| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 28(1); 2022 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
FOOTNOTES
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Supplementary Figure 4.
Supplementary Figure 5.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table 3.
Figure 2.

Figure 3.
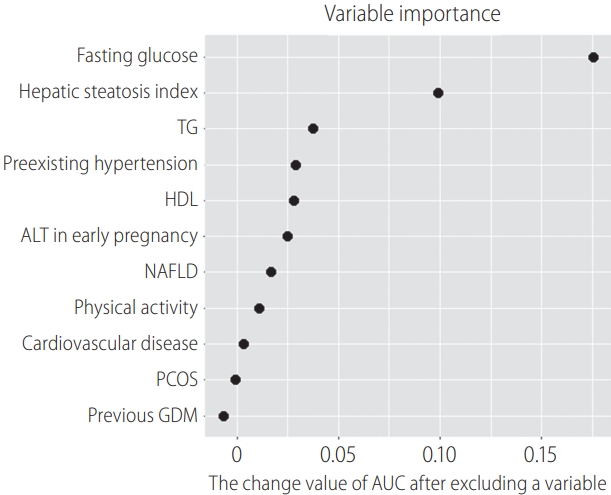
Table 1.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; γ-GT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; HSI, hepatic steatosis index; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Table 2.
| Characteristic | No GDM (n=1,357) | GDM (n=86) | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk factors in old criteria, 1998 [2] | |||||
| Classified as high-risk women by old criteria | 387 (28.5) | 51 (59.3) | <0.001 | ||
| Severe obesity, BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 51 (3.8) | 13 (15.1) | <0.001 | ||
| Family history of type 2 diabetes | 290 (21.4) | 31 (36.0) | 0.002 | ||
| Previous GDM | 24 (1.8) | 7 (8.1) | <0.001 | ||
| Impaired fasting glucose | 20 (1.5) | 18 (20.9) | <0.001 | ||
| Glucosuria | 35 (2.6) | 8 (9.3) | 0.001 | ||
| Risk factors in new ACOG criteria, 2018 [4] | |||||
| Classified as high-risk women by new criteria | 194 (14.3) | 36 (41.9) | <0.001 | ||
| Overweight or obese, BMI ≥23 kg/m2 | 418 (30.8) | 47 (54.7) | <0.001 | ||
| Physical inactivity | 161 (11.9) | 10 (11.6) | 1.000 | ||
| Family history of type 2 diabetes | 290 (21.4) | 31 (36.0) | 0.002 | ||
| High-risk race or ethnicity | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | ||
| Previous macrosomia | 15 (1.1) | 1 (1.2) | 1.000 | ||
| Previous GDM | 24 (1.8) | 7 (8.1) | <0.001 | ||
| Preexisting hypertension | 11 (0.8) | 3 (3.5) | 0.059 | ||
| Low HDL, <35 mg/dL | 13/1,350 (1.0) | 1/84 (1.2) | 1.000 | ||
| High TG, >250 mg/dL | 14/1,350 (1.0) | 6/84 (7.1) | <0.001 | ||
| PCOS | 23 (1.7) | 2 (2.3) | 0.993 | ||
| Impaired fasting glucose | 20 (1.5) | 18 (20.9) | <0.001 | ||
| History of cardiovascular disease | 8 (0.6) | 1 (1.2) | 1.000 | ||
| Severe obesity, BMI ≥30 kg/m2 | 51 (3.8) | 13 (15.1) | <0.001 | ||
Values are presented as number (%).
The risk factors in the old criteria were from the 4th International Workshop Conference on GDM in 1998; [2] the risk factors in the new criteria were based on the recommendation of the American Diabetes Association, which defined high-risk women as overweight or obese women with one of the risk factors. [3]
GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; BMI, body mass index; ACOG, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; TG, triglycerides; PCOS, polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Table 3.
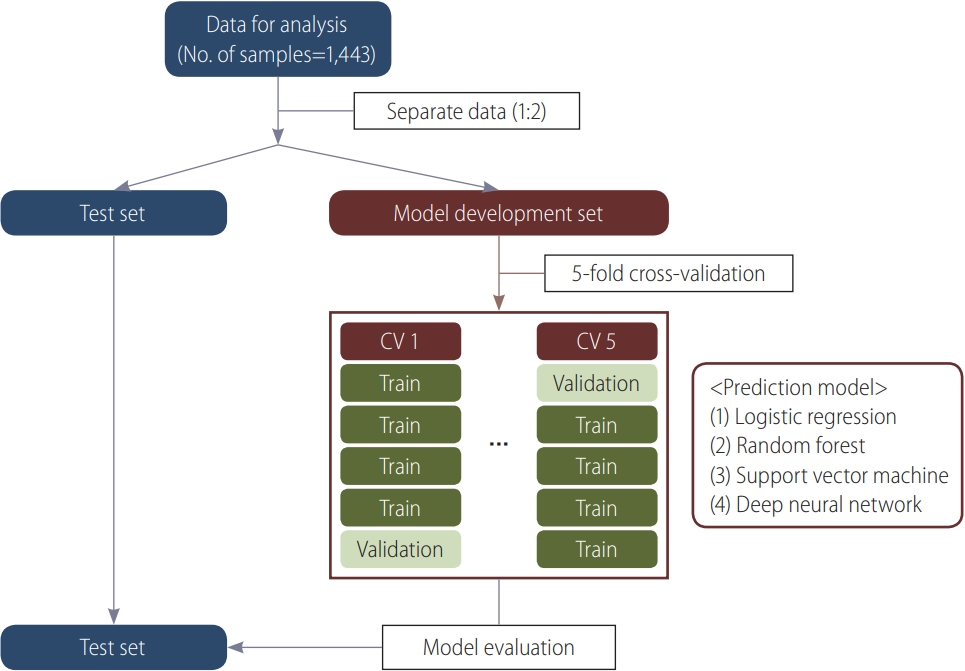
| Setting | Variables used | Prediction model |
Model development set |
Test set |
P-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Sen | Spe | P-value | AUC | Sen | Spe | P-value | ||||
| Setting 1 | (1) Conventional ACOG risk factors | LR | 0.728 | 0.649 | 0.723 | <0.001 | 0.609∥ | 0.483 | 0.698 | 0.041 | 0.194* |
| RF | 0.667 | 0.368 | 0.961 | <0.001 | 0.565 | 0.172 | 0.962 | 0.082 | 0.003† | ||
| SVM | 0.713 | 0.649 | 0.723 | <0.001 | 0.600 | 0.483 | 0.698 | 0.053 | 0.003‡ | ||
| DNN | 0.683 | 0.525 | 0.817 | <0.001 | 0.585 | 0.359 | 0.796 | 0.042 | 0.023§ | ||
| Setting 2 | (1) + (2) New ACOG risk factors form 2017 | LR | 0.777 | 0.719 | 0.734 | <0.001 | 0.563 | 0.481 | 0.728 | 0.364 | 0.105* |
| RF | 0.702 | 0.456 | 0.945 | <0.001 | 0.578 | 0.222 | 0.951 | 0.069 | 0.009† | ||
| SVM | 0.729 | 0.737 | 0.667 | <0.001 | 0.697∥ | 0.704 | 0.666 | <0.001 | 0.084‡ | ||
| DNN | 0.686 | 0.631 | 0.672 | <0.001 | 0.609 | 0.548 | 0.616 | 0.135 | 0.054§ | ||
| Setting 3 | (1) + (2) + (3) Routine clinical variables | LR | 0.842 | 0.809 | 0.761 | <0.001 | 0.617 | 0.520 | 0.758 | 0.104 | 0.297* |
| RF | 0.983 | 0.915 | 0.955 | <0.001 | 0.643∥ | 0.440 | 0.859 | 0.033 | 0.167† | ||
| SVM | 0.810 | 0.638 | 0.870 | <0.001 | 0.605 | 0.520 | 0.725 | 0.095 | 0.008‡ | ||
| DNN | 0.615 | 0.545 | 0.599 | 0.035 | 0.597 | 0.480 | 0.628 | 0.250 | 0.014§ | ||
| Setting 4 | (1) + (2) + (3) + (4) Variables associated with NAFLD | LR | 0.881 | 0.800 | 0.868 | <0.001 | 0.740 | 0.500 | 0.929 | <0.001 | 0.652* |
| RF | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.781∥ | 0.750 | 0.670 | <0.001 | 0.647† | ||
| SVM | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.756 | 0.708 | 0.747 | <0.001 | 0.246‡ | ||
| DNN | 0.800 | 0.572 | 0.807 | <0.001 | 0.745 | 0.517 | 0.836 | <0.001 | 0.457§ | ||
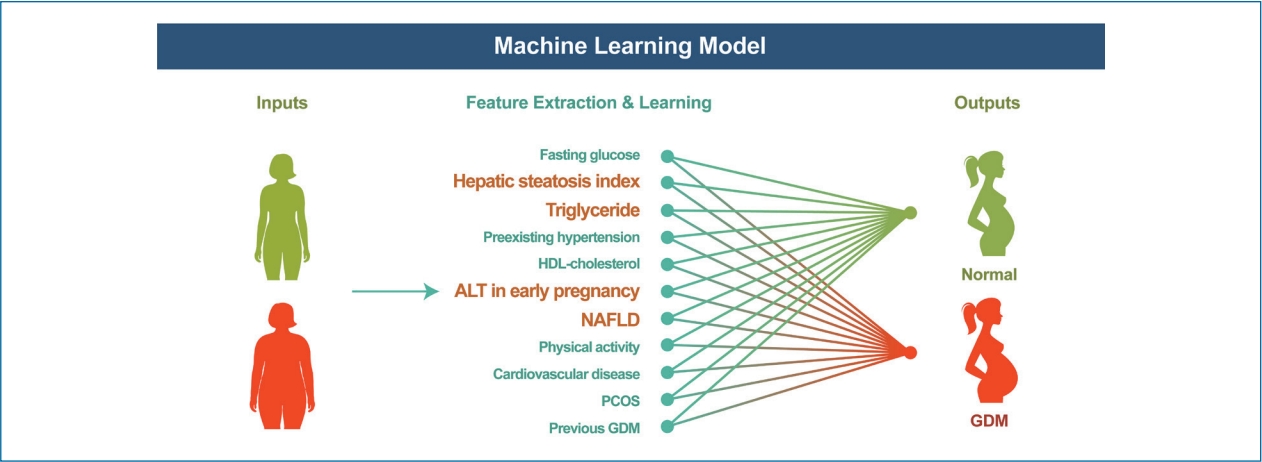
| Setting 5 | Top 11 important variables selected | LR | 0.840 | 0.778 | 0.779 | <0.001 | 0.719 | 0.542 | 0.872 | 0.001 | 1 |
| RF | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.996 | <0.001 | 0.763 | 0.708 | 0.755 | <0.001 | 1 | ||
| SVM | 0.800 | 0.733 | 0.775 | <0.001 | 0.819∥ | 0.708 | 0.866 | <0.001 | 1 | ||
| DNN | 0.806 | 0.759 | 0.678 | <0.001 | 0.777 | 0.750 | 0.654 | <0.001 | 1 | ||
Sen (i.e., sensitivity) and Spe (i.e., specificity) are represented as the values at the threshold with the maximum balanced accuracy.
AUC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; Sen, sensitivity; Spe, specificity; ACOG, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; LR, logistic regression; RF, random forest; SVM, support vector machine; DNN, deep neural network; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Abbreviations
REFERENCES
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Taesung Park

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8294-590XJoong Shin Park

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5246-0477 - Related articles
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and non-liver comorbidities2023 February;29(Suppl)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print



