| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 18(4); 2012 > Article |
ABSTRACT
Because of the anatomical position and its unique vascular system, the liver is susceptible to the exposure to the microbial products from the gut. Although large amount of microbes colonize in the gut, translocation of the microbes or microbial products into the liver and systemic circulation is prevented by gut epithelial barrier function and cleansing and detoxifying functions of the liver in healthy subjects. However, when the intestinal barrier function is disrupted, large amount of bacterial products can enter into the liver and systemic circulation and induce inflammation through their receptors. Nowadays, there have been various reports suggesting the role of gut flora and bacterial translocation in the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease and portal hypertension. This review summarizes the current knowledge about bacterial translocation and its contribution to the pathogenesis of chronic liver diseases and portal hypertension.
The liver receives a blood supply both from the portal vein and the hepatic artery. Portal venous blood, which is derived from the mesenteric veins, constitutes approximately 75% of total blood flow to the liver.1 Because large amount of microbes colonize in the gut, blood from the intestine contains not only products of digestion but also microbial products. Therefore, the liver, the initial site of filtration of gut-derived products, is susceptible to the exposure to the microbial products from the gut, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS).1
In normal condition, translocation of the microbial products from the gut to extraintestinal space, including systemic circulation, is effectively prevented by our defense mechanisms: the barrier function of the gut and cleansing and detoxifying function of the liver.2 However, disruption of these defense mechanisms can lead bacterial translocation to extraintestinal space and aberrant activation of immune system, which can trigger harmful or chronic inflammations in the liver.3
The importance of bacterial translocation in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease has been shown in various previous studies: impairment of the function of intestinal tight junction4-7 and bacterial proliferation8,9 by alcohol and/or its metabolites, such as acetaldehyde, enhance bacterial translocation into the liver, which induce activation of immune cells, including Kupffer cells, to release various pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (Fig. 1).10,11 Furthermore, various studies suggested that bacterial translocation also plays an important role in the development and progression of other types of liver diseases.12-16 Endotoxemia is frequently found in patients with cirrhosis, and the degree of endotoxemia is correlated with the degree of liver failure.17,18 In this review, we highlight the current knowledge about bacterial translocation and its contribution to the pathogenesis of chronic liver diseases and portal hypertension.
LPS, glycolipids derived from the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, is a potent activator of immune responses: very tiny amount of LPS can induce the manifestations of septic shock in human.19,20 Fortunately, the mammals have effective defensive mechanisms to prevent this harmful effect of LPS. In healthy animals, LPS is cleared from the circulation within a few minutes after intravenous injection.21,22 Peripheral blood endotoxin concentration is significantly lower than portal venous endotoxin concentration, even in patients with liver cirrhosis.23
These defensive mechanisms mainly depend on the barrier functions of the gut and the detoxifying capacity of the liver.24 The gut epithelium acts as a first-line barrier to the gut microbes and prevents exposure of the gut microbes to the host immune system. The epithelial cells maintain barrier integrity by microvilli, tight junctions, and production of antimicrobial peptides.25-27 These barrier systems of intestinal epithelial cells prevent translocation of most of microbial products of gut and only tiny amount of microbial products can reach the liver in healthy condition.28
The liver plays a central role for prevention of translocation of gut-derived microbial products to the systemic circulation by cleansing and detoxifying microbial products.29 Microbial products in the portal venous blood eventually reach to the sinusoids in the liver, which contain diverse immunologically active cells, including the Kupffer cells, liver dendritic cells, T cells, natural killer T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.28 Not only these immune cells, but also liver nonparenchymal cells such as hepatic stellate cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, express the LPS receptor and remove this molecule to protect the systemic circulation from the endotoxemia.30 A previous animal study demonstrated that about 40-50% of intravenously administered LPS was quickly removed by the liver, suggesting the role of the hepatic uptake and detoxification in the immune homeostasis.31,32 Beside the LPS uptake, several other mechanisms also play a role in preventing significant immune response to LPS, including LPS-binding molecules, enzymes which degrade the lipid A moiety of LPS to decrease its activity, and LPS neutralization by serum lipoproteins.33-36 Furthermore, the liver usually tolerates bacterial products to avoid harmful responses.28 The hepatic immune system, including Kupffer cells, NK cells, NKT cells, T cells, and B cells, strictly regulate the liver immune system including liver tolerance.3
It is well known that bacterial translocation is closely associated with the development of complications of liver cirrhosis, such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, the hyperdynamic circulatory state, and hepatic encephalopathy.37-39 Bacterial translocation is defined as the migration of bacteria or bacterial products from the gut to the extraintestinal space.40 Increased intestinal permeability induced by disruption of the intestinal epithelial barrier function contributes to the development of bacterial translocation.3,28,41 In addition, intestinal bacterial overgrowth and changes in the composition of bacterial flora in the gut can promote bacterial translocation.39,40,42
The gut epithelium plays an important role in the immune homeostasis in the gut by acting as the first barrier against the bacterial translocation of gut microbiota.43-44 Because gut barrier system by intestinal epithelial cells prevent translocation of large amounts of bacteria and bacterial products from the gut, only very small amount of them can reach the liver in a healthy state.28 However, this effective gut barrier function can be disrupted by various pathological conditions and this disruption leads to bacterial translocation.3,28,41 For example, alcohol can play a role in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease by disrupting the gut barrier function: alcohol itself as well as its metabolite, acetaldehyde, inhibit tight junction protein expression;44,45 alcohol can impair microtubule cytoskeleton in intestinal epithelial cells by inducing nitric oxide;46 and transepithelial electrical resistance is reduced in alcohol-exposed colon epithelial cells, which leads to impaired barrier function.24 In addition, liver-derived inflammatory cytokines can further increase gut permeability by disruption of gut epithelial tight junctions.47
Bile acid secretion is decreased in patients with liver cirrhosis and this could lead bacterial overgrowth and compositional change in the intestine in these patients.48,49 In addition, the fact that liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension could impair intestinal motility may also contribute to the development of intestinal bacterial overgrowth.50 Previous study suggested that gastrointestinal transit is delayed in patients with liver cirrhosis and this delay could be improved with antibiotic therapy.51 Several studies suggested that the duration of the migrating motor complex are prolonged and the frequency of clustered contractions are increased in patients with liver cirrhosis, and these small intestinal motility disturbances are related with the severity of liver failure in these patients.52,53
The composition of the intestinal bacteria is influenced by the environment, diet, and host factors.25,54,55 It could be changed by certain diseases, including liver cirrhosis. In liver cirrhosis, the normal intestinal microbial community is disrupted due to the decrease in gastric acidity, intestinal motility, and biliary secretions.56,57 Actually, a previous analysis of fecal microbiome in patients with cirrhosis suggested that fecal microbial communities are significantly different when compared to those in healthy individuals: increased prevalence of pathogenic bacteria, such as Enterobacteriaceae and Streptococcaceae, and decreased beneficial Bifidobacteria and Lachnospiraceae were noted in patients with liver cirrhosis.58,59 A previous animal study also reported the increased aerobic/anaerobic bacterial ratio in mice with liver fibrosis.60 In addition, liver cirrhosis induced by CCl4 in rats was also associated with high levels of Enterobacteriaceae.61 They also suggested that treatment with antibiotics or probiotics lead decrease in Enterobacter as well as increase in Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which in turn lead to decreased systemic endotoxin levels and improve in the liver function.61 Similarly, treatment with probiotics or antibiotics in patients with liver cirrhosis reduced the prevalence of bacterial infection and hepatic enephalopathy62-64 and partially reversed the hyperdynamic circulatory state in these patients.65 A very recent study suggested that modulation of the intestinal microbiota is a critical determinant of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) as well as multiple other aspects of metabolic syndrome.66
In normal condition, only very small amount of bacteria or bacterial products, such as LPS, can enter the liver by the action of gut barrier function, where they are sensed and cleared by immune cells, particularly by Kupffer cells. However, in the pathologic condition with disrupted gut barrier function, the entry of bacteria and bacterial products to the liver is increased and homeostasis of the gut-liver axis is impaired, which eventually induce activation of liver immune cells, particularly Kupffer cells, to produce pro-inflammatory mediators.67-69 Previous studies suggested that bacterial translocation and resultant Kupffer cell activation are the main mechanisms of the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease.70 This suggestion is supported by the finding in animal models that alcoholic liver disease could be attenuated by gut sterilization with antibiotics or Kupffer cell elimination.71-73 Translocated bacterial products activate the hepatic immune cells through pattern recognition receptors, such as toll-like receptors (TLRs) and NOD-like receptors (NLRs). Recent studies suggested that TLR4 in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) also responds to LPS to activate Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) kinase and NF╬║B.74 Oxidative stress induced by alcohol and its metabolites is also involved in the induction of liver fibrosis by sensitizing HSC to LPS.75,76
TLRs, a family of pattern-recognition receptors, are transmembrane proteins originally identified in mammals on the basis of their homology with Toll, a Drosophila receptor that contributes to development in the embryo, and the production of antimicrobial peptides against microorganism invasion in the adult fly.77,78 TLRs recognize pathogen-derived molecules-i.e., structural components unique to bacteria, fungi, and virus-and activate inflammatory responses including cytokine and type I interferon (IFN) production in response to this recognition.79 Previous studies suggested that hepatic non-immune cells, including HSCs and endothelial cells, respond to bacterial products through TLRs.3,28 Until now, ten TLRs have been identified in humans,80 while TLR4 was the first identified isoform that responds primarily to LPS.79
TLR4 plays a pivotal role in the activation of innate immune responses to LPS.81,82 TLR4 cannot directly bind to LPS and therefore, co-receptors, CD14 or MD-2, are needed for LPS binding to TLR4 and TLR4 activation.83-85 Two pathways for downstream signaling of TLR4 activation are demonstrated: MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent pathways.86 In the MyD88-dependent signaling pathway, association of the intracellular TLR domain of TLR4 with the adapter molecule MyD86 through TRAM, which results in downstream activation of the IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1)/4/tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) complex and further activation of the I╬║B kinase (IKK) kinase complex that phosphorylates I╬║B to allow nuclear translocation of NF-╬║B.87 NF-╬║B binding to the NF-╬║B responsive element in the promoter region of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes results in the production of TNF╬▒, and other pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.88 MAP kinases including c-JNK and p38 activate transcription factor AP-1. Activation of these transcription factors induces transcription of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-╬▒, IL-6, and IL-1╬▓.89 Except for TLR3, all TLRs activate the MyD88-dependent pathway. In the MyD88-independent signaling pathway, recruitment of the adaptor TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-╬▓ (TRIF), TRAF6, to TLR4 and TANK-binding kinase (TBK)/IKK╬Ą phosphorylation induce phosphorylation of the interleukin regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), which in turn leads to IRF3 nuclear translocation and induction of type-I IFNs.88,90 Both MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent pathways are activated after LPS-TLR4 interaction, while only one of these pathways are activated in other TLRs.
The importance of the TLR4 signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease is evidenced by the previous animal study showing that decreased steatosis and inflammation and significantly reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including serum TNF-╬▒ and IL-6, in the TLR4-deficient mice after chronic alcohol feeding.91 In addition, a previous study suggested that chronic alcohol exposure not only results in immune cell activation, but also sensitizes cells to LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signals by reduction in the expression of IRAK-M, a negative regulator of TLR4 activation.67 A critical role of LPS and TLR4 is suggested also in the pathogenesis of NAFLD: lipid accumulation, inflammation and fibrosis were significantly attenuated in TLR4 knockout mice after methionine choline-deficient diet.14,92
Recent studies suggested that TLR4 signaling can be activated not only by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), but also by some endogenous ligands, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), from cellular compartments which are released from damaged cells or tissues.79 DAMPs-induced TLR4 activation also can induce inflammation, which is called sterile inflammation because this inflammation is caused without infections.93 Therefore, DAMPs as well as PAMPs play a role in the pathogenesis and progression of liver diseases through activation of TLR signaling.3
NLRs is the members of the pattern recognition receptor family and they forms cytoplasmic multi-protein complexes, inflammasomes, with pro-caspase-1, the effector molecule, with or without the adapter molecule, such as the apoptosis-associated speck like CARD-domain containing protein (ASC).94-96 Inflammasomes are activated by sensing PAMPs or DAMPs via NLRs,97,98 and leads to activation of inactive pro-caspase-1 into active caspase-1, which in turn, induce cleavage of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including pro-interleukin (IL)-1╬▓ and pro-IL-18, into active forms of IL-1╬▓ and IL-18, respectively.94,99 IL-1╬▓ is a pro-inflammatory cytokine and plays a central role in regulation of inflammation by binding to the IL-1 receptor. IL-18 induces activation and IFN╬│ production of NK cells.100
Alcohol can disrupt the intestinal epithelial cell tight junctions to impair the gut barrier function, which induce bacterial translocation and elevated endotoxin levels in the portal blood flow.105-107 Impaired gut permeability was also reported in NAFLD.12,16 A recent study suggested that modulation of the intestinal microbiota through multiple inflammasome components is a critical determinant of NAFLD/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis progression as well as multiple other aspects of metabolic syndrome such as weight gain and glucose homeostasis.66 In liver cirrhosis, the changes in intestinal motility and subsequent alteration of microflora content, decreased mucosal integrity, and suppressed immunity in hepatic fibrosis contribute to failure of the intestinal mucosal barrier with subsequent increases in bacterial translocation and LPS levels in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.40,108-112
Consistently, plasma level of LPS is increased in patients with chronic liver diseases by viral hepatitis,31,112 alcohol,114,115 and NAFLD.116 Liver injury can be prevented by elimination of gram-negative microflora with Lactobacillus or antibiotics or Kupffer cell depletion with gadolinium chloride.71,72,117 Therefore, LPS-induced Kupffer cell activation is currently considered as a main mechanism for pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease.118 Similarly, genetically obese rodents showed increased sensitivity to endotoxin119 and LPS challenge enhance the liver injury and induce inflammatory cytokine in mice with NAFLD.120 Some studies suggested that gut flora contribute to the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis in mice with fatty liver121 and treatment with probiotics reduce hepatic injury in obese mice.122 Furthermore, a previous study suggested that LPS-induced inflammation is involved in the pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis.123 Intraperitoneal administration of LPS can increase portal pressure124 and increased portal pressure can increase intestinal permeability.23,125,126 Bacterial translocation and increased production of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide further impair contractility of mesenteric vessels in patients with cirrhosis, which could further increase portal pressure.127,128
A previous study reported that liver fibrosis and inflammation were significantly reduced after bile duct ligation in the TLR4-mutant mice and they suggested that LPS-TLR4 pathway play a crucial role in the hepatic fibrogenesis.129 It is supported by a large cohort study demonstrating that the TLR4 single nucleotide polymorphism predicts the risk of liver cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection.130
Various evidences suggest the gut-liver axis-from disruption of gut barrier function, bacterial translocation, and increase in LPS in the liver and systemic circulation to TLR and/or inflammasomes activation and production of proinflammatory cytokines-as the main mechanism of chronic liver disease and portal hypertension. Therefore, understanding this axis and the signaling pathway may provide new targets for the prevention or treatment of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
Abbreviations
ASC
apoptosis-associated speck like CARD-domain containing protein
DAMPs
damage-associated molecular patterns
HSCs
hepatic stellate cells
IFN
interferon
IKK
I╬║B kinase
IL
interleukin
IRF3
interleukin regulatory factor 3
IRAK
IL-1 receptor-associated kinase
JNK
Jun N-terminal kinases
LPS
lipopolysaccharide
NAFLD
non alcoholic fatty liver disease
NASH
non alcoholic steatohepatitis
NK cells
natural killer cells
NLRs
NOD-like receptors
PAMPs
pathogen-associated molecular patterns
TBK
TANK-binding kinase
TLRs
toll-like receptors TRAF, tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factor
TRIF
TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-╬▓
REFERENCES
1. Shah VJ, Kamath PS. In: Feldman M, Fridman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Portal hypertension and gastrointestinal bleeding. Sleisenger and Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease. 2010. 9th ed. Philadelphia PA: Saunders Elsevier; p. 1489-1516.

2. Rao R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009;50:638-644. 19575462.


3. Seki E, Brenner DA. Toll-like receptors and adaptor molecules in liver disease: update. Hepatology 2008;48:322-335. 18506843.


4. Rao RK, Seth A, Sheth P. Recent Advances in Alcoholic Liver Disease I. Role of intestinal permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2004;286:G881-G884. 15132946.


5. Rao RK. Acetaldehyde-induced increase in paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1998;22:1724-1730. 9835287.


6. Keshavarzian A, Farhadi A, Forsyth CB, Rangan J, Jakate S, Shaikh M, et al. Evidence that chronic alcohol exposure promotes intestinal oxidative stress, intestinal hyperpermeability and endotoxemia prior to development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. J Hepatol 2009;50:538-547. 19155080.


7. Keshavarzian A, Holmes EW, Patel M, Iber F, Fields JZ, Pethkar S. Leaky gut in alcoholic cirrhosis: a possible mechanism for alcohol-induced liver damage. Am J Gastroenterol 1999;94:200-207. 9934756.


8. Yumuk Z, Ozdemirci S, Erden BF, Dundar V. The effect of long-term ethanol feeding on Brucella melitensis infection of rats. Alcohol Alcohol 2001;36:314-317. 11468131.



9. Kavanaugh MJ, Clark C, Goto M, Kovacs EJ, Gamelli RL, Sayeed MM, et al. Effect of acute alcohol ingestion prior to burn injury on intestinal bacterial growth and barrier function. Burns 2005;31:290-296. 15774282.


10. Wheeler MD, Kono H, Yin M, Nakagami M, Uesugi T, Arteel GE, et al. The role of Kupffer cell oxidant production in early ethanol-induced liver disease. Free Radic Biol Med 2001;31:1544-1549. 11744328.


11. Thakur V, McMullen MR, Pritchard MT, Nagy LE. Regulation of macrophage activation in alcoholic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;22(Suppl 1):S53-S56. 17567466.


12. Miele L, Valenza V, La Torre G, Montalto M, Cammarota G, Ricci R, et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009;49:1877-1887. 19291785.


13. Huang Y, Blatt LM, Taylor MW. Type 1 interferon as an antiinflammatory agent: inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1 beta and induction of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1995;15:317-321. 7627806.


14. Csak T, Velayudham A, Hritz I, Petrasek J, Levin I, Lippai D, et al. Deficiency in myeloid differentiation factor-2 and toll-like receptor 4 expression attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2011;300:G433-G441. 21233280.



15. Bergheim I, Weber S, Vos M, Kr├żmer S, Volynets V, Kaserouni S, et al. Antibiotics protect against fructose-induced hepatic lipid accumulation in mice: role of endotoxin. J Hepatol 2008;48:983-992. 18395289.


16. Farhadi A, Gundlapalli S, Shaikh M, Frantzides C, Harrell L, Kwasny MM, et al. Susceptibility to gut leakiness: a possible mechanism for endotoxaemia in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int 2008;28:1026-1033. 18397235.



17. Bigatello LM, Broitman SA, Fattori L, Di Paoli M, Pontello M, Bevilacqua G, et al. Endotoxemia, encephalopathy, and mortality in cirrhotic patients. Am J Gastroenterol 1987;82:11-15. 3799574.

18. Lin RS, Lee FY, Lee SD, Tsai YT, Lin HC, Lu RH, et al. Endotoxemia in patients with chronic liver diseases: relationship to severity of liver diseases, presence of esophageal varices, and hyperdynamic circulation. J Hepatol 1995;22:165-172. 7790704.


19. Michie HR, Manogue KR, Spriggs DR, Revhaug A, O'Dwyer S, Dinarello CA, et al. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med 1988;318:1481-1486. 2835680.


20. van Deventer SJ, B├╝ller HR, ten Cate JW, Aarden LA, Hack CE, Sturk A. Experimental endotoxemia in humans: analysis of cytokine release and coagulation, fibrinolytic, and complement pathways. Blood 1990;76:2520-2526. 2124934.



21. Mathison JC, Ulevitch RJ. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol 1979;123:2133-2143. 489976.

22. Zlydaszyk JC, Moon RJ. Fate of 51Cr-labeled lipopolysaccharide in tissue culture cells and livers of normal mice. Infect Immun 1976;14:100-105. 780270.


23. Lumsden AB, Henderson JM, Kutner MH. Endotoxin levels measured by a chromogenic assay in portal, hepatic and peripheral venous blood in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1988;8:232-236. 3281884.


24. Szabo G, Bala S, Petrasek J, Gattu A. Gut-liver axis and sensing microbes. Dig Dis 2010;28:737-744. 21525758.


25. Artis D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 2008;8:411-420. 18469830.



26. Varol C, Zigmond E, Jung S. Securing the immune tightrope: mononuclear phagocytes in the intestinal lamina propria. Nat Rev Immunol 2010;10:415-426. 20498668.



27. Varol C, Vallon-Eberhard A, Elinav E, Aychek T, Shapira Y, Luche H, et al. Intestinal lamina propria dendritic cell subsets have different origin and functions. Immunity 2009;31:502-512. 19733097.


29. Nakao A, Taki S, Yasui M, Kimura Y, Nonami T, Harada A, et al. The fate of intravenously injected endotoxin in normal rats and in rats with liver failure. Hepatology 1994;19:1251-1256. 8175149.


30. Catal├Ī M, Ant├│n A, Portol├®s MT. Characterization of the simultaneous binding of Escherichia coli endotoxin to Kupffer and endothelial liver cells by flow cytometry. Cytometry 1999;36:123-130. 10554160.


31. Dolganiuc A, Norkina O, Kodys K, Catalano D, Bakis G, Marshall C, et al. Viral and host factors induce macrophage activation and loss of toll-like receptor tolerance in chronic HCV infection. Gastroenterology 2007;133:1627-1636. 17916356.



32. Roth J, McClellan JL, Kluger MJ, Zeisberger E. Attenuation of fever and release of cytokines after repeated injections of lipopolysaccharide in guinea-pigs. J Physiol 1994;477:177-185. 8071885.



33. Szabo G, Mandrekar P, Girouard L, Catalano D. Regulation of human monocyte functions by acute ethanol treatment: decreased tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta and elevated interleukin-10, and transforming growth factor-beta production. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1996;20:900-907. 8865966.


34. McClain CJ, Cohen DA. Increased tumor necrosis factor production by monocytes in alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology 1989;9:349-351. 2920991.


35. Vreugdenhil AC, Snoek AM, van't Veer C, Greve JW, Buurman WA. LPS-binding protein circulates in association with apoB-containing lipoproteins and enhances endotoxin-LDL/VLDL interaction. J Clin Invest 2001;107:225-234. 11160139.



36. Medvedev AE, Lentschat A, Wahl LM, Golenbock DT, Vogel SN. Dysregulation of LPS-induced Toll-like receptor 4-MyD88 complex formation and IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 activation in endotoxin-tolerant cells. J Immunol 2002;169:5209-5216. 12391239.


37. Garcia-Tsao G, Wiest R. Gut microflora in the pathogenesis of the complications of cirrhosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2004;18:353-372. 15123075.


38. Riordan SM, Williams R. Gut flora and hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1140-1142. 20335591.


39. Berg RD, Garlington AW. Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect Immun 1979;23:403-411. 154474.


40. Wiest R, Garcia-Tsao G. Bacterial translocation (BT) in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2005;41:422-433. 15723320.


41. Pradere JP, Troeger JS, Dapito DH, Mencin AA, Schwabe RF. Toll-like receptor 4 and hepatic fibrogenesis. Semin Liver Dis 2010;30:232-244. 20665376.




42. Son G, Kremer M, Hines IN. Contribution of gut bacteria to liver pathobiology. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010;2010:pii: 453563.


43. Artis D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 2008;8:411-420. 18469830.



44. B├żckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005;307:1915-1920. 15790844.


45. Rao RK. Acetaldehyde-induced barrier disruption and paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Methods Mol Biol 2008;447:171-183. 18369919.


46. Tang Y, Forsyth CB, Farhadi A, Rangan J, Jakate S, Shaikh M, et al. Nitric oxide-mediated intestinal injury is required for alcohol-induced gut leakiness and liver damage. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2009;33:1220-1230. 19389191.



47. Yajima S, Morisaki H, Serita R, Suzuki T, Katori N, Asahara T, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates hyperglycemia-augmented gut barrier dysfunction in endotoxemia. Crit Care Med 2009;37:1024-1030. 19237913.


48. Miettinen TA. Lipid absorption, bile acids, and cholesterol metabolism in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut 1972;13:682-689. 4118161.



49. Sung JY, Shaffer EA, Costerton JW. Antibacterial activity of bile salts against common biliary pathogens. Effects of hydrophobicity of the molecule and in the presence of phospholipids. Dig Dis Sci 1993;38:2104-2112. 8223087.


50. Gunnarsdottir SA, Sadik R, Shev S, Simr├®n M, Sj├Čvall H, Stotzer PO, et al. Small intestinal motility disturbances and bacterial overgrowth in patients with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:1362-1370. 12818282.


51. Van Thiel DH, Fagiuoli S, Wright HI, Chien MC, Gavaler JS. Gastrointestinal transit in cirrhotic patients: effect of hepatic encephalopathy and its treatment. Hepatology 1994;19:67-71. 8276369.


52. Madrid AM, Cumsille F, Defilippi C. Altered small bowel motility in patients with liver cirrhosis depends on severity of liver disease. Dig Dis Sci 1997;42:738-742. 9125642.


53. Madrid AM, Brahm J, Buckel E, Silva G, Defilippi C. Orthotopic liver transplantation improves small bowel motility disorders in cirrhotic patients. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:1044-1045. 9177529.

54. Robinson CJ, Bohannan BJ, Young VB. From structure to function: the ecology of host-associated microbial communities. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2010;74:453-476. 20805407.



55. Gillevet P, Sikaroodi M, Keshavarzian A, Mutlu EA. Quantitative assessment of the human gut microbiome using multitag pyrosequencing. Chem Biodivers 2010;7:1065-1075. 20491064.



57. Norman K, Pirlich M. Gastrointestinal tract in liver disease: which organ is sick? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2008;11:613-619. 18685458.


58. Chen Y, Yang F, Lu H, Wang B, Chen Y, Lei D, et al. Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011;54:562-572. 21574172.


59. Lu H, Wu Z, Xu W, Yang J, Chen Y, Li L. Intestinal microbiota was assessed in cirrhotic patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Intestinal microbiota of HBV cirrhotic patients. Microb Ecol 2011;61:693-703. 21286703.


60. G├│mez-Hurtado I, Santacruz A, Peir├│ G, Zapater P, Guti├®rrez A, P├®rez-Mateo M, et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis is associated with inflammation and bacterial translocation in mice with CCl4-induced fibrosis. PLoS One 2011;6:e23037. 21829583.



61. Zhang W, Gu Y, Chen Y, Deng H, Chen L, Chen S, et al. Intestinal flora imbalance results in altered bacterial translocation and liver function in rats with experimental cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;22:1481-1486. 20739895.


62. Grang├® JD, Roulot D, Pelletier G, Pariente EA, Denis J, Ink O, et al. Norfloxacin primary prophylaxis of bacterial infections in cirrhotic patients with ascites: a double-blind randomized trial. J Hepatol 1998;29:430-436. 9764990.


63. Liu Q, Duan ZP, Ha DK, Bengmark S, Kurtovic J, Riordan SM. Synbiotic modulation of gut flora: effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004;39:1441-1449. 15122774.


64. Novella M, Sol├Ā R, Soriano G, Andreu M, Gana J, Ortiz J, et al. Continuous versus inpatient prophylaxis of the first episode of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis with norfloxacin. Hepatology 1997;25:532-536. 9049193.


65. Rasaratnam B, Kaye D, Jennings G, Dudley F, Chin-Dusting J. The effect of selective intestinal decontamination on the hyperdynamic circulatory state in cirrhosis. A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2003;139:186-193. 12899586.


66. Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Jin C, Hao L, Mehal WZ, Strowig T, et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012;482:179-185. 22297845.




67. Mandrekar P, Bala S, Catalano D, Kodys K, Szabo G. The opposite effects of acute and chronic alcohol on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation are linked to IRAK-M in human monocytes. J Immunol 2009;183:1320-1327. 19561104.


68. Nagy LE. Recent insights into the role of the innate immune system in the development of alcoholic liver disease. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2003;228:882-890. 12968059.


69. Wu D, Cederbaum AI. Oxidative stress and alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 2009;29:141-154. 19387914.



70. Szabo G, Mandrekar P, Petrasek J, Catalano D. The unfolding web of innate immune dysregulation in alcoholic liver injury. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2011;35:782-786. 21284666.



71. Adachi Y, Bradford BU, Gao W, Bojes HK, Thurman RG. Inactivation of Kupffer cells prevents early alcohol-induced liver injury. Hepatology 1994;20:453-460. 8045507.


72. Adachi Y, Moore LE, Bradford BU, Gao W, Thurman RG. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology 1995;108:218-224. 7806045.


73. van Rooijen N, Sanders A, van den Berg TK. Apoptosis of macrophages induced by liposome-mediated intracellular delivery of clodronate and propamidine. J Immunol Methods 1996;193:93-99. 8690935.


74. Paik YH, Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Russo MP, Jobin C, Brenner DA. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2003;37:1043-1055. 12717385.


75. Karaa A, Thompson KJ, McKillop IH, Clemens MG, Schrum LW. S-adenosyl-L-methionine attenuates oxidative stress and hepatic stellate cell activation in an ethanol-LPS-induced fibrotic rat model. Shock 2008;30:197-205. 18180699.


76. Quiroz SC, Bucio L, Souza V, Hern├Īndez E, Gonz├Īlez E, G├│mez-Quiroz L, et al. Effect of endotoxin pretreatment on hepatic stellate cell response to ethanol and acetaldehyde. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001;16:1267-1273. 11903746.


77. Rock FL, Hardiman G, Timans JC, Kastelein RA, Bazan JF. A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:588-593. 9435236.



78. Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr. A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 1997;388:394-397. 9237759.



79. Guo J, Friedman SL. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in liver injury and hepatic fibrogenesis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2010;3:21. 20964825.



80. Szabo G, Dolganiuc A, Mandrekar P. Pattern recognition receptors: a contemporary view on liver diseases. Hepatology 2006;44:287-298. 16871558.


81. Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010;140:805-820. 20303872.


82. Yamamoto M, Takeda K. Current views of toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010;2010:240365. 21197425.




83. Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998;282:2085-2088. 9851930.


84. Shimazu R, Akashi S, Ogata H, Nagai Y, Fukudome K, Miyake K, et al. MD-2, a molecule that confers lipopolysaccharide responsiveness on Toll-like receptor 4. J Exp Med 1999;189:1777-1782. 10359581.



85. Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ, Mathison JC. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 1990;249:1431-1433. 1698311.


86. Mandrekar P, Szabo G. Signalling pathways in alcohol-induced liver inflammation. J Hepatol 2009;50:1258-1266. 19398236.



87. Verstak B, Nagpal K, Bottomley SP, Golenbock DT, Hertzog PJ, Mansell A. MyD88 adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP interaction with TRAF6 is critical for TLR2- and TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB proinflammatory responses. J Biol Chem 2009;284:24192-24203. 19592497.



88. Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006;124:783-801. 16497588.


89. Seki E, Schnabl B. Role of innate immunity and the microbiota in liver fibrosis: crosstalk between the liver and gut. J Physiol 2012;590:447-458. 22124143.


90. Schafer SL, Lin R, Moore PA, Hiscott J, Pitha PM. Regulation of type I interferon gene expression by interferon regulatory factor-3. J Biol Chem 1998;273:2714-2720. 9446577.


91. Hritz I, Mandrekar P, Velayudham A, Catalano D, Dolganiuc A, Kodys K, et al. The critical role of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 in alcoholic liver disease is independent of the common TLR adapter MyD88. Hepatology 2008;48:1224-1231. 18792393.


92. Rivera CA, Adegboyega P, van Rooijen N, Tagalicud A, Allman M, Wallace M. Toll-like receptor-4 signaling and Kupffer cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol 2007;47:571-579. 17644211.



93. Chen GY, Nu├▒ez G. Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol 2010;10:826-837. 21088683.




94. Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J. The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell 2002;10:417-426. 12191486.


95. Ye Z, Ting JP. NLR, the nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing gene family. Curr Opin Immunol 2008;20:3-9. 18280719.


96. Bauernfeind F, Ablasser A, Bartok E, Kim S, Schmid-Burgk J, Cavlar T, et al. Inflammasomes: current understanding and open questions. Cell Mol Life Sci 2011;68:765-783. 21072676.


97. Sutterwala FS, Ogura Y, Flavell RA. The inflammasome in pathogen recognition and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 2007;82:259-264. 17470531.


98. Martinon F, Mayor A, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes: guardians of the body. Annu Rev Immunol 2009;27:229-265. 19302040.


99. Agostini L, Martinon F, Burns K, McDermott MF, Hawkins PN, Tschopp J. NALP3 forms an IL-1beta-processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle-Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity 2004;20:319-325. 15030775.


100. Dinarello CA. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol 2009;27:519-550. 19302047.


101. Bauernfeind F, Bartok E, Rieger A, Franchi L, N├║├▒ez G, Hornung V. Cutting edge: reactive oxygen species inhibitors block priming, but not activation, of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Immunol 2011;187:613-617. 21677136.



102. Ganz M, Csak T, Nath B, Szabo G. Lipopolysaccharide induces and activates the Nalp3 inflammasome in the liver. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17:4772-4778. 22147977.



103. McClain CJ, Cohen DA, Dinarello CA, Cannon JG, Shedlofsky SI, Kaplan AM. Serum interleukin-1 (IL-1) activity in alcoholic hepatitis. Life Sci 1986;39:1479-1485. 3490610.


104. Valles SL, Blanco AM, Azorin I, Guasch R, Pascual M, Gomez-Lechon MJ, et al. Chronic ethanol consumption enhances interleukin-1-mediated signal transduction in rat liver and in cultured hepatocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2003;27:1979-1986. 14691386.


105. Bjarnason I, Peters TJ, Wise RJ. The leaky gut of alcoholism: possible route of entry for toxic compounds. Lancet 1984;1:179-182. 6141332.


106. Draper LR, Gyure LA, Hall JG, Robertson D. Effect of alcohol on the integrity of the intestinal epithelium. Gut 1983;24:399-404. 6840613.



107. Parlesak A, Sch├żfer C, Sch├╝tz T, Bode JC, Bode C. Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in different stages of alcohol-induced liver disease. J Hepatol 2000;32:742-747. 10845660.


108. Chesta J, Defilippi C. Abnormalities in proximal small bowel motility in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1993;17:828-832. 8491451.

109. Guarner C, Runyon BA, Young S, Heck M, Sheikh MY. Intestinal bacterial overgrowth and bacterial translocation in cirrhotic rats with ascites. J Hepatol 1997;26:1372-1378. 9210626.


110. Ramachandran A, Prabhu R, Thomas S, Reddy JB, Pulimood A, Balasubramanian KA. Intestinal mucosal alterations in experimental cirrhosis in the rat: role of oxygen free radicals. Hepatology 2002;35:622-629. 11870376.


111. Rajkovic IA, Williams R. Abnormalities of neutrophil phagocytosis, intracellular killing and metabolic activity in alcoholic cirrhosis and hepatitis. Hepatology 1986;6:252-262. 3007318.


112. Garcia-Tsao G, Lee FY, Barden GE, Cartun R, West AB. Bacterial translocation to mesenteric lymph nodes is increased in cirrhotic rats with ascites. Gastroenterology 1995;108:1835-1841. 7768390.


113. Gaeta GB, Perna P, Adinolfi LE, Utili R, Ruggiero G. Endotoxemia in a series of 104 patients with chronic liver diseases: prevalence and significance. Digestion 1982;23:239-244. 6183161.


114. Bode C, Kugler V, Bode JC. Endotoxemia in patients with alcoholic and non-alcoholic cirrhosis and in subjects with no evidence of chronic liver disease following acute alcohol excess. J Hepatol 1987;4:8-14. 3571935.


115. Urbaschek R, McCuskey RS, Rudi V, Becker KP, Stickel F, Urbaschek B, et al. Endotoxin, endotoxin-neutralizing-capacity, sCD14, sICAM-1, and cytokines in patients with various degrees of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2001;25:261-268. 11236841.


116. Harte AL, da Silva NF, Creely SJ, McGee KC, Billyard T, Youssef-Elabd EM, et al. Elevated endotoxin levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Inflamm (Lond) 2010;7:15. 20353583.



117. Nanji AA, Khettry U, Sadrzadeh SM. Lactobacillus feeding reduces endotoxemia and severity of experimental alcoholic liver (disease). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1994;205:243-247. 8171045.


118. Schwabe RF, Seki E, Brenner DA. Toll-like receptor signaling in the liver. Gastroenterology 2006 5;130(6):1886-1900. 16697751.


119. Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Lane MD, Clemens M, Diehl AM. Obesity increases sensitivity to endotoxin liver injury: implications for the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997;94:2557-2562. 9122234.



120. Szabo G, Velayudham A, Romics L Jr, Mandrekar P. Modulation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by pattern recognition receptors in mice: the role of toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2005;29(11 Suppl):140S-145S. 16344599.


121. Solga SF, Diehl AM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: lumen-liver interactions and possible role for probiotics. J Hepatol 2003;38:681-687. 12713883.


122. Li Z, Yang S, Lin H, Huang J, Watkins PA, Moser AB, et al. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2003;37:343-350. 12540784.


123. Sandler NG, Koh C, Roque A, Eccleston JL, Siegel RB, Demino M, et al. Host response to translocated microbial products predicts outcomes of patients with HBV or HCV infection. Gastroenterology 2011;141:1220-1230. 1230.e1-1230.e3. 21726511.



124. Steib CJ, Hartmann AC, v Hesler C, Benesic A, Hennenberg M, Bilzer M, et al. Intraperitoneal LPS amplifies portal hypertension in rat liver fibrosis. Lab Invest 2010;90:1024-1032. 20212458.



125. Chiva M, Guarner C, Peralta C, Llovet T, G├│mez G, Soriano G, et al. Intestinal mucosal oxidative damage and bacterial translocation in cirrhotic rats. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003;15:145-150. 12560758.


126. Clements WD, Erwin P, McCaigue MD, Halliday I, Barclay GR, Rowlands BJ. Conclusive evidence of endotoxaemia in biliary obstruction. Gut 1998;42:293-299. 9536958.



127. Wiest R, Das S, Cadelina G, Garcia-Tsao G, Milstien S, Groszmann RJ. Bacterial translocation in cirrhotic rats stimulates eNOS-derived NO production and impairs mesenteric vascular contractility. J Clin Invest 1999;104:1223-1233. 10545521.



128. Tazi KA, Moreau R, Herv├® P, Dauvergne A, Cazals-Hatem D, Bert F, et al. Norfloxacin reduces aortic NO synthases and proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation in cirrhotic rats: role of Akt signaling. Gastroenterology 2005;129:303-314. 16012955.


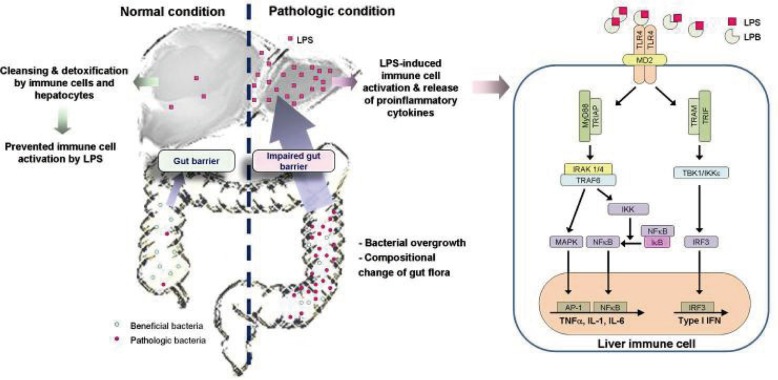
Figure┬Ā1
Schematic presentation of the gut-liver axis and bacterial translocation. In normal condition, bacterial translocation from the gut to the liver is effectively prevented by gut barrier function. Furthermore, although small amount of bacteria or its products, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), can enter into the liver, they are rapidly removed by cleansing and detoxifying function of the liver. Therefore, activation of the immune cells and subsequent induction of inflammation is effectively prevented. However, in the pathologic condition, bacterial translocation is increased by impaired barrier function, bacterial overgrowth, and compositional change of gut flora (the increase of pathologic bacteria). Therefore, large amount of LPS can enter into the liver and induce immune cell activation and inflammation. In liver immune cells, particularly in the Kupffer cells, LPS induces proinflammatory pathway via TLR4 to produce proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and interferons.
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
The current trends in the health burden of primary liver cancer across the globe2023 April;29(2)



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



