| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 28(2); 2022 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Chronic hepatitis B is a major cause of liver disease worldwide and is currently incurable. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA is a key form of the virus responsible for its persistence and is the transcriptional template for all viral transcripts. The field is focussed on methods to clear HBV cccDNA but this been limited by technical difficulties in its quantification due to: identical sequence to other forms of HBV DNA; low copy number per cell; and high resistance to denaturation by heat, leading to difficulty using polymerase chain reaction or hybridization methods for detection. A number of assays have been developed in order to overcome these hurdles either directly or detecting cccDNA levels indirectly via its transcriptional products. In this review, we summarize the approaches to cccDNA quantification that are currently used, and outline key open questions in the cccDNA biology field which remain to be answered due to the limitations of current methods.
Over 296 million people worldwide currently live with chronic hepatitis B, which causes liver damage, liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [1]. Approximately 900,000 people each year die from hepatitis B-related disease. The World Health Organization estimate that only 10.5% of people with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are aware of their status and only 16.7% of those diagnosed are on treatment [1].
Current therapies in the form of nucleos(t)ide analogues (NA; such as entecavir, tenofovir disoproxil or tenofovir alafenamide) suppress viral replication and can prevent disease progression and subsequent HCC development [2,3]. However, such treatments need to be taken indefinitely as they do not affect the HBV covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA, the template for all viral transcripts that stably persists in the host cell nucleus [4]. Moreover, the incurability and high risk of liver disease mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B cause multiple psychosocial impacts, e.g., fear, stigma and discrimination [5]. The complete elimination of cccDNA from the liver would represent a cure for chronic hepatitis B, preventing ongoing disease impacts. As such, the induction of cccDNA clearance is a major goal of therapeutic drug development [6,7].
There are many barriers to achieving clearance of cccDNA, one of which is the technical difficulty associated with sensitively, accurately, and precisely quantifying cccDNA levels. This review aims to discuss the importance and challenges of cccDNA quantification, and explore the current molecular methods used for measuring levels in a research environment.
Hepatitis B is caused by infection with the HBV, a blood-borne, hepatotropic virus belonging to the genus Orthohepadnavirus of the Hepadnaviridae family. The virion is composed of a small (3.2 kbp) partially double stranded (ds) DNA genome encapsidated in a viral nucleocapsid that enveloped by a host-derived membrane studded with viral envelope proteins (HBV surface antigen [HBsAg]).
The HBV replication cycle begins with a reversible non-specific interaction between the viral HBsAg on the viral surface to cellular heparan sulphate proteoglycans, particularly glypican 5 [8-10]. The HBsAg on the virus surface then engages in strong irreversible interactions with the cellular sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP), expressed only on the basolateral membrane of hepatocytes and conveying liver-specific tropism of the virus. Multiple other co-receptors and host factors also contribute to efficient viral entry. NTCP is localised to the cell membrane through interaction with E-cadherin [11], and complexes with epidermal growth factor receptor in order to mediate viral entry through clathrin-dependent endocytosis [12-14]. Low-density lipoprotein receptor has also recently been implicated in HBV entry, likely by assisting viral attachment via binding to HBV-associated apolipoprotien E [15]. It is probable that additional unknown host factors assist in viral entry. The virus nucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm and transported to the nucleus along microtubules, where the viral relaxed circular (rc) DNA is released [16].
In the nucleoplasm, rcDNA is repaired by numerous host factors (including TDP2, Pol-K, PCNA, the RFC complex, POL╬┤, FEN-1 and LIG1 [17-20]) and is converted to cccDNA. cccDNA is complexed with histones [4] and acts as a transcriptional template for the five viral transcripts sufficient for efficient production of virions: 1) the HBx mRNA, translated the viral transcriptional trans-activator (HBV X protein); 2) the PreS and S mRNAs, encoding for HBsAg (large, medium, and small versions); 3) the pregenomic (pg) RNA, which can be translated into the capsid subunit HBV core protein (HBc); 4) the viral polymerase (pol); and 5) the precore RNA, which codes for the secreted protein preCore/core(HBe).
Expression of these transcripts can be affected by acetylation status of histones bound to the cccDNA molecules [21], its chromatin organisation [22], and viral variants that develop over the course of a chronic infection (e.g., mutations in the basal core promoter and precore regions [23-25]).
Transcribed pgRNA and translated pol binds to pgRNA, which triggers encapsidatation by multiple subunits of HBc forming an immature nucleocapsid containing viral RNA [26,27]. HBV pol initiates and carries out reverse transcription of the pgRNA [27-29] through a complicated series of molecular events [30]. Briefly, pol binds to the 5ŌĆÖ-epsilon region of the pgRNA and uses this as a template to synthesise a three nucleotide oligonucleotide [31]. This complex translocates to a direct repeat 1 region on the 3ŌĆÖ end of the pgRNA and initiates reverse transcription producing a negative-sense single stranded (ss) DNA strand. During reverse transcription, pol hydrolyses the pgRNA with its ribonuclease H activity 18nt behind the site of reverse transcription [32]. Upon reaching the end of the pgRNA, the pol produces a looped negative sense DNA strand and an 18nt RNA fragment remaining from the pgRNA [33], the latter of which acts as the primer for the synthesis of the positive-sense ssDNA [34]. In 90% of nucleocapsids, the primer translocates to the 5ŌĆÖ end of the ssDNA leading to the synthesis of rcDNA. However in 10% of cases, it remains bound to the 3ŌĆÖ end of the ssDNA, leading to the formation of double stranded linear (dsl) DNA [35]. The mature nucleocapsids (containing HBV DNA) are subsequently enveloped and secreted out of the cell as virions through yet-uncharacterised signals [36].
HBV-infected cells also secrete HBV e antigen (HBeAg) and HBsAg. HBeAg is produced from cccDNA and can be neutralised by host antibodies during robust antiviral response in later phases of infection. On the other hand, HBsAg can be expressed from either cccDNA or integrated HBV DNA (formed when HBV dslDNA is inserted into the host DNA, previously reviewed by Tu et al. [37]). In addition to forming the envelope of virions, HBsAg is also secreted as two forms of non-infectious sub-viral particles: 25 nm diameter spheres, and 22 nm diameter filaments of variable length. Sub-viral particles are produced in excess to virions (by a factor of 1,000- to 100,000-fold) and therefore comprise the major form of HBsAg in the serum [38].
Given it is sufficient and necessary for viral replication (and therefore maintaining viral persistence), HBV cccDNA is key to overcoming chronic HBV infections [18]. Elimination of cccDNA is considered a complete cure for HBV infection, and allows for the cessation of therapy without the risk of viral rebound. Understanding of HBV cccDNA biology and the development novel therapeutics inducing its clearance have been hindered by the lack of a simple, specific, sensitive, precise, and high-throughput assay for cccDNA quantification [39]. These technical challenges should each be addressed to improve cccDNA quantification and facilitate ongoing HBV cure research.
cccDNA has an identical DNA sequence to all other intracellular and extracellular forms of HBV DNA, including rcDNA, dslDNA, and ssDNA [40]. These different structural forms of HBV DNA present a high risk for false positives. These other forms are present in excess infected cells at ~100ŌĆō1,000 copies per cell compared to cccDNA at 1ŌĆō10 copies per infected cell [41].
In some instances, only small numbers of infected cells are present (e.g., HBeAg-negative patients) or can be isolated from patients (e.g., fine needle aspirates). Given cccDNA can be present at very low levels (<1 cccDNA molecule per 1,000 cells) [42], high sensitivity is necessary for assays to be broadly applicable [42].
Intrinsic to its covalently closed structure, cccDNA resists heat denaturation and thus can be difficult to quantify precisely and accurately by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or hybridisation methods due to different detection efficiencies [4].
Indirect quantification of cccDNA can be carried out by measuring the levels of secreted virus gene products (Table 1, Fig. 1). These approaches serve an important role in monitoring levels of HBV patients, as these assays are non-invasive and do not require a traditional core liver biopsy (unlike direct quantification of cccDNA). These viral markers have been linked to disease progression and the development of HCC, suggesting a role for cccDNA levels and clinical outcomes [43]. They have also been used as a highthroughput method to determine cccDNA levels in reporter cell lines and other in vitro systems. In general, however, these indirect cccDNA measures can lack specificity and accuracy for total cccDNA, as they are strongly affected by transcriptional activity of the cccDNA, antiviral therapy, host immune response, and viral factors.
Secreted HBV DNA (in the form of HBV virions) generally correlates with cccDNA, as virions can only be produced by cells containing cccDNA. However, any factor that inhibits replication steps downstream from cccDNA formation will affect HBV DNA levels. This is seen most obviously with NA therapy, which inhibits reverse transcription and dramatically reduces circulating HBV DNA levels, despite not affecting cccDNA levels significantly [44]. The same is true for experimental agents that affect cccDNA transcription, translation, or secretion. Thus, total HBV DNA is not specific enough for many experimental applications. Secreted HBV DNA is currently detected using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) [45].
Serum HBsAg is an important marker for diagnosis of HBV infection. HBsAg is currently detected using automated chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) or electrochemiluminescence immunoassay [46], however can also be detected using a standard enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) [47].
HBsAg has been shown to correlate with intrahepatic cccDNA levels in some studies [48-50]. Moreover, serum HBsAg decline during NA therapy has been associated with reduced levels of intrahepatic cccDNA [42]. Other studies, however, have also reported either weak or no correlation with cccDNA levels [51-54].
These disparate findings are potentially be explained by HBsAg originating from the non-replicative integrated form of HBV DNA, making its association with cccDNA unreliable [54]. While the relative level of integration-derived HBsAg is negligible in HBeAg-positive patients (leading to good correlation to cccDNA), a combination of lower cccDNA levels and increased frequency of HBV DNA integrations in later phases [55,56] mean that the majority of HBsAg can be encoded by integrated HBV DNA in HBeAg-negative patients [25,57].
Moreover, it has been reported that HBsAg levels remain relatively static in response to combined peg-interferon (IFN) and lamivudine therapy while cccDNA levels decreased, indicating that there may be a compensatory mechanism related to an increased production of subviral products [58]. Thus, HBsAg cannot be considered an accurate marker for cccDNA levels in HBeAg-negative patients or patients on peg-IFN therapy.
HBeAg is used as a clinical marker for HBV infection. Seroconversion to an anti-HBe state indicates active host immune clearance. During the natural history of the infection, HBeAg levels drop due to both a neutralising antibody response against the antigen and reduction in intrahepatic cccDNA levels as infected cells are cleared by a cell-mediated antiviral immune response. Moreover, under this immune selection, HBV cccDNA variants that cease to express HBeAg can emerge and become fixed in the hepatocyte population. Due to the multiple factors associated with free circulating HBeAg levels, they are poor indicators of cccDNA levels.
In the absence of the complications of an immune system, HBeAg has been used as a reporter for cccDNA in in vitro systems. HepAD38 cells contain an over-length replication-competent HBV DNA transgene, whereby the expression of HBV precore mRNA (and by extension secretion of its translational product HBeAg) is dependent both on cccDNA levels and the activation of the transgene by a tetracycline-controlled promoter [59,60]. To improve the specificity of this system, the HepDE19 cell line was developed so that the HBeAg ORF and its 5ŌĆÖ RNA leader are separated on the transgene, and only become complete following formation of cccDNA [61]. Detection of HBeAg by ELISA therefore would indicate cccDNA levels, useful for high throughput screening of cccDNA targeting drugs [61]. However, a complicating feature came from the high homology between HBeAg and hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg), the latter of which is secreted in a cccDNA-independent manner by the integrated transgene. To address this, an additional modification to these cells was made: HepBHAe82 were developed to introduce a human influenza hemagglutinin (HA) tag into the precore region, thereby encoding a secreted HA-tagged HBeAg specifically detectable by CLEIA and eliminating interference from HBcAg [62]. HepBHAe82 now can provide the basis of a relatively high-throughput platform to screen for compounds that affect levels of transcriptionally-active cccDNA.
HBcrAg is a relatively new biomarker detecting the 149 base pair sequence shared between HBcAg, HBeAg and core related protein, p22 [63]. Levels of HBcrAg can be detected using a CLEIA, which is relatively inexpensive and simple compared to PCR for serum HBV DNA.
HBcrAg has the advantage of remaining detectable in many patients with undetectable levels of serum HBV DNA due to NA therapy (106/124 [85%] detectable HBcrAg compared to 36/124 [29%] detectable HBV DNA) [54]. HBcrAg levels have been shown to correlate reasonably well with cccDNA levels [64,65]. However, the standard assay used (Lumipulse G® HBcrAg assay by Fujirebio Europe, Gent, Belgium) has a narrow quantifiable range of 3.0 log10 to 6.8 log10 U/mL, and is therefore somewhat insensitive. In a population of 1,409 untreated HBV patients in the USA, HBcrAg level of many study participants fell below the lower limit of quantification (516/1,409; 36.6%) or had a level higher than the upper limit (318/1,409; 22.6%), which prevented quantification [65]. Samples can be diluted with reagent and retested however, this slows the process down and mitigates the benefit of having a high-throughput system [66].
Considering the main component of HBcrAg is HBeAg, patients in HBeAg-negative phase have lower levels of HBcrAg compared to HBeAg-positive patients [67]. HBcrAg levels are undetectable in many HBeAg-negative patients using current assays (33/94 [35%] undetectable with CLEIA [66]). Correlation with cccDNA levels is dependent on HBeAg levels, with HBcrAg having a good correlation in HBeAg positive patients (r=0.80, P<0.0001), but middling to none in HBeAg-negative patients (r=0.47, P=0.05 in chronic infection patients; r=0.25, P=not significant in chronic hepatitis patients) [66].
Serum HBV RNA (in the form of secreted virus particles containing immature nucleocapsids) has been investigated as a potential biomarker for intrahepatic cccDNA transcriptional activity as detected by qPCR [68]. As NA therapy has no effect on cccDNA transcriptional activity, HBV pgRNA-containing virus particles continue to be secreted by hepatocytes with active cccDNA [68] and makes it a superior biomarker compared to serum HBV DNA in patients undergoing treatment, even when HBsAg loss occurs [69].
Serum HBV RNA correlates with intrahepatic HBV-RNA (r=0.73, P<0.001), as well as to the ratio of intrahepatic HBV-RNA to cccDNA (r=0.58, P=0.001). However, HBV RNA is poorly associated with the intrahepatic cccDNA pool (missing 5.62ŌĆō40.23% of total cccDNA), indicating that some cccDNA forms, e.g., transcriptionally-inactive forms, are undetectable by this method [70,71]. This suggests that serum HBV RNA cannot be used to detect the copy numbers of intrahepatic cccDNA, but can be used to measure cccDNA transcriptional activity.
Despite the usefulness of these surrogate markers, indirect measurements of cccDNA are not perfect replacements for direct measurement. These markers measure transcriptional activity of cccDNA and the rate of conversion from transcriptionally inactive to active forms of cccDNA is still unknown. Therefore, indirect methods cannot give an indication of the actual cccDNA pool size within the liver or determine the potential for viral reactivation.
Another issue which some markers face is their suppression by various therapies that target viral replication downstream of cccDNA formation. Total serum HBV DNA is suppressed by current NA therapies, due to their inhibition of reverse transcription just directly upstream of HBV DNA. In a similar fashion, siRNA-mediated transcriptional suppression silences viral antigens expression, and therefore prevent their detection (despite cccDNA not being affected) [72]. Likewise, core protein allosteric modulators reduce detected HBeAg signals by interfering with assembly or secretion of HBV capsids, but do not affect cccDNA levels [73].
Many techniques have been developed to detect and quantify cccDNA itself (including transcriptionally-inactive forms), making them more sensitive and accurate compared to indirect methods (Table 2, Figs. 2, 3). These types of assays however are more invasive in patients or animal models (requiring sampling of the liver) and more destructive in cell culture models (killing the cell to extract DNA or otherwise detect cccDNA). Moreover, direct quantification assays generally take more time to process compared to indirect methods, affecting throughput.
Several techniques have been used to enrich for HBV cccDNA (away from other forms of HBV DNA) and improve specificity prior to its detection with the assays described below. Total DNA is generally extracted by lysing the cell and digesting proteins in the solution, followed by separation of DNA from RNA and protein (e.g., by phenol chloroform extraction or binding to silica membranes) [6]. By omitting digestion with proteinase K, protein-bound DNA (including HBV rcDNA) is selectively removed during the extraction process [72].
The Hirt DNA extraction procedure is another method of DNA extraction that selectively isolates low-molecular weight, protein-free (PF) DNA [74,75], including cccDNA and deproteinated rcDNA (an intermediate HBV DNA form produced during the conversion of rcDNA to cccDNA in the nucleus). This method involves lysing cells in a detergent lysis/salt precipitation buffer without proteinase K and extracting the DNA from the supernatant with phenol: chloroform, followed by ethanol precipitation of the DNA. The original Hirt procedure has also been modified to use a silica membrane column for purification of the supernatant [76]. This method, while effective, is laborious and time-consuming even with spin column-based modifications.
Moreover, there is an unknown reduction in cellular DNA extracted for all of these enrichment methods, complicating normalisation and compromising assay precision. Finally, these techniques generally require large amounts of DNA input (microgram range), reducing sensitivity and limiting the source tissues able to be measured.
Southern blot hybridisation is considered the ŌĆ£gold standardŌĆØ in cccDNA detection as it unambiguously separates out the different forms of HBV DNA out based on electrophoretic motility through an agarose gel [77]. Given the relative low abundance of cccDNA in human infection systems, samples analysed by Southern blot hybridisation are usually first enriched using the Hirt DNA extraction procedure [74,75]. After gel electrophoresis and transfer onto a hybridisation membrane, ssDNA oligonucleotides are used to probe for and visualise HBV DNA.
Southern blot assays are complex, lengthy (~3 days), and insensitive (lower limit of detection ~105 ŌĆō106 copies of cccDNA) compared to PCR-based assays. Moreover, only a dozen samples can be run on the same gel simultaneously. These drawbacks prevent this method from being used in a high throughput settings, though it is seen as a reliable method for the confirmation of other assays [6].
FISH-based assays have been used to detect nuclear HBV DNA in cell lines [78]. Using this method, the frequency distribution of nuclear HBV DNA (presumably cccDNA, but may include deproteinated-rcDNA) was shown to average between 8 and 11 molecules per cell in HepAD38 cells. This method of detecting cccDNA can visualise copy numbers of nuclear HBV DNA at a single cell scale, however is time-consuming, labour-intensive, and low-throughput as image analysis requires specialist software. These drawbacks limit its use for methods such as drug screening, but can be a powerful technique for understanding spatial and frequency distribution of HBV cccDNA.
Many variations of qPCR have been used to quantify cccDNA, which is simpler, faster and higher throughput compared to hybridisation-based methods [79]. Conventional qPCR was first used by K├Čck and Schlicht [80] in 1993 using cccDNA-specific primers which span the gap region of rcDNA, preventing rcDNA amplification due to elongation termination at the 5ŌĆÖ end. However, homology between rcDNA and cccDNA-derived products during PCR amplification results in a substantial decrease in specificity, particularly in the presence of excess rcDNA. To resolve this issue, qPCR has been combined with several approaches to enrich for cccDNA over non-cccDNA templates (see ŌĆ£DNA SAMPLE ENRICHMENTŌĆØ above).
Enzymatic digestion of DNA (either total or Hirt extracted) with exonucleases can be used to remove excess replicative intermediates based on their exposed DNA termini that are absent in cccDNA forms. This approach can be effective, but they risk either: 1) over-digestion and destruction of cccDNA nicked during the extraction procedure; or 2) under-digestion, leading to lower specificity from retention of replicative intermediates. Identifying how long to digest input DNA can be difficult in some instances (e.g., in the presence of high levels of HBV replicative intermediates or when low amounts of total DNA are available). In addition, digestion with these enzymes hydrolyse cellular DNA, and thus complicates precise quantification due to the lack of reliable housekeeping genes for normalisation [73].
Plasmid safe DNase is an enzyme originally used for removing bacterial chromosomal DNA from plasmid preparations. It preferentially hydrolyses dslDNA, but is less effective against linear and closed circular ssDNAs, and is poorly active against closed circular supercoiled DNA and nicked circular double-stranded DNA [81]. Thus, hydrolysis will retain cccDNA, but also result in incomplete digestion of rcDNA, retaining up to 90% of rcDNA [82-84]. Thus, the specificity of plasmid safe DNase pre-treatment combined with qPCR can be low.
T5 exonuclease has been reported to degrade rcDNA for cccDNA purification, showing complete digestion of HBV DNA intermediates, unlike plasmid safe DNase [82]. T5 exonuclease initiates at 5ŌĆÖ termini and degrades both ssDNA and dsDNA in the 5ŌĆÖ to 3ŌĆÖ direction, which allows it to act on nicked dsDNA [82]. Caution is therefore advised for using T5 exonuclease as nicks can be introduced into cccDNA during the DNA extraction process. In addition, care must be taken not to leave T5 exonuclease incubating for too long, as a previous report showed that 16 hours incubation of 5 U T5 exonuclease results in a 60% decrease in supercoiled DNA, while digestion for 60 minutes showed no such effect [82].
A combination of exonuclease I and exonuclease III can be used in order to remove HBV DNA intermediates, with similar efficacy to T5 exonuclease [82]. Both enzymes act in the 3ŌĆÖ to 5ŌĆÖ direction, however exonuclease I specifically degrades ssDNA while exonuclease III is dsDNA specific, preferentially attacking blunt or recessed 3ŌĆÖ-protuding termini. These exonucleases lack the single strand endonuclease function of T5 exonuclease, thereby preserving circular ssDNA. This theoretically prevents hydrolysis of cccDNA nicked during the extraction process, increasing accuracy. However, digestion with exonuclease I and exonuclease III also preserves PF-rcDNA intermediates, including a newly discovered HBV DNA form with a covalently closed minus strand with an open plus strand [85,86]. It is currently unknown whether these are true replicative intermediates in formation of cccDNA [85], or if they are simply stable by-products of its generation [86]. Existence of these DNA forms suggests that repair of each DNA strand during cccDNA formation is an independent event [18].
cinqPCR is a qPCR-based method for detecting cccDNA from total DNA extracts without complete hydrolysis of cellular DNA, allowing normalisation to host genes [73]. Using a series of restriction enzyme digestion and ligation steps [87], HBV cccDNA is converted into an inverted linear form which is efficiently amplified using PCR. Other forms of HBV DNA however are not inverted due to the presence of nicks in a specific region of the viral genome. Together, this means cinqPCR has high accuracy, precision and sensitivity. Our group has now quantified cccDNA in as few as 5 cell equivalents of input DNA and regularly run this assay on a 96-well format. However, this assay is more complicated than the exonuclease-based methods described above and is restricted to detection of the ŌĆ£GalibertŌĆØ lab strain of HBV, preventing analysis of clinical samples [73].
Due to its high precision, this assay could identify the limited role of HBc on cccDNA levels. We found that wild-type HBV produced similar levels of cccDNA compared to replication-deficient HBV mutant, indicating de novo HBc synthesis was not important for maintaining the cccDNA pool in HBV-infected hepatoma cell lines and primary hepatocytes [88]. Our group had also confirmed the mode of action of different therapeutics (e.g., late treatment with capsid inhibitors does not affect cccDNA levels) [73].
Many key questions concerning cccDNA biology remain unanswered due to the current limitations of cccDNA quantification. If a highly accurate, precise, and versatile assay were available however, it is possible that cccDNA may be more fully understood and open up novel approaches to remove it thereby curing chronic HBV.
The intrinsic lifespan or half-life of cccDNA is of key interest to treating a chronic HBV infection. As new cccDNA formation can be markedly suppressed by current and upcoming therapies, the life-span of cccDNA in the liver determines how effective therapies need to be and how long they must be administered to induce an eventual cure. An ideal cccDNA assay would be able to identify the lifespan of cccDNA by consistent monitoring of cccDNA levels.
Duck HBV models have been combined with mathematical models to estimate cccDNA half-life [89-91], however cccDNA half-life in the human liver is yet to be formally established. Indeed, whether cccDNA decays during therapy or if it even conforms to exponential decay (as implied by the commonly-used term ŌĆ£cccDNA half-lifeŌĆØ) has not been shown.
Moreover, partial survival of woodchuck hepatitis virus cccDNA has also been reported. In six out of 10 woodchucks with waning or undetectable surface antigen levels, intrahepatic cccDNA was detected even several years after functional cure [92]. This indicates that either there is low level replication of cccDNA or that cccDNA is highly stable in the liver. Both may be the case: immunosuppression of these woodchucks induced new replication and viral recrudesce [92].
Recent mathematical modelling has indicated that ŌĆ£cccDNA half-lifeŌĆØ may vary over the course of infection, depending on host and viral factors. High viral load was associated with a longer and more stable cccDNA half-life of 61 days, while a low viral load was associated with a lower half-life of 26 days [89]. Given this data, it seems unlikely that cccDNA itself has an intrinsic decay rate, but instead its loss is likely mediated by host and viral factors (e.g., cytolytic and non-cytolytic immune responses against HBV-infected cells, cell mitosis, HBV replication and reinfection of hepatocytes). This is consistent with non-dividing in vitro infection models, in which cccDNA levels remained static over 9 weeks [88]. However, this is different to the calculated half-life of duck HBV (3ŌĆō5 days in culture) [91], suggesting differences between hepadnaviruses of different hosts.
Our group and others have shown that cccDNA is highly stable in infected cells not undergoing mitosis [88,91,93]. For example, we found that cccDNA levels were not significantly different between infections with a replication-deficient mutant HBV compared to infections with replication-competent HBV in Huh-7-NTCP, HepG2-NTCP, HepaRG-NTCP and primary human hepatocytes [88]. This strongly suggested that no renewal of cccDNA levels occurs over time within a given infected cell. Thus, direct induction of cccDNA loss (and not inhibition of de novo cccDNA formation) is likely the most efficient approach for complete cure.
Further, chimpanzee studies combined with mathematical modelling have suggested that purely cytopathic methods of cccDNA eradication are unlikely to successfully clear virus [94]. In this model of acute infection, modelling predicted ~11 livers turnovers was required for the observed cccDNA loss, but only ~3 liver turnovers had occurred based on PCNA staining of the liver. To explain the inconsistency, the authors suggested that CD8+ T cells produce IFN-╬│ within the liver, destabilising cccDNA. An ideal cccDNA assay could possibly identify if or when this process occurred and perhaps even differentiate full-length cccDNA from the destabilised fragments.
Understanding and therapeutically inducing the destabilisation of cccDNA is an intriguing strategy to curing chronic HBV. Interferon-mediated degradation of cccDNA (possibly through regulation of HIF1╬▒) has been reported to induce cccDNA loss [95,96]. Other groups have reported that approaches such as gene editing or epigenetic silencing could also target cccDNA directly and induce its degradation, replication deficiency or transcriptional-silencing [97,98].
Mitosis of host cells has been suggested to deplete episomal cccDNA [83], although this has been challenged by other studies indicating the survival of cccDNA in the daughter cells [99]. Reaiche-Miller et al. [99] reported that duck HBV cccDNA could partially survive mitosis based on mathematical models and experimentally derived cccDNA levels in growing duck HBV-infected ducks on NA therapy. Woodchuck models have also shown evidence for some cccDNA molecules being distributed to daughter cells [93]. In contrast, human liver chimeric mice seeded with HBV-infected cells have shown dramatic reductions of cccDNA during cell mitosis, consistent with complete cccDNA loss [83]. Such disparate findings in different animal models must be resolved in order to answer the question on the fate of cccDNA following mitosis of the host cell. A highly-sensitive and -specific cccDNA assay could quantify cccDNA on a single-cell level to directly determine if loss, unequal partitioning, or survival of cccDNA occurs in daughter cells upon mitosis.
HBV cccDNA is central to the maintenance of chronic infection and key questions in cccDNA biology still remain unanswered. To improve our knowledge and facilitate HBV cure research, cccDNA must be accurately quantified and monitored over time, either through indirect biomarkers or via direct measurement. All current methodologies have strengths and weaknesses, with indirect measures being generally faster and less invasive but less accurate, and direct methods slower and more precise. Open questions on cccDNA biology will remain until more advanced methods of quantification can be developed.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
T.T. is funded by Australian Centre for HIV and Hepatitis grant (annual grant) and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (Ideas Grant GNT2002565).
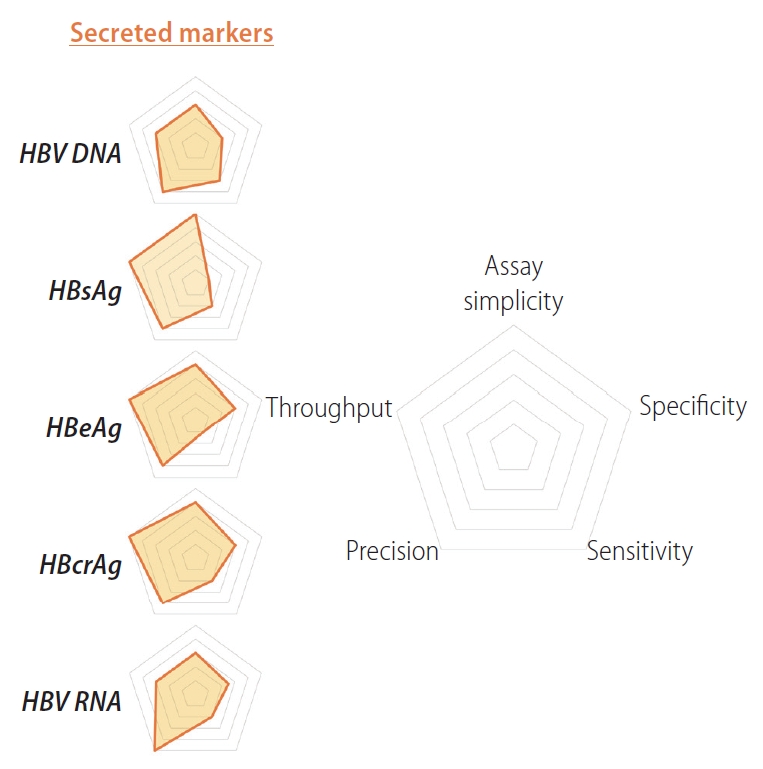
Figure┬Ā1.
Relative strengths and weaknesses of indirect biomarkers for cccDNA quantification. Radar charts comparing strengths and weaknesses of secreted biomarkers for cccDNA quantification (HBV DNA, HBsAg, HBeAg, HBcrAg and HBV RNA) are plotted on five axes representing: assay simplicity, specificity, sensitivity, precision and throughput. HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBsAg, HBV surface antigen; HBeAg, HBV e antigen; HBcrAg, hepatitis B core related antigen; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA.
Figure┬Ā2.
Relative strengths and weaknesses of direct methods for cccDNA quantification. Radar chart comparing relative merits of several approaches to direct cccDNA quantification. Hybridisation methods (green) include Southern blot hybridisation, and fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH). qPCR based methods (blue) include qPCR only, or prior enzymatic digestion with plasmid safe DNase (PSD), T5 exonuclease (T5 Exo), and exonuclease 1 and 3 (ExoI/III). Another approach involves serial restriction enzyme digestion and ligation steps prior to qPCR (cccDNA inversion quantitative PCR, cinqPCR). Relative strengths and weaknesses are plotted on the axes as per Figure 1. qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA.

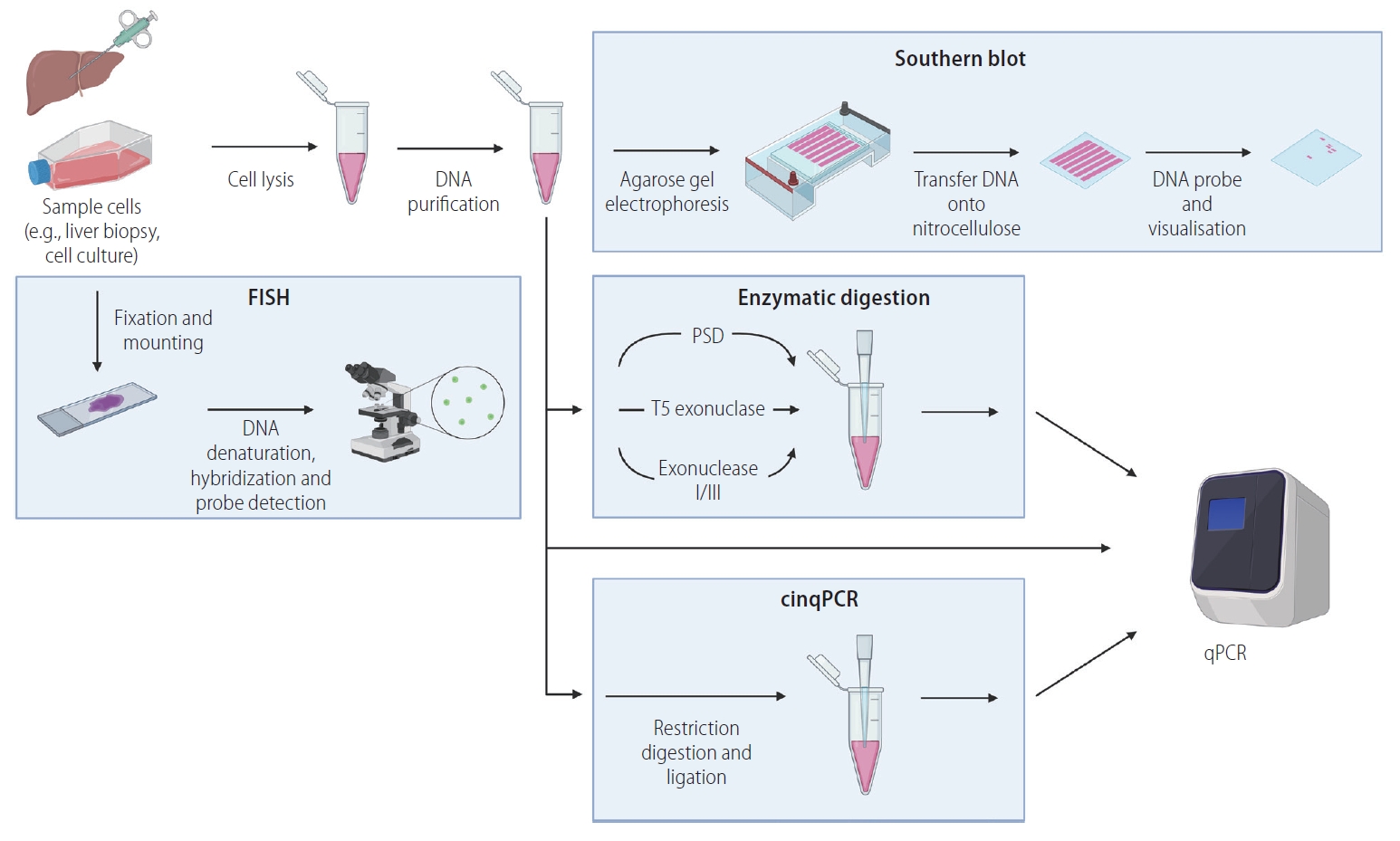
Figure┬Ā3.
Pathways to directly quantify cccDNA. Several potential technological strategies can be used in combination to directly quantify cccDNA. First, sample enrichment for HBV cccDNA: cells are lysed, and proteins are digested, DNA is purified by precipitation or binding to silica membrane, separating out protein and RNA. Analysis of enriched DNA can then be quantified by Southern blot hybridisation (separation of HBV DNA based on electrophoretic motility through an agarose gel, followed by transfer onto a nitrocellulose membrane and hybridisation with a ssDNA probe). Alternatively, qPCR can be used to quantify cccDNA directly from total DNA, enriched DNA, or after enzymatic digestion (plasmid-safe DNase [PSD], T5 exonuclease, exonuclease I/III, or through cinqPCR). As a third approach, cccDNA can be directly detected by fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH): sample cells are fixed and mounted before processing to hybridise DNA with fluorescently marked probes, visualised by immunofluorescent microscopy. Figure created with BioRender.com. cinqPCR, cccDNA inversion quantitative polymerase chain reaction; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; HBV, hepatitis B virus; ssDNA, single stranded DNA.
Table┬Ā1.
Indirect biomarkers used in cccDNA quantification
| Analyte | Advantage | Disadvantage | Assays used | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secreted HBV DNA | Good correlation with cccDNA levels (r=0.664, P<0.001) | Undetectable in patients under NA therapy | qPCR | [100-102] |
| Lengthy: 7 hours | ||||
| HBsAg | Reasonable indicator of cccDNA levels in HBeAg-positive patients (r=0.54, P=0.004) | Little to no correlation with cccDNA in HBeAgnegative patients (r=-0.27, P=0.15) | CLEIA, ECLEIA | [53,102-107] |
| Can be produced from integrated HBV | ||||
| Low specificity | ||||
| HBeAg | Used as a cccDNA specific reporter in vitro for screening of cccDNA drugs | In patients, HBeAg is neutralised by host antibodies | ELISA, CLEIA | [59,61,62,108] |
| Pre-core nonsense or pre-mature stop mutations in HBeAg-negative patients | ||||
| HBcrAg | Good correlation with cccDNA (r=0.70, P<0.0001) | Low sensitivity: undetectable in 35% of HBeAg-negative patients | CLEIA | [54,65] |
| Serum HBV RNA | Reasonable measure of cccDNA transcriptional activity (r=0.58, P=0.001) | Low specificity | qPCR | [65,71,100,102] |
| No standardised method in the field | ||||
| All indirect biomarkers | Non-invasive/non-destructive to cells | Can only measure transcriptionally-active cccDNA | ||
| High throughput | Inhibition of viral replication steps downstream of cccDNA formation may affect marker levels |
cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; Ref., reference; HBV, hepatitis B virus; NA, nucleos(t)ide analogues; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; HBsAg, HBV surface antigen; CLEIA, chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay; ECLEIA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay; HBeAg, HBV e antigen; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunoassay; HBcrAg, hepatitis B core related antigen.
Table┬Ā2.
Direct methods of cccDNA quantification
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southern blot | Specific and well-established method for cccDNA quantification | Complex and lengthy | [77] |
| Insensitive: ~106 copies required (~105-fold more than other assays) | |||
| Lack of genomic DNA to use for normalisation | |||
| FISH | Can visualise location of cccDNA | Time consuming and complex | [78] |
| Not specific to cccDNA (can detect nuclear rcDNA) | |||
| qPCR | Simple | Nonspecific detection of HBV intermediate forms | [79,82] |
| Sensitive | Lack of genomic DNA to use for normalisation | ||
| Cheap | |||
| qPCR + plasmid safe Dnase | Effective against dslDNA | Not effective in removing rcDNA and integrated linear DNA | [82] |
| Lack of genomic DNA to use for normalisation | |||
| qPCR + T5 exonuclease | Very effective removal of HBV DNA intermediate forms | Possible over-digestion and loss of cccDNA | [82] |
| Lack of genomic DNA to use for normalisation | |||
| qPCR + exonuclease I + exonuclease III | Very effective removal of HBV DNA intermediate forms | Retains closed minus strand rcDNA | [82,85] |
| Lack of genomic DNA to use for normalisation | |||
| cinqPCR | Highly sensitive and specific | Limited to detection of ŌĆ£GalibertŌĆØ lab strain of HBV | [73] |
| Can standardise to cellular reference genes in duplex PCR reaction |
Abbreviations
cccDNA
covalently closed circular DNA
cinqPCR
cccDNA inversion quantitative PCR
CLEIA
chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay
dsDNA
double stranded DNA
dslDNA
double stranded linear DNA
ELISA
enzyme-linked immunoassay
FISH
fluorescence in situ hybridisation
HA
hemagglutinin
HBc
HBV core protein
HBcAg
hepatitis B core antigen
HBcrAg
hepatitis B core related antigen
HBeAg
HBV e antigen
HBsAg
HBV surface antigen
HBV
hepatitis B virus
HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
IFN
interferon
NA
nucleos(t)ide analogues
NTCP
sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide
PCR
polymerase chain reaction
PF
protein-free
pgRNA
pregenomic RNA
pol
viral polymerase
qPCR
quantitative PCR
rcDNA
relaxed circular DNA
ssDNA
single stranded DNA
REFERENCES
1. World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H, et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1521-1531.


3. Marcellin P, Heathcote EJ, Buti M, Gane E, de Man RA, Krastev Z, et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2008;359:2442-2455.


4. Newbold JE, Xin H, Tencza M, Sherman G, Dean J, Bowden S, et al. The covalently closed duplex form of the hepadnavirus genome exists in situ as a heterogeneous population of viral minichromosomes. J Virol 1995;69:3350-3357.



5. Tu T, Block JM, Wang S, Cohen C, Douglas MW. The lived experience of chronic hepatitis B: a broader view of its impacts and why we need a cure. Viruses 2020;12:515.



6. Li X, Zhao J, Yuan Q, Xia N. Detection of HBV covalently closed circular DNA. Viruses 2017;9:139.



7. Lok AS, Zoulim F, Dusheiko G, Ghany MG. Hepatitis B cure: from discovery to regulatory approval. J Hepatol 2017;67:847-861.


8. Urban S, Schulze A, Dandri M, Petersen J. The replication cycle of hepatitis B virus. J Hepatol 2010;52:282-284.


9. Tu T, Urban S. Virus entry and its inhibition to prevent and treat hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus infections. Curr Opin Virol 2018;30:68-79.


10. Verrier ER, Colpitts CC, Bach C, Heydmann L, Weiss A, Renaud M, et al. A targeted functional RNA interference screen uncovers glypican 5 as an entry factor for hepatitis B and D viruses. Hepatology 2016;63:35-48.


11. Hu Q, Zhang F, Duan L, Wang B, Ye Y, Li P, et al. E-cadherin plays a role in hepatitis B virus entry through affecting glycosylated sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide distribution. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020;10:74.



12. Iwamoto M, Saso W, Sugiyama R, Ishii K, Ohki M, Nagamori S, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a host-entry cofactor triggering hepatitis B virus internalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019;116:8487-8492.



13. Huang HC, Chen CC, Chang WC, Tao MH, Huang C. Entry of hepatitis B virus into immortalized human primary hepatocytes by clathrin-dependent endocytosis. J Virol 2012;86:9443-9453.



14. Herrscher C, Pastor F, Burlaud-Gaillard J, Dumans A, Seigneuret F, Moreau A, et al. Hepatitis B virus entry into HepG2-NTCP cells requires clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Cell Microbiol 2020;22:e13205.

15. Li Y, Luo G. Human low-density lipoprotein receptor plays an important role in hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS Pathog 2021;17:e1009722.



16. Rabe B, Vlachou A, Pant├® N, Helenius A, Kann M. Nuclear import of hepatitis B virus capsids and release of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:9849-9854.



17. Wei L, Ploss A. Core components of DNA lagging strand synthesis machinery are essential for hepatitis B virus cccDNA formation. Nat Microbiol 2020;5:715-726.



18. Wei L, Ploss A. Hepatitis B virus cccDNA is formed through distinct repair processes of each strand. Nat Commun 2021;12:1591.



19. K├Čniger C, Wingert I, Marsmann M, R├Čsler C, Beck J, Nassal M. Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014;111:E4244-E4253.



20. Qi Y, Gao Z, Xu G, Peng B, Liu C, Yan H, et al. DNA polymerase ╬║ is a key cellular factor for the formation of covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus. PLoS Pathog 2016;12:e1005893.



21. Pollicino T, Belloni L, Raffa G, Pediconi N, Squadrito G, Raimondo G, et al. Hepatitis B virus replication is regulated by the acetylation status of hepatitis B virus cccDNA-bound H3 and H4 histones. Gastroenterology 2006;130:823-837.


22. Tropberger P, Mercier A, Robinson M, Zhong W, Ganem DE, Holdorf M. Mapping of histone modifications in episomal HBV cccDNA uncovers an unusual chromatin organization amenable to epigenetic manipulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015;112:E5715-E5724.



23. Levrero M, Pollicino T, Petersen J, Belloni L, Raimondo G, Dandri M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2009;51:581-592.


24. Koepke A, Volz T, Lutgehetmann M, Lohse AW, Dandri M, Petersen J. Genetic variability on the cccdna regulatory regions changes significantly in the different phases of chronic HBV infection. Hepatology 2008;48:683A-683A.
25. Volz T, Lutgehetmann M, Wachtler P, Jacob A, Quaas A, Murray JM, et al. Impaired intrahepatic hepatitis B virus productivity contributes to low viremia in most HBeAg-negative patients. Gastroenterology 2007;133:843-852.


26. Bartenschlager R, Junker-Niepmann M, Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol 1990;64:5324-5332.



27. Hirsch RC, Lavine JE, Chang LJ, Varmus HE, Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as well as for reverse transcription. Nature 1990;344:552-555.


28. Summers J, Mason WS. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B-like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell 1982;29:403-415.


29. Bavand M, Feitelson M, Laub O. The hepatitis B virus-associated reverse transcriptase is encoded by the viral pol gene. J Virol 1989;63:1019-1021.



30. Seeger C, Ganem D, Varmus HE. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the hepatitis B virus replication strategy. Science 1986;232:477-484.


31. Junker-Niepmann M, Bartenschlager R, Schaller H. A short cisacting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J 1990;9:3389-3396.



32. Radziwill G, Tucker W, Schaller H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: domain structure and RNase H activity. J Virol 1990;64:613-620.



33. Fu TB, Taylor J. When retroviral reverse transcriptases reach the end of their RNA templates. J Virol 1992;66:4271-4278.



34. Loeb DD, Hirsch RC, Ganem D. Sequence-independent RNA cleavages generate the primers for plus strand DNA synthesis in hepatitis B viruses: implications for other reverse transcribing elements. EMBO J 1991;10:3533-3540.



35. Staprans S, Loeb DD, Ganem D. Mutations affecting hepadnavirus plus-strand DNA synthesis dissociate primer cleavage from translocation and reveal the origin of linear viral DNA. J Virol 1991;65:1255-1262.



36. Hu J, Liu K. Complete and incomplete hepatitis B virus particles: formation, function, and application. Viruses 2017;9:56.



37. Tu T, Budzinska MA, Shackel NA, Urban S. HBV DNA integration: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Viruses 2017;9:75.



38. Chai N, Chang HE, Nicolas E, Han Z, Jarnik M, Taylor J. Properties of subviral particles of hepatitis B virus. J Virol 2008;82:7812-7817.



39. Laras A, Koskinas J, Dimou E, Kostamena A, Hadziyannis SJ. Intrahepatic levels and replicative activity of covalently closed circular hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected patients. Hepatology 2006;44:694-702.


40. Nassal M. HBV cccDNA: viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015;64:1972-1984.


41. Zhang YY, Zhang BH, Theele D, Litwin S, Toll E, Summers J. Single-cell analysis of covalently closed circular DNA copy numbers in a hepadnavirus-infected liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:12372-12377.



42. Werle-Lapostolle B, Bowden S, Locarnini S, Wursthorn K, Petersen J, Lau G, et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1750-1758.


43. Liu Y, Veeraraghavan V, Pinkerton M, Fu J, Douglas MW, George J, et al. Viral biomarkers for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence and recurrence. Front Microbiol 2021;12:665201.



44. Dandri M, Petersen J. cccDNA maintenance in chronic hepatitis B - targeting the matrix of viral replication. Infect Drug Resist 2020;13:3873-3886.


45. Liu C, Chang L, Jia T, Guo F, Zhang L, Ji H, et al. Real-time PCR assays for hepatitis B virus DNA quantification may require two different targets. Virol J 2017;14:94.



46. Takeda K, Maruki M, Yamagaito T, Muramatsu M, Sakai Y, Tobimatsu H, et al. Highly sensitive detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen by use of a semiautomated immune complex transfer chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol 2013;51:2238-2244.



47. Kim SH. ELISA for quantitative determination of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Immune Netw 2017;17:451-459.



48. Tantiwetrueangdet A, Panvichian R, Sornmayura P, Sueangoen N, Leelaudomlipi S. Reduced HBV cccDNA and HBsAg in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Med Oncol 2018;35:127.



49. Seto WK, Hui AJ, Wong VW, Wong GL, Liu KS, Lai CL, et al. Treatment cessation of entecavir in Asian patients with hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B: a multicentre prospective study. Gut 2015;64:667-672.


50. Yang N, Feng J, Zhou T, Li Z, Chen Z, Ming K, et al. Relationship between serum quantitative HBsAg and HBV DNA levels in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Med Virol 2018;90:1240-1245.


51. Fu S, Li N, Zhou PC, Huang Y, Zhou RR, Fan XG. Detection of HBV DNA and antigens in HBsAg-positive patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2017;41:415-423.


52. Wang Q, Luan W, Warren L, Fiel MI, Blank S, Kadri H, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen correlates with tissue covalently closed circular DNA in patients with hepatitis B-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol 2016;88:244-251.


53. Lin LY, Wong VW, Zhou HJ, Chan HY, Gui HL, Guo SM, et al. Relationship between serum hepatitis B virus DNA and surface antigen with covalently closed circular DNA in HBeAg-negative patients. J Med Virol 2010;82:1494-1500.


54. Wong DK, Seto WK, Cheung KS, Chong CK, Huang FY, Fung J, et al. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen as a surrogate marker for covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int 2017;37:995-1001.


55. Tu T, Mason WS, Clouston AD, Shackel NA, McCaughan GW, Yeh MM, et al. Clonal expansion of hepatocytes with a selective advantage occurs during all stages of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat 2015;22:737-753.


56. Mason WS, Gill US, Litwin S, Zhou Y, Peri S, Pop O, et al. HBV DNA integration and clonal hepatocyte expansion in chronic hepatitis B patients considered immune tolerant. Gastroenterology 2016;151:986-998.e4.



57. Chan HL, Wong VW, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HY, Sung JJ. A longitudinal study on the natural history of serum hepatitis B surface antigen changes in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2010;52:1232-1241.


58. Chan HL, Wong VW, Tse AM, Tse CH, Chim AM, Chan HY, et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can reflect hepatitis B virus in the liver and predict treatment response. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:1462-1468.


59. Zhou T, Guo H, Guo JT, Cuconati A, Mehta A, Block TM. Hepatitis B virus e antigen production is dependent upon covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA in HepAD38 cell cultures and may serve as a cccDNA surrogate in antiviral screening assays. Antiviral Res 2006;72:116-124.


60. Ladner SK, Otto MJ, Barker CS, Zaifert K, Wang GH, Guo JT, et al. Inducible expression of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) in stably transfected hepatoblastoma cells: a novel system for screening potential inhibitors of HBV replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1997;41:1715-1720.



61. Cai D, Mills C, Yu W, Yan R, Aldrich CE, Saputelli JR, et al. Identification of disubstituted sulfonamide compounds as specific inhibitors of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012;56:4277-4288.



62. Cai D, Wang X, Yan R, Mao R, Liu Y, Ji C, et al. Establishment of an inducible HBV stable cell line that expresses cccDNA-dependent epitope-tagged HBeAg for screening of cccDNA modulators. Antiviral Res 2016;132:26-37.



64. Suzuki F, Miyakoshi H, Kobayashi M, Kumada H. Correlation between serum hepatitis B virus core-related antigen and intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Med Virol 2009;81:27-33.


65. Ghany MG, King WC, Lisker-Melman M, Lok ASF, Terrault N, Janssen HLA, et al. Comparison of HBV RNA and hepatitis B core related antigen with conventional HBV markers among untreated adults with chronic hepatitis B in North America. Hepatology 2021;74:2395-2409.



66. Testoni B, Leboss├® F, Scholtes C, Berby F, Miaglia C, Subic M, et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Hepatol 2019;70:615-625.


67. Hong X, Luckenbaugh L, Mendenhall M, Walsh R, Cabuang L, Soppe S, et al. Characterization of hepatitis B precore/core-related antigens. J Virol 2021;95:e01695-20.



68. Wang J, Shen T, Huang X, Kumar GR, Chen X, Zeng Z, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound. J Hepatol 2016;65:700-710.


69. Mak LY, Wong DK, Cheung KS, Seto WK, Lai CL, Yuen MF. Review article: hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): an emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2018;47:43-54.


70. Huang H, Wang J, Li W, Chen R, Chen X, Zhang F, et al. Serum HBV DNA plus RNA shows superiority in reflecting the activity of intrahepatic cccDNA in treatment-naïve HBV-infected individuals. J Clin Virol 2018;99-100:71-78.


71. Wang J, Yu Y, Li G, Shen C, Meng Z, Zheng J, et al. Relationship between serum HBV-RNA levels and intrahepatic viral as well as histologic activity markers in entecavir-treated patients. J Hepatol 2018;68:16-24.

72. Allweiss L, Giersch K, Pirosu A, Volz T, Muench RC, Beran RK, et al. Therapeutic shutdown of HBV transcripts promotes reappearance of the SMC5/6 complex and silencing of the viral genome in vivo. Gut 2022;71:372-381.



73. Tu T, Zehnder B, Qu B, Ni Y, Main N, Allweiss L, et al. A novel method to precisely quantify hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular (ccc)DNA formation and maintenance. Antiviral Res 2020;181:104865.


74. Cai D, Nie H, Yan R, Guo JT, Block TM, Guo H. A southern blot assay for detection of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA from cell cultures. Methods Mol Biol 2013;1030:151-161.



75. Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol 1967;26:365-369.


76. Arad U. Modified Hirt procedure for rapid purification of extrachromosomal DNA from mammalian cells. Biotechniques 1998;24:760-762.


77. Southern EM. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 1975;98:503-517.


78. Li M, Sohn JA, Seeger C. Distribution of hepatitis B virus nuclear DNA. J Virol 2017;92:e01391-17.



79. He ML, Wu J, Chen Y, Lin MC, Lau GK, Kung HF. A new and sensitive method for the quantification of HBV cccDNA by real-time PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;295:1102-1107.


80. K├Čck J, Schlicht HJ. Analysis of the earliest steps of hepadnavirus replication: genome repair after infectious entry into hepatocytes does not depend on viral polymerase activity. J Virol 1993;67:4867-4874.



81. Lucigen. Plasmid-Safe ATP-Dependent DNase. Lucigen web site, <https://www.lucigen.com/docs/manuals/plasmid-safe-atp-dependent-dnase.pdf>. Accessed 17 Aug 2021.
82. Qu B, Ni Y, Lempp FA, Vondran FWR, Urban S. T5 exonuclease hydrolysis of hepatitis B virus replicative intermediates allows reliable quantification and fast drug efficacy testing of covalently closed circular DNA by PCR. J Virol 2018;92:e01117-18.



83. Allweiss L, Volz T, Giersch K, Kah J, Raffa G, Petersen J, et al. Proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and prevention of hepatitis B virus reinfection efficiently deplete nuclear cccDNA in vivo. Gut 2018;67:542-552.


84. Gao YT, Han T, Li Y, Yang B, Wang YJ, Wang FM, et al. Enhanced specificity of real-time PCR for measurement of hepatitis B virus cccDNA using restriction endonuclease and plasmid-safe ATP-dependent DNase and selective primers. J Virol Methods 2010;169:181-187.


85. Luo J, Cui X, Gao L, Hu J. Identification of an intermediate in hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular (CCC) DNA formation and sensitive and selective CCC DNA detection. J Virol 2017;91:e00539-17.



86. Marchetti AL, Guo H. New insights on molecular mechanism of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA formation. Cells 2020;9:2430.



87. Zehnder B, Urban S, Tu T. A sensitive and specific PCR-based assay to quantify hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular (ccc) DNA while preserving cellular DNA. Bio Protoc 2021;11:e3986.



88. Tu T, Zehnder B, Qu B, Urban S. De novo synthesis of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids is dispensable for the maintenance and transcriptional regulation of cccDNA. JHEP Rep 2020;3:100195.



89. Lythgoe KA, Lumley SF, Pellis L, McKeating JA, Matthews PC. Estimating hepatitis B virus cccDNA persistence in chronic infection. Virus Evol 2020;7:veaa063.



90. Addison WR, Walters KA, Wong WW, Wilson JS, Madej D, Jewell LD, et al. Half-life of the duck hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA pool in vivo following inhibition of viral replication. J Virol 2002;76:6356-6363.



91. Civitico GM, Locarnini SA. The half-life of duck hepatitis B virus supercoiled DNA in congenitally infected primary hepatocyte cultures. Virology 1994;203:81-89.


92. Menne S, Cote PJ, Butler SD, Toshkov IA, Gerin JL, Tennant BC. Immunosuppression reactivates viral replication long after resolution of woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology 2007;45:614-622.


93. Zhu Y, Yamamoto T, Cullen J, Saputelli J, Aldrich CE, Miller DS, et al. Kinetics of hepadnavirus loss from the liver during inhibition of viral DNA synthesis. J Virol 2020;75:311-322.



94. Murray JM, Wieland SF, Purcell RH, Chisari FV. Dynamics of hepatitis B virus clearance in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:17780-17785.



95. Lucifora J, Xia Y, Reisinger F, Zhang K, Stadler D, Cheng X, et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014;343:1221-1228.



96. Riedl T, Faure-Dupuy S, Rolland M, Schuehle S, Hizir Z, Calderazzo S, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-mediated RelB/APOBEC3B down-regulation allows hepatitis B virus persistence. Hepatology 2021;74:1766-1781.



97. Martinez MG, Villeret F, Testoni B, Zoulim F. Can we cure hepatitis B virus with novel direct-acting antivirals? Liver Int 2020;40 Suppl 1:27-34.


98. Wang L, Zhu Q, Zeng J, Yan Z, Feng A, Young J, et al. PS-074-A first-in-class orally available HBV cccDNA destabilizer ccc_R08 achieved sustainable HBsAg and HBV DNA suppression in the HBV circle mouse model through elimination of cccDNA-like molecules in the mouse liver. J Hepatol 2019;70:e48.

99. Reaiche-Miller GY, Thorpe M, Low HC, Qiao Q, Scougall CA, Mason WS, et al. Duck hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA appears to survive hepatocyte mitosis in the growing liver. Virology 2013;446:357-364.


100. Wang X, Chi X, Wu R, Xu H, Gao X, Yu L, et al. Serum HBV RNA correlated with intrahepatic cccDNA more strongly than other HBV markers during peg-interferon treatment. Virol J 2021;18:4.



101. Inoue T, Kusumoto S, Iio E, Ogawa S, Suzuki T, Yagi S, et al. Clinical efficacy of a novel, high-sensitivity HBcrAg assay in the management of chronic hepatitis B and HBV reactivation. J Hepatol 2021;75:302-310.


102. Liu Y, Jiang M, Xue J, Yan H, Liang X. Serum HBV RNA quantification: useful for monitoring natural history of chronic hepatitis B infection. BMC Gastroenterol 2019;19:53.



103. Meier MA, Calabrese D, Suslov A, Terracciano LM, Heim MH, Wieland S. Ubiquitous expression of HBsAg from integrated HBV DNA in patients with low viral load. J Hepatol 2021;75:840-847.


104. Aden DP, Fogel A, Plotkin S, Damjanov I, Knowles BB. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature 1979;282:615-616.


105. Knowles BB, Howe CC, Aden DP. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science 1980;209:497-499.


106. Alexander J, Bey E, Whitcutt JM, Gear JH. Adaptation of cells derived from human malignant tumours to growth in vitro. S Afr J Med Sci 1976;41:89-98.

- TOOLS



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print





