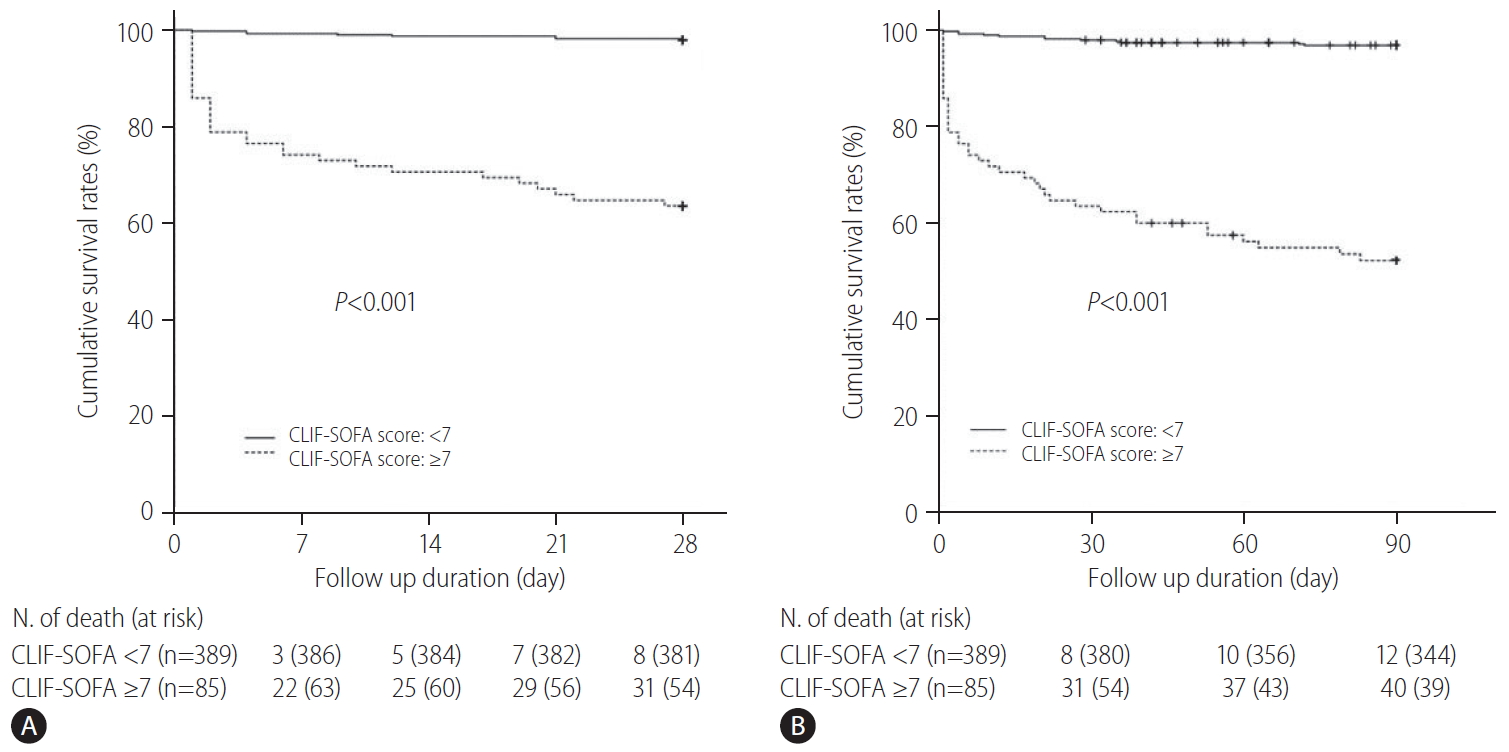
Figure┬Ā4.
Table┬Ā1.
| Variable | All (n=474) | Non-ACLF (n=413) | ACLF (n=61) | P-value* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 54.8 (17ŌĆō88) | 54.6 (17ŌĆō88) | 56.6 (34ŌĆō84) | 0.202 |
| Gender, male | 372 (78.5) | 323 (78.2) | 49 (80.3) | 0.707 |
| WBC (├Ś103/uL) | 8.8 (0.08ŌĆō3.01) | 8.3 (0.8ŌĆō30.1) | 12.1 (3.1ŌĆō26.9) | <0.001 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 8.6 (2.6ŌĆō19.1) | 8.7 (2.6ŌĆō16.8) | 8.0 (3.0ŌĆō19.1) | 0.048 |
| Platelets (├Ś103/uL) | 102 (12ŌĆō659) | 102 .3 (12ŌĆō659) | 102.4 (12ŌĆō247) | 0.999 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.9 (1.3ŌĆō4.8) | 3.0 (1.5ŌĆō4.8) | 2.5 (1.3ŌĆō4.0) | <0.001 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 2.9 (0.2ŌĆō40.3) | 2.3 (0.2ŌĆō35.0) | 7.2 (0.3ŌĆō40.3) | <0.001 |
| AST (IU/L) | 112.2 (4ŌĆō3,399) | 98.0 (4ŌĆō3,399) | 209.0 (17ŌĆō2,620) | 0.002 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 54.2 (4ŌĆō2,886) | 50.4 (4ŌĆō2,886) | 80.0 (8ŌĆō807) | 0.186 |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 1.5 (0.9ŌĆō5.6) | 1.4 (0.9ŌĆō3.1) | 2.1 (1.0ŌĆō5.6) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.46 (0.01ŌĆō28.5) | 0.43 (0.1ŌĆō28.5) | 0.64 (0.03ŌĆō26.8) | 0.036 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 136.9 (111ŌĆō162) | 137.3 (111ŌĆō153) | 134.7 (118ŌĆō162) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 (0.1ŌĆō11.2) | 0.9 (0.1ŌĆō1.9) | 2.8 (0.7ŌĆō11.2) | <0.001 |
| Ascites, presence | 28 (5.9) | 23 (5.6) | 5 (8.2) | 0.416 |
| HE, presence | 21 (4.4) | 13 (3.1) | 8 (13.1) | <0.001 |
| Infection, presence | 5 (1.1) | 3 (0.7) | 2 (3.3) | 0.069ŌĆĀ |
| MELD score | 14.7 (6ŌĆō26) | 13.0 (6ŌĆō26) | 26.3 (13ŌĆō47) | <0.001 |
| CTP score | 7.8 (5ŌĆō15) | 7.5 (5ŌĆō12) | 10.0 (6ŌĆō15) | <0.001 |
| CLIF-SOFA score | 4.5 (0ŌĆō21) | 3.7 (0ŌĆō10) | 9.8 (3ŌĆō21) | <0.001 |
| Etiology of CLD | 0.145ŌĆĀ | |||
| ŌĆāViral, HBV or HCV | 92 (19.4) | 85 (20.6) | 7 (11.5) | |
| ŌĆāAlcohol | 320 (67.6) | 271 (65.6) | 49 (80.3) | |
| ŌĆāViral+alcohol | 31 (6.5) | 28 (6.8) | 3 (4.9) | |
| ŌĆāOthers | 31 (6.5) | 29 (7.0) | 2 (3.3) |
Values are presented as median (range) or number (%).
ACLF, acute on chronic liver failure; WBC, white blood cell; Hb, hemoglobin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international ratio; CRP, C-reactive protein; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; MELD, model of end-stage liver disease; CTP, Child-Turcotte-Pugh; CLIF SOFA, the chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment; CLD, chronic liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus.
Table┬Ā2.
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; WBC, white blood cell; Hb, hemoglobin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international ratio; CRP, C-reactive protein; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; MELD, model of end-stage liver disease; CTP, Child-Turcotte-Pugh; CLIF SOFA, the chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment.
Table┬Ā3.
ACLF, acute on chronic liver failure; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; WBC, white blood cell; Hb, hemoglobin; AST, aspartate transaminase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; INR, international ratio; CRP, C-reactive protein; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; MELD, model of end-stage liver disease; CTP, Child-Turcotte-Pugh; CLIF SOFA, the chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment; CLD, chronic liver disease; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus.
Table┬Ā4.
Values are presented as number (95% confidence interval).
CTP, Child-Turcotte-Pugh; MELD, model of end-stage liver disease; Na, sodium; CLIF-SOFA, the chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value.
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Young-Joo Jin

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7449-2461 - Related articles
-
Acute-on-chronic liver failure: a new syndrome in cirrhosis2016 March;22(1)
Important predictor of mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease2013 June;19(2)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print



