| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 30(3); 2024 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
Background/Aims
Oral EDP-514 is a potent core protein inhibitor of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication, which produced a >4-log viral load reduction in HBV-infected chimeric mice with human liver cells. This study evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of three doses of EDP-514 in treatment-naive viremic patients with HBeAgpositive or -negative chronic HBV infection.
Methods
Patients with HBsAg detectable at screening and at least 6 months previously were eligible. HBeAg-positive and -negative patients had a serum/plasma HBV DNA level Ōēź20,000 and Ōēź2,000 IU/mL, respectively. Twenty-five patients were randomized to EDP-514 200 (n=6), 400 (n=6) or 800 mg (n=7) or placebo (n=6) once daily for 28 days.
Results
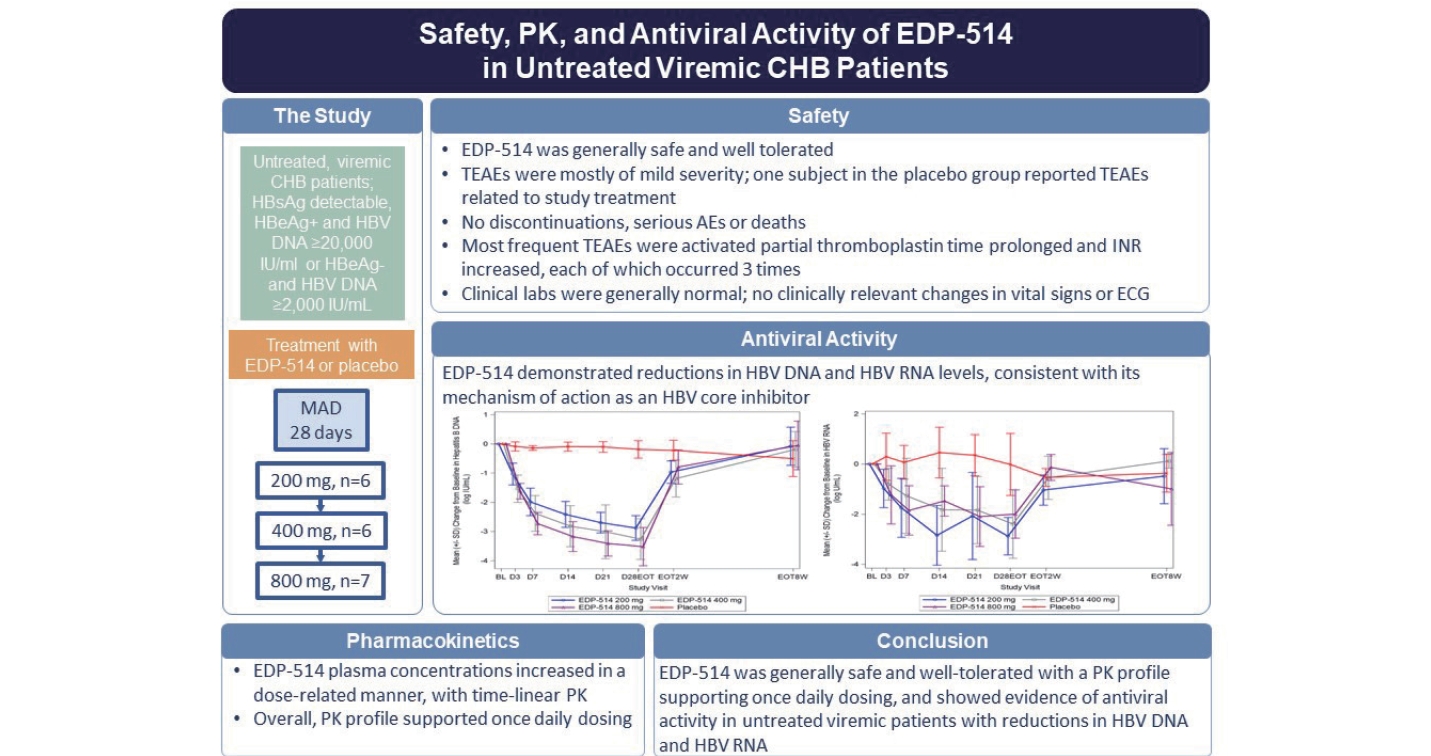
A dose-related increase in EDP-514 exposure (AUClast and Cmax) was observed across doses. At Day 28, mean reductions in HBV DNA were ŌĆō2.9, ŌĆō3.3, ŌĆō3.5 and ŌĆō0.2 log10 IU/mL with EDP-514 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. The corresponding mean change from baseline for HBV RNA levels was ŌĆō2.9, ŌĆō2.4, ŌĆō2.0, and ŌĆō0.02 log10 U/mL. No virologic failures were observed. No clinically meaningful changes from baseline were observed for HBsAg, HBeAg or HBcrAg. Nine patients reported treatment emergent adverse events of mild or moderate severity with no discontinuations, serious AEs or deaths.
Graphical Abstract
Infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a common cause of hepatic cirrhosis and the most common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma [1]. Worldwide, almost 300 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with HBV, and 1.5 million new infections/year are reported resulting in >800,000 deaths annually [2]. HBV infection can be prevented with widely available HBV vaccines [3,4], however, the majority of people are unvaccinated, especially in lower- and middle-income countries. Standard treatment for HBV infection includes pegylated interferon (pegIFN) and nucleos(t)ide analogues (NUCs). These effectively suppress the infection through immunomodulation and inhibition of viral replication, respectively. NUCs are associated with an excellent safety/tolerability profile and potent antiviral activity for suppressing hepatitis B DNA levels but is needed to be taken long-term, whereas, pegIFN provides a satisfactory response in a very limited number of patients [3,4].
Hence, a need exists for treatments providing a sustained clinical response and functional cure, which is defined as a sustained loss of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), with or without acquisition of hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs), and undetectable HBV DNA 6 months after completing treatment [5,6]. Current therapies only achieve functional cure in a limited number of patients. Treatment with pegIFN achieves functional cure in approximately 11% of patients after 3 years [4], and treatment with NUC produces a functional cure in Ōēż10% of patients after 5 years of treatment [7,8]. As a result, patients with HBV infection frequently require lifelong maintenance therapy, which imparts a substantial economic burden and may be associated with a risk of breakthrough drug resistance and drug toxicity [9,10]. Further, the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma is reduced but not eliminated with these currently available treatments [11,12].
Novel drugs, which offer the potential for a functional cure, are in early clinical development for HBV infection including viral entry inhibitors, drugs for epigenetic control of cccDNA, immune modulators, RNA interference agents, ribonuclease H inhibitors, and core protein inhibitors [5]. Two types of core protein inhibitors are recognized, both of which accelerate the kinetics of core protein interactions. Treatment with Type I inhibitors in vitro leads to the intracellular core protein aggregation and degradation, while in vitro treatment with Type II inhibitors results in production of empty capsids that lack the RNA polymerase complex-required for HBV replication [13]. Interestingly, in addition to suppressing replication by preventing pgRNA encapsidation, inhibitors of both these classes have been described to prevent de novo formation of cccDNA by preventing delivery of intact capsids to the nucleus. Treatment with core protein inhibitors in patients with HBV infection demonstrated a 2 to 3 log10 IU/mL reduction in the mean HBV DNA concentrations in viremic chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients [14-16].
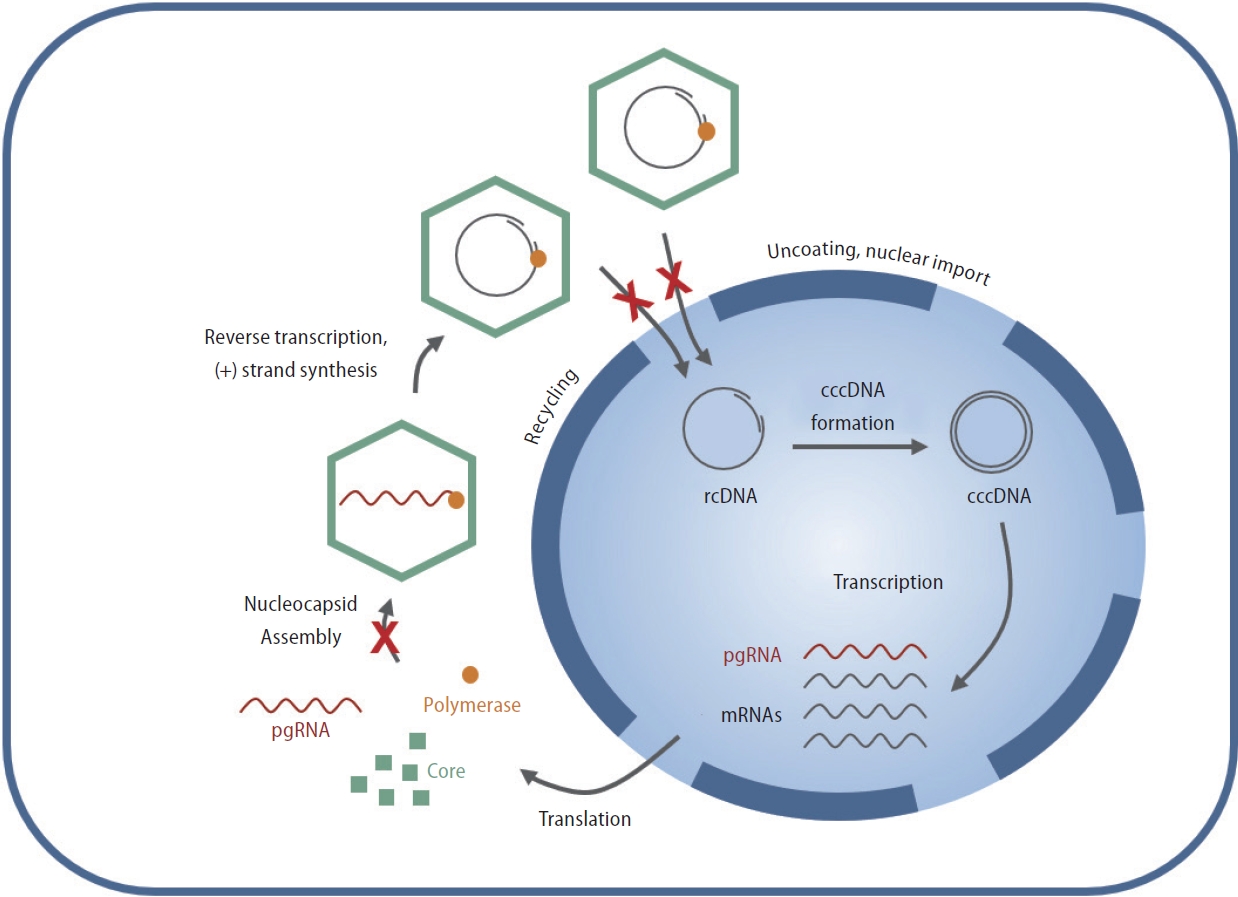
EDP-514 is a novel HBV core protein inhibitor that is in clinical development to treat chronic HBV infection. EDP-514 is a Type II core protein inhibitor that stimulates core assembly and prevents encapsulation of viral pregenomic RNA to block HBV replication resulting in the production of empty capsids (Fig. 1) [17]. EDP-514 potently inhibited encapsidation of viral RNA and production of viral DNA in stable cell lines expressing HBV and prevented HBV cccDNA establishment in cell lines or primary human hepatocytes when present at the time of viral infection. EDP-514 was equally active across HBV genotypes (A to H) and NUC-resistant variants with no cytotoxicity and exhibited a promising safety and pharmacological profile in nonclinical studies. In a first-in-human study of the safety and pharmacokinetics (PK) of oral EDP-514 in healthy volunteers and NUC-suppressed patients with CHB, EDP-514 was well-tolerated, exhibited a PK profile supportive of once daily dosing, and reduced antiviral activity in NUC-suppressed CHB patients [18].
This study evaluated the safety, PK, and antiviral activity of three doses of oral EDP-514 in treatment-naive, viremic patients with either hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive or -negative chronic HBV infection. The inclusion of patients with CHB who are viremic and not currently on treatment provides an opportunity to evaluate initial safety and efficacy for EDP-514 in CHB patients. In addition, the present study would provide supportive data allowing for adequate dose selection and choice of appropriate endpoints for future studies in patients with CHB including those receiving NUC therapy.
The present study was conducted in compliance with the International Conference on Harmonisation-Good Clinical Practices guidelines, the Declaration of Helsinki, and national regulations for clinical trials. The study protocol and informed consent were reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Boards of participating institutions. Written informed consents were obtained from all participants prior to any study procedures. This study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04470388.
This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1b study. The study consisted of three cohorts of viremic patients with CHB not currently on treatment. Each cohort enrolled patients who were randomized to EDP-514 200 mg, 400 mg or 800 mg or placebo once daily for 28 days. A safety follow-up was conducted 2 and 8 weeks after the last dose of study drug. Following dosing for the initial 200 mg cohort with EDP-514,subsequent cohorts were dosed following review of available blinded safety and PK data from the previous cohort.
Men or women aged 18 to 70 years with a body mass index (BMI) of 18 to 35 kg/m2 were eligible if they had HBsAg detectable in serum/plasma at screening and in the most recent HBsAg serum/plasma testing within the past 6 months. At screening, all patients who were HBeAg-positive had a screening serum/plasma HBV DNA level Ōēź20,000 IU/mL or for those who were HBeAg-negative, a screening serum/plasma HBV DNA level Ōēź2,000 IU/mL, and no HBV DNA serum/plasma test values <1,000 IU/mL over the previous 12 months. Patients were not taking prescribed anti-HBV treatment, specifically pegIFN and/or NUC therapy for at least 12 months prior to screening.
Patients were excluded if there was a prior diagnosis of cirrhosis or history of hepatic decompensation (ascites, encephalopathy or variceal hemorrhage) or documented extensive bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis defined by any one of the following: a) Metavir Ōēź3 or Ishak fibrosis score Ōēź4 by a prior liver biopsy; b) FibroSure at screening with a score of Ōēź0.48 and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) to platelet ratio index Ōēź0.45; or c) FibroScan with a result Ōēź9 kPa at screening or within 6 months of screening. Patients also were excluded if they had coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis C virus(HCV), hepatitis D virus(HDV), hepatitis A virus (HAV) or hepatitis E virus (HEV); prior history of hepatocellular carcinoma, evidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, by imaging in the past 3 months or screening alpha-fetoprotein Ōēź50 ng/mL without imaging. Patients also were excluded if there were usage of any prescription medication or St. JohnŌĆÖs Wort or receipt of any vaccine or investigational drugs within 28 days or 5 half-lives prior to the first dose of study drug; or use of nonprescription drugs, dietary or herbal supplements, hormone replacement therapy or cytochrome P450 3A4 or p-glycoprotein inducers or inhibitors within 14 days of study drug.
Full eligibility criteria are provided in Supplementary Material A.
Safety was assessed by physical examination, vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, body temperature), clinical laboratory testing (chemistry, hematology, urinalysis), 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG), and reports of adverse events (AEs). Partial thromboplastin time (PTT), prothrombin time (PT), and international normalized ratio (INR) were measured at each study visit. Patients were assessed at screening for the presence of HAV, HDV, HCV, HEV, and HIV. HBV DNA, HBsAg, hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg), HBeAg, and HBV RNA were assessed at each study visit. The lower limits of quantification for HBV DNA, HBsAg, HBcrAg, HBeAg, and HBV RNA were 1.3 log10 IU/mL, 0.05 IU/ mL, 2.75 log10 U/mL, 0.59 PEI-U/mL, and 1.65 log10 U/mL, respectively. Serious AEs, grade 3 or 4 AEs considered at least possibly related to the study drug, all clinically significant grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) Ōēź2 ├Ś baseline with signs of hepatic decompensation and/or laboratory changes suggestive of worsening hepatic function, ALT elevations >3 ├Ś upper limit of normal (ULN) and Ōēź2 ├Ś baseline, and ALT elevations >10 ├Ś ULN were monitored and managed according to protocol-specific guidelines (Supplementary Material B). AEs and laboratory abnormalities were graded according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 5.0.
Blood samples were collected for PK analysis on Day 1 and Day 28 (or EOT) predose and at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8 hours postdose, and on Days 3, 7, 14, and 21 predose and at 1 to 3 hours postdose and at least 1 hour later but before administration of the next dose.
No formal sample size calculations were performed. A total of 24 viremic CHB patients not currently on treatment were planned to be enrolled, which was considered sufficient to characterize the efficacy, safety, tolerability, and PK for each EDP-514 dose level.
For safety data, no formal statistical analyses were performed. Plasma PK parameters for each dose level were calculated from the concentrations of EDP-514 and its major metabolites measured in predose and postdose plasma samples. For each EDP-514 dose level, descriptive statistics (sample size, arithmetic means, geometric means,standard deviation, % coefficient of variation [CV], % geometric CV, minimum, median, and maximum) were reported. Dose proportionality was assessed using a linear regression. PK parameters included Cmax, Ctrough, and AUC0-last for plasma EDP-514 and its major metabolites.
For each EDP-514 dose cohort, HBV-specific biomarkers were evaluated at baseline, on treatment through Day 28, and at 2 and 8 weeks posttreatment. The primary antiviral endpoint was HBV DNA levels through Day 28. HBV DNA levels were summarized by treatment using descriptive statistics. The percentage of patients with virologic failure/viral breakthrough defined as a confirmed increase in serum/plasma HBV DNA level Ōēź1.0 log10 IU/mL from nadir while receiving EDP-514 would be reported. For all patients with virologic failure, resistance testing was attempted if HBV DNA levels were adequate. Other antiviral parameters assessed over time included HBsAg, HBeAg, HBcrAg, and HBV RNA levels (log10 U/mL). Additionally, HBsAg (reflex anti-HBs) and HBeAg (reflex anti-HBe in patients who were HBeAg-positive at baseline) were assessed serologically at the end of treatment.
The safety population included all patients who received at least one dose of study drug, the PK population consisted of all patients who received active study drug and had any measurable plasma concentration of study drug, and the antiviral population was all patients who received at least one dose of study drug and had any on-treatment HBV DNA data.
Twenty-five patients were randomized to treatment and completed the study. Patients were mostly male (60.0%) and all were Asian. The mean age was 46.3 years (range: 24 to 60 years), and the mean BMI was 25.8 kg/m2 (range: 18.8 to 34.7 kg/m2) (Table 1). Baseline HBV DNA and HBV RNA levels were similar in all EDP-514 treatment groups and placebo. All patients had detectable HBsAg and the baseline levels were variable in all groups. Two patients in the 800 mg group, one patient each in the EDP-514 400 mg and placebo groups, and no patient in the 200 mg group were HBeAg-positive.
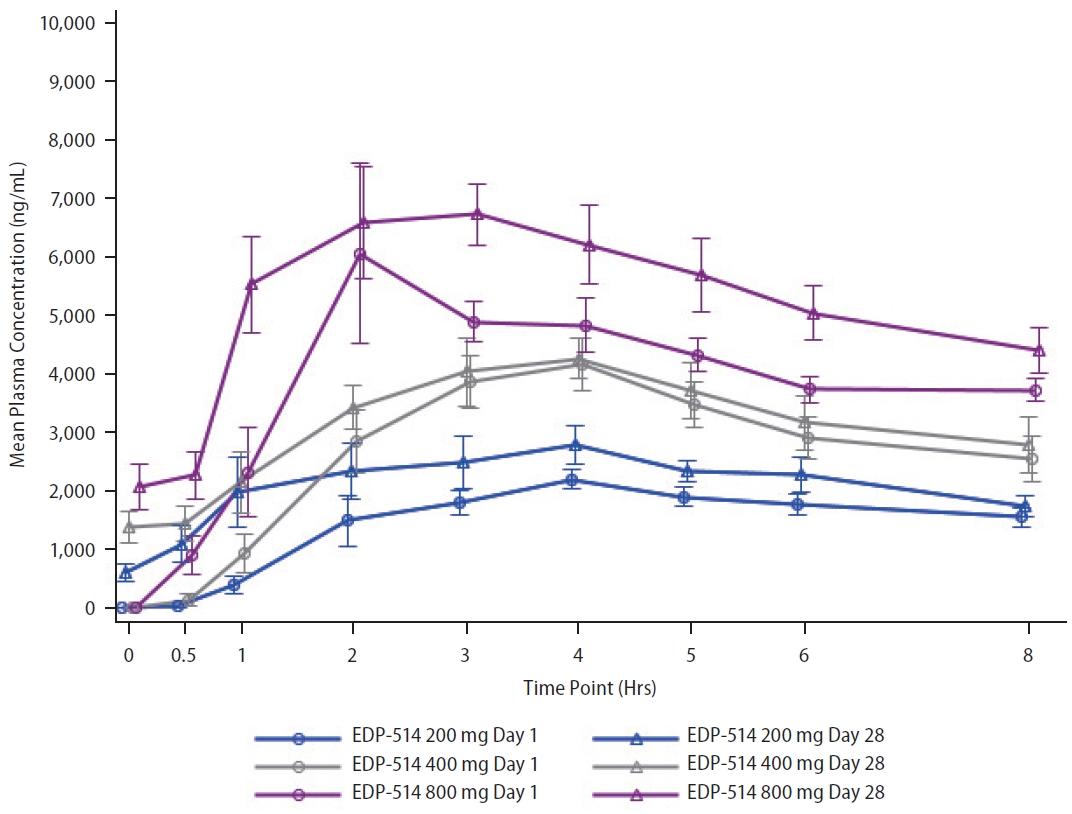
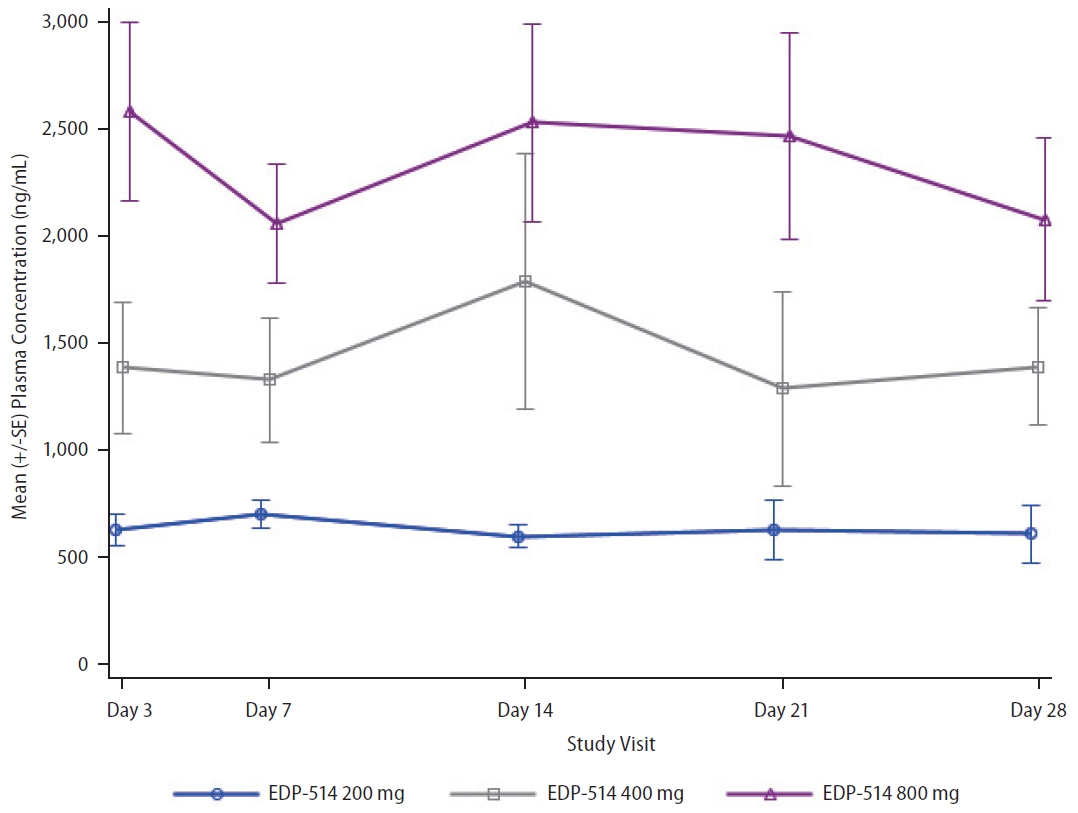
Following once daily oral administration, mean EDP-514 plasma concentrations increased with dose from 200 mg to 800 mg at most time points on Day 1 and Day 28, respectively (Fig. 2). EDP-514 was absorbed within approximately 2.0 to 4.0 hours post dose, with median Tmax between approximately 2.9 to 4.0 hours across all doses on Day 1 and between 2.0 to 3.4 hours across all doses on Day 28. A dose-related increase in EDP-514 exposure (AUClast and Cmax) was observed on both Day 1 and Day 28 (Table 2). Exposures on Day 28 were higher than on Day 1 indicating some evidence for accumulation with multiple daily dosing. The PK profile was supportive of once daily dosing, with median Ctrough at Day 28 ~9-fold for 200 mg, ~20-fold for 400 mg, and ~24-fold for 800 mg doses above the protein-adjusted EC50 (71 ng/mL) (Fig. 3).
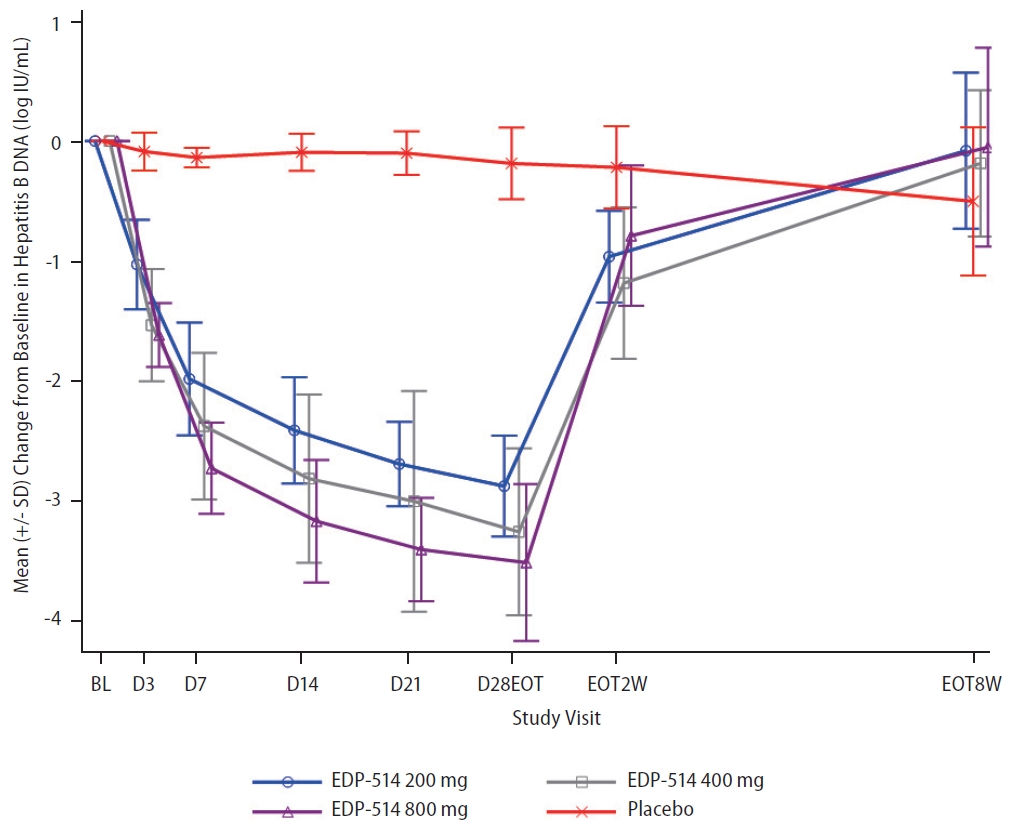
EDP-514 showed both dose- and time-dependent decreases in HBV DNA levels when administered to viremic CHB patients not currently on treatment (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Fig. 1). Mean HBV DNA levels decreased with increasing EDP514 dose at all measurements between Day 3 and Day 28, with the greatest decrease in the EDP-514 800 mg at all time points. At Day 28, mean reductions in HBV DNA levels were ŌĆō2.9, ŌĆō3.3, ŌĆō3.5, and ŌĆō0.2 log10 IU/mL in the 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Once treatment was discontinued, HBV DNA levels returned to near baseline levels for all EDP-514 treatment groups. No virologic failures were observed.
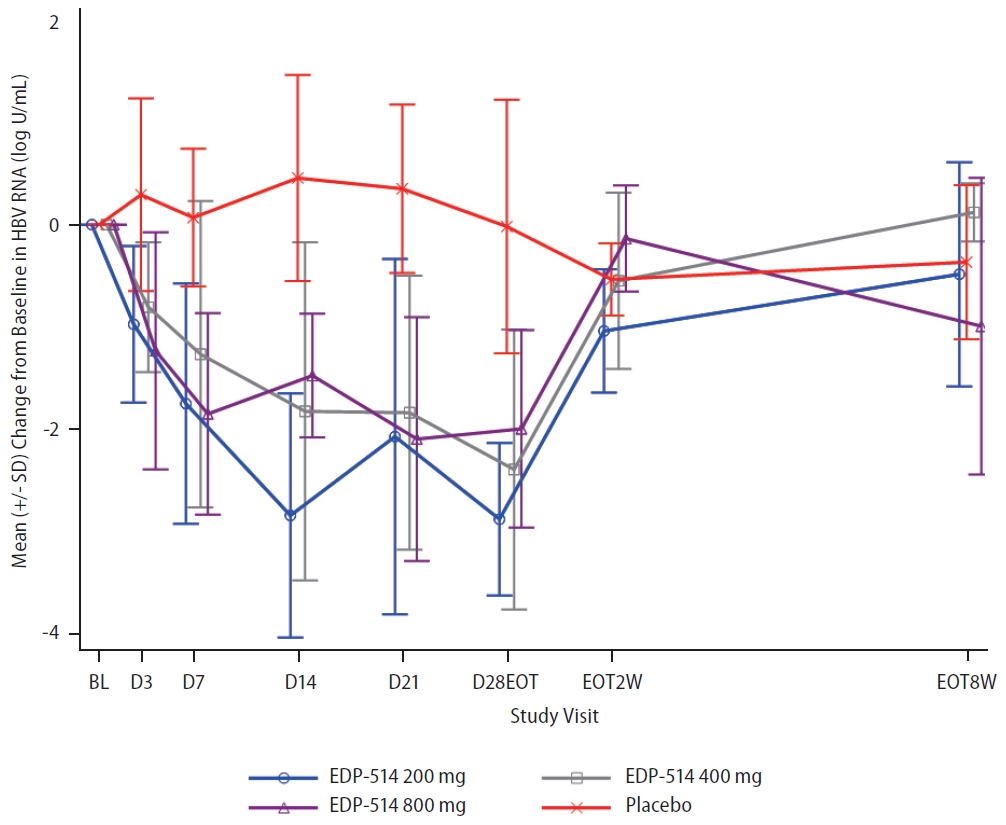
Twenty-two patients had quantifiable HBV RNA levels at baseline (200 mg, n=6; 400 mg, n=5; 800 mg, n=6; placebo, n=5) (Table 1). EDP-514 also showed increasing inhibition of HBV RNA levels with increasing duration of treatment, but no clear dose-dependent effects were observed (Fig. 5 and Supplementary Fig. 2). By Day 28, mean change from baseline for HBV RNA levels was ŌĆō2.9, ŌĆō2.4, ŌĆō2.0, and ŌĆō0.02 log10 U/mL with the 200 mg, 400 mg, 800 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. Following discontinuation of study treatments, HBV RNA levels increased to approach baseline levels in all treatment groups.
No clinically meaningful changes from baseline were observed in patients with quantifiable levels at baseline for HBsAg, HBeAg (n=4) or HBcrAg (n=21) (Table 1 and Supplementary Figs. 3 and 4).
No discontinuations, serious AEs or deaths were reported with EDP-514 treatment. Overall, nine patients reported treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) (Table 3). All TEAEs were mild or moderate, and none were severe. No individual TEAE occurred more than once with any dose of EDP-514. One patient in the placebo group experienced gastrointestinal disorder, prolonged activated PTT and increased INR that were considered possibly related to placebo therapy. Clinical laboratory findings were generally normal with no clinically relevant changes in the EDP-514 treatment groups except for one patient who experienced prolonged activated PTT and increased INR and one patient who experienced prolonged PT, both in the EDP-514 200 mg group. Mean change from baseline of ALT, AST, gamma glutamyl transferase, bilirubin, triglycerides, and cholesterol are shown in Supplementary Figures 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10. No ALT elevations indicative of HBV viral flares was observed in the study. No clinically relevant changes in the physical examination, vital signs or ECG were observed with EDP-514.
The HBV core protein plays an indispensable role in the viral life cycle by packaging the viral pregenomic RNA along with the viral polymerase into capsids. This packaging enables the reverse transcription of pregenomic RNA into relaxed circular DNA to produce the infectious form of the viral genome. The core protein itself also displays limited sequence polymorphisms across HBV genotypes, which coupled with the critical role of the protein in producing infectious virus and sustaining the viral cccDNA pool, makes it an important target for novel antivirals to treat HBV infection [19,20].
In this phase 1b study of EDP-514, positive data were obtained from all three dose cohorts in patients with viremic CHB infection not currently treated with pegIFN or NUC. The incidence of mild or moderate AEs was similar between EDP-514 groups and placebo with no dose-related increase in AEs. No AEs occurred more than once in any patient, and no patients discontinued the study for an AE. EDP-514 displayed a PK profile demonstrating a dose-related increase in exposure and supporting once-daily dosing, with median Ctrough at Day 28 ~9-fold for 200 mg, ~20-fold for 400 mg, and ~24-fold for 800 mg doses above the protein-adjusted EC50 (71 ng/mL). Marked reductions in HBV DNA and HBV RNA levels occurred rapidly with all three EDP-514 doses compared with placebo, and levels returned to baseline after discontinuing study treatment. Overall, these results were consistent with a previous study of EDP-514 in healthy patients [18]. At Day 28 in the study reported here, mean reductions in HBV DNA levels were ŌĆō2.9, ŌĆō3.3, and ŌĆō3.5 with the 200 mg, 400 mg, and 800 mg doses of EDP-514, and mean reductions in HBV RNA levels were ŌĆō2.9, ŌĆō2.4, and ŌĆō2.0. The lack of dose proportional response in HBV RNA may be due to potentially attaining the maximal effect in HBV RNA reduction with 200 mg, the small number of patients evaluated, or that the majority of patients were HBeAg negative whose HBV RNA levels are typically low [21]. As a whole, other studies of drug therapy for treatment-naive patients with HBV reported similar findings [13,15,22-24]. While the clinical significance of circulating HBV RNA remains unknown, it has been suggested HBV RNA levels may be a marker for treatment response and cccDNA activity in patients with chronic HBV infection [25-29]. This viral biomarker is one that remains largely unchanged with short term NUC therapy and highlights the differentiated mechanism of action of EDP-514. The addition of a potent core protein inhibitor such as EDP-514 to NUC treatment could potentially lower HBV DNA and RNA levels more rapidly and profoundly, which may result in a lower incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. The addition of an early generation core protein inhibitor vebicorvir to patients taking NUCs further suppressed HBV DNA and HBV RNA more than with NUCs alone [24,30]. In this manner, an EDP-514 and NUC combination treatment may have clinical benefit in treatment-naive highly viremic HBeAg-positive patients where NUC treatment takes longer than a year to achieve undetectable HBV DNA levels and NUC-treated patients with residual HBV DNA and HBV RNA are detectable in circulation by highly sensitive assays.
In the present study of 4 weeks dosing of EDP-514, a reduction in HBsAg was not observed. Recently, another core protein inhibitor ALG-000184 demonstrated an HBsAg reduction beginning at approximately 4 weeks to 36 weeks of treatment [31]. According to the present study, EDP-514 appears to have a similar potency of HBV DNA and HBV RNA suppressions when compared with ALG-000184 (mean HBV DNA and HBV RNA reductions of 3.8 log10 IU/mL and 1.9 log10 copies/mL after 4 weeks of treatment, respectively) [32]. Whether a longer treatment duration of EDP-514 than 4 weeks could also show an HBsAg reduction would be interesting to explore in the future.
Limitations to this study included a small sample size, a short treatment duration, and limited diversity in the patient population. However, this study was specifically designed to evaluate safety, PK, and antiviral activity in a previously untreated population with CHB and help to confirm results from an earlier study that evaluated EDP-514 in healthy subjects and NUC-suppressed patients [18]. Studies enrolling larger numbers of more diverse patients with HBV infections with longer treatment duration and follow-up will be necessary to further elucidate the role of EDP-514 for treating CHB.
Overall, these results demonstrate that EDP-514, a novel oral HBV core protein inhibitor, was well tolerated and had a favorable safety profile for viremic, treatment-naive CHB patients. In this population of patients with chronic HBV infection, EDP-514 for 28 days resulted in a mean reduction in both HBV DNA and HBV RNA of 2 to 3.5 log10 that is highly suggestive of antiviral activity as a potent HBV core protein inhibitor. These results encourage continued investigation of EDP-514 for viremic, treatment-naive patients with CHB.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank all volunteers, investigators and study personnel who participated in the clinical studies. The authors acknowledge Jason Yu for assistance with preparation of figures, Michael Vaine, PhD, for critical review of the manuscript, and editorial assistance of Richard S. Perry, PharmD, which were supported by Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Watertown, MA.
The study was funded by Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and was designed in conjunction with the authors. Enanta was involved in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, and writing of the report. All authors had full access to all the data in the study, participated in drafting and editing the manuscript and were responsible for the decision to submit for publication.
Enanta Clinical Trial Number: EDP 514-002
FOOTNOTES
AuthorsŌĆÖ contribution
GDLR, AA, EL, ALC contributed to data analysis, interpretation, and manuscript preparation. All other authors conducted the clinical study and contributed to data interpretation. All authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Man-Fung Yuen: Advisory/consultant for AbbVie, Aligos Therarpeutics, AiCuris, Antios Therapeutics, Assembly Biosciences, Arbutus Biopharma, Bluejay Therapeutics, Clear B Therapeutics, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Finch Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Janssen, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Hoffmann-La Roche, Vir Biotechnology; grant/research supports from AbbVie, Assembly Biosciences, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Arbutus Biopharma, Bristol Myer Squibb, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Fujirebio Incorporation, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Immunocore, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Hoffmann-La Roche; sponsored lectures for Menarini, Gilead Sciences, Janssen.
Wan-Long Chuang: Consultant for Gilead Sciences, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, Vaccitech, PharmaEssentia; Speaker for Gilead Sciences, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, PharmaEssentia; Sponsored lectures for Gilead Sciences, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, PharmaEssentia.
Cheng-Yuan Peng: Advisory board for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences and Hoffman-La Roche.
Wen-Juei Jeng: Speaker for Bristol Myers Squibb and Gilead Sciences; Grants from Chang Gung Medical Foundation; National Science Council, Taiwan.
Wei-Wen Su: Speaker for Gilead Sciences, Eisai, AbbVie.
Ting-Tsung Chang: Nothing to disclose.
Chi-Yi Chen: Nothing to disclose.
Yao-Chun Hsu: Consultant for Gilead Sciences; sponsored lectures for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Novartis; grants from Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan, E-Da Hospital, Taiwan, Tomorrow Medical Foundation, and Gilead Sciences.
Annie L. Conery, Alaa Ahmad, Ed Luo, Guy De La Rosa: Employee and stockholder for Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Watertown, MA at the time the work was performed.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplementary material is available at Clinical and Molecular Hepatology website (http://www.e-cmh.org).
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā1.
Change in baseline in HBV DNA (log IU/mL) in individual patients. HBV, hepatitis B virus.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā2.
Change in baseline in HBV RNA (log U/mL) in individual patients. HBV, hepatitis B virus.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā3.
Change in baseline in HBcrAg (log U/mL) in individual patients. HBcrAg, hepatitis B core-related antigen.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā4.
Change in baseline in HBsAg (IU/mL) in individual patients. HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā5.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in ALT over time. ALT, alanine aminotransferase.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā6.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in AST over time. AST, aspartate aminotransferase.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā7.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in Gamma Glutamyl Transferase over time.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā8.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in Bilirubin over time.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā9.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in Triglycerides over time.
Supplementary┬ĀFigure┬Ā10.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in Cholesterol over time.
Figure┬Ā1.
Mechanism of action of core inhibitors in the HBV life cycle. EDP-514 is a type II core protein inhibitor that suppresses HBV replication by modulating the kinetics of capsid assembly and disassembly. This prevents both pgRNA encapsidation and delivery of rcDNA to the nucleus, resulting in suppression of rcDNA and de novo cccDNA formation. HBV, hepatitis B virus; rcDNA, relaxed circular DNA; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; pgRNA, pregenomic RNA; mRNAs, messenger RNAs.
Figure┬Ā4.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in HBV DNA concentrations over time. HBV, hepatitis B virus.
Figure┬Ā5.
Mean (standard deviation [SD]) change from baseline in HBV RNA concentrations over time. HBV, hepatitis B virus.
Table┬Ā1.
Baseline characteristics
| Characteristic |
EDP-514 |
Placebo (n=6)ŌĆĀ | Total (n=25) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg (n=6)ŌĆĀ | 400 mg (n=6)ŌĆĀ | 800 mg (n=7)ŌĆĀ | |||
| Age (yr)* | 48.7┬▒4.8 | 42.8┬▒6.6 | 47.9┬▒8.0 | 45.5┬▒12.0 | 46.3┬▒8.0 |
| Male, n (%) | 4 (66.7) | 4 (66.7) | 6 (85.7) | 1 (16.7) | 15 (60.0) |
| Weight (kg)* | 70.9┬▒12.2 | 73.2┬▒7.7 | 82.4┬▒15.7 | 60.3┬▒13.7 | 72.1┬▒14.5 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2)* | 24.8┬▒3.8 | 26.4┬▒5.0 | 28.9┬▒4.0 | 22.9┬▒3.7 | 25.8┬▒4.5 |
| Asian, n (%) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 7 (100) | 6 (100) | 25 (100) |
| HBV Genotype | |||||
| ŌĆāB | 6 (100) | 5 (83.3) | 5 (71.4) | 5 (83.3) | 21 (84) |
| ŌĆāC | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 2 (28.6) | 1 (16.7) | 4 (16) |
| HBV DNA levels (log10 IU/mL)* | 4.57┬▒0.75 | 5.37┬▒1.59 | 5.54┬▒1.70 | 4.91┬▒1.38 | 5.12┬▒1.38 |
| HBV RNA >LLOQ, n (%) | 6 (100) | 5 (83.3) | 6 (85.7) | 5 (83.3) | 22 (88) |
| HBV RNA levels (log10 U/mL) | 3.22┬▒0.95 | 3.58┬▒2.30 | 3.77┬▒2.17 | 3.34┬▒1.97 | 3.49┬▒1.82 |
| HBsAg levels (IU/mL)* | 1,384.25┬▒1,316.87 | 23,874.62┬▒46,178.28 | 6,972.28┬▒14,771.62 | 2,601.11┬▒4,827.76 | 8,638.63┬▒24,189.61 |
| HBeAg positive, n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (16.7) | 2 (28.6) | 1 (16.7) | 4 (16) |
| HBeAg levels (PEI-U/mL)* | 0.30┬▒0.00 | 398.39┬▒975.14 | 45.24┬▒118.02 | 11.21┬▒26.73 | 111.04┬▒478.74 |
| HBcrAg >LLOQ, n (%) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 5 (71.4) | 4 (66.7) | 21 (84) |
| HBcrAg levels (log10 U/mL)* | 3.6┬▒0.7 | 4.9┬▒1.9 | 4.1┬▒2.6 | 3.5┬▒2.4 | 4.0┬▒2.0 |
Table┬Ā2.
Geometric mean plasma PK parameters for EDP-514 at Day 1 and Day 28
Table┬Ā3.
Incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) with EDP-514
Abbreviations
ALT
alanine aminotransferase
AST
aspartate aminotransferase
BMI
body mass index
CHB
chronic hepatitis B
CV
coefficient of variation
cccDNA
covalently closed circular DNA
CpAMs
core protein allosteric modulators
EC50
concentration that is 50% effective
HAV
hepatitis A virus
HBcrAg
hepatitis B core-related antigen
HBsAg
hepatitis B surface antigen
HBeAg
hepatitis B e antigen
anti-HBs
hepatitis B surface antibody
HBV
hepatitis B virus
HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
HDV
hepatitis D virus
HEV
hepatitis E virus
NUC
nucleos(t)ide analogue
PT
prothrombin time
PTT
partial thromboplastin time
pegIFN
pegylated interferon
TEAE
treatment-emergent adverse event
ULN
upper limit of normal
REFERENCES
1. Prifti GM, Moianos D, Giannakopoulou E, Pardali V, Tavis JE, Zoidis G. Recent advances in hepatitis B treatment. Pharmaceuticals(Basel) 2021;14:417.



2. World Health Organization (WHO). World Health Organization Hepatitis B-Key Facts. WHO web site, <https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b>. Accessed 14 Mar 2021.
3. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017;67:370-398.


4. Terrault NA, Lok ASF, McMahon BJ, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018;67:1560-1599.




6. Tsounis EP, Tourkochristou E, Mouzaki A, Triantos C. Toward a new era of hepatitis B virus therapeutics: The pursuit of a functional cure. World J Gastroenterol 2021;27:2727-2757.



7. Gish RG, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Given BD, Lai CL, Locarnini SA, et al. Synthetic RNAi triggers and their use in chronic hepatitis B therapies with curative intent. Antiviral Res 2015;121:97-108.


8. Zoulim F, Durantel D. Antiviral therapies and prospects for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2015;5:a021501.



9. Park H, Jeong D, Nguyen P, Henry L, Hoang J, Kim Y, et al. Economic and clinical burden of viral hepatitis in California: A population-based study with longitudinal analysis. PLoS One 2018;13:e0196452.



10. Sbarigia U, Kariburyo F, Sah J, Colasurdo J, Xie L, Katz EG, et al. Evaluating the effect of standard of care treatment on burden of chronic hepatitis B: A retrospective analysis of the United States Veterans population. Adv Ther 2020;37:1156-1172.




11. Dandri M, Petersen J. cccDNA Maintenance in chronic hepatitis B - Targeting the matrix of viral replication. Infect Drug Resist 2020;13:3873-3886.


12. Testoni B, Durantel D, Zoulim F. Novel targets for hepatitis B virustherapy. Liver Int 2017;37 Suppl 1:33-39.



13. Zhang X, Cheng J, Ma J, Hu Z, Wu S, Hwang N, et al. Discovery of novel hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid assembly inhibitors. ACS Infect Dis 2019;5:759-768.



14. Yuen MF, Agarwal K, Gane EJ, Schwabe C, Ahn SH, Kim DJ, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral effects of ABI-H0731, a hepatitis B virus core inhibitor: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;5:152-166.


15. Yuen MF, Zhou X, Gane E, Schwabe C, Tanwandee T, Feng S, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of RO7049389, a core protein allosteric modulator, in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;6:723-732.


16. Zoulim F, Lenz O, Vandenbossche JJ, Talloen W, Verbinnen T, Moscalu I, et al. JNJ-56136379, an HBV capsid assembly modulator, is well-tolerated and has antiviral activity in a phase 1 study of patients with chronic infection. Gastroenterology 2020;159:521-533.e9.


17. Vaine M, Dellisola V, Clugston S, Cao H, Gao X, Kass J, et al. FRI191-EDP-514, a novel HBV core inhibitor with potent antiviral activity both in vitro and in vivo. J Hepatol 2019;70:e474-e475.

18. Feld JJ, Lawitz E, Nguyen T, Lalezari J, Hassanein T, Martin P, et al. EDP-514 in healthy subjects and nucleos(t)ide reverse transcriptase inhibitor-suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. Antivir Ther 2022;27:13596535221127848.



19. Levrero M, Pollicino T, Petersen J, Belloni L, Raimondo G, Dandri M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2009;51:581-592.


20. Chain BM, Myers R. Variability and conservation in hepatitis B virus core protein. BMC Microbiol 2005;5:33.



21. Mak LY, Cloherty G, Wong DK, Gersch J, Seto WK, Fung J, et al. HBV RNA profiles in patients with chronic hepatitis B under different disease phases and antiviral therapy. Hepatology 2021;73:2167-2179.



22. Gane EJ, Schwabe C, Berliba E, Tangkijvanich P, Jucov A, Ghicavii N, et al. Safety, antiviral activity and pharmacokinetics of JNJ-64530440, a novel capsid assembly modulator, as 4 week monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virusinfection. J Antimicrob Chemother 2022;77:1102-1110.




23. Zhang H, Hu Y, Wu M, Liu J, Zhu X, Li X, et al. Randomised clinical trial: safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of HS-10234 versus tenofovir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2021;53:243-252.


24. Sulkowski MS, Agarwal K, Ma X, Nguyen TT, Schiff ER, Hann HL, et al. Safety and efficacy of vebicorvir administered with entecavir in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2022;77:1265-1275.


25. Giersch K, Allweiss L, Volz T, Dandri M, L├╝tgehetmann M. Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity. J Hepatol 2017;66:460-462.


26. Jansen L, Kootstra NA, van Dort KA, Takkenberg RB, Reesink HW, Zaaijer HL. Hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA is present in virions in plasma and is associated with a response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a and nucleos(t)ide analogues. J Infect Dis 2016;213:224-232.


27. Tsuge M, Murakami E, Imamura M, Abe H, Miki D, Hiraga N, et al. Serum HBV RNA and HBeAg are useful markers for the safe discontinuation of nucleotide analogue treatments in chronic hepatitis B patients. J Gastroenterol 2013;48:1188-1204.



28. van B├Čmmel F, Bartens A, Mysickova A, Hofmann J, Kr├╝ger DH, Berg T, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA levels as an early predictor of hepatitis B envelope antigen seroconversion during treatment with polymerase inhibitors. Hepatology 2015;61:66-76.


29. Wang J, Shen T, Huang X, Kumar GR, Chen X, Zeng Z, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound. J Hepatol 2016;65:700-710.


30. Yuen MF, Agarwal K, Ma X, Nguyen TT, Schiff ER, Hann HL, et al. Safety and efficacy of vebicorvir in virologically suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2022;77:642-652.


31. Hou J, Yanhua D, Junqi N, XieŌĆÖer L, Massetto B, Le K, et al. ALG000184, a capsid assembly modulator, dosed with entecavir for up to 28 weeks is well tolerated and resulted in substantial declines in surface antigen levels in untreated hepatitis B e antigen positive subjects with chronic hepatitis. Paper presented at: 2023 European Association for the Study of the Liver; 2023; Vienna, Austria. Poster LBP-18.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 992 View
- 69 Download
- ORCID iDs
-
Annie L. Conery

https://orcid.org/0009-0009-1400-3468 - Related articles



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement1
Supplement1 Print
Print



