| Clin Mol Hepatol > Volume 21(4); 2015 > Article |
ABSTRACT
Radiological imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as the noninvasive diagnosis of HCC in high-risk patients by typical imaging findings alone is widely adopted in major practice guidelines for HCC. While imaging techniques have markedly improved in detecting small liver lesions, they often detect incidental benign liver lesions and non-hepatocellular malignancy that can be misdiagnosed as HCC. The most common mimicker of HCC in cirrhotic liver is nontumorous arterioportal shunts that are seen as focal hypervascular liver lesions on dynamic contrast-enhanced cross-sectional imaging. Rapidly enhancing hemangiomas can be easily misdiagnosed as HCC especially on MR imaging with liver-specific contrast agent. Focal inflammatory liver lesions mimic HCC by demonstrating arterial-phase hypervascularity and subsequent washout on dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging. It is important to recognize the suggestive imaging findings for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (CC) as the management of CC is largely different from that of HCC. There are other benign mimickers of HCC such as angiomyolipomas and focal nodular hyperplasia-like nodules. Recognition of their typical imaging findings can reduce false-positive HCC diagnosis.
Recent advances of radiological imaging techniques enable us to diagnose small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) lesions that are amenable to various options of potentially curative treatment. On the other hand, increased sensitivity of the imaging to detect small HCC inevitably results in a substantial number of false-positive lesions that are often misdiagnosed as HCC. The false-positive HCC diagnosis potentially has a substantial negative impact on patient's management by unnecessary invasive procedures or preventing the patients from appropriate treatments.
There are number of focal benign liver lesions that often mimic the imaging appearance of HCC. These include nontumorous arterioportal shunts, fast-filling hemangiomas, focal fat sparing/deposit, inflammatory lesions, confluent fibrosis, angiomyolipoma (AML), focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) -like nodules, and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). False positive HCC diagnosis can be avoided by applying strict imaging diagnostic criteria for HCC. A multi-modality imaging approach is useful to reach the correct diagnosis if one imaging modality is not conclusive. Cholangiocarcinoma (CC) is infrequently detected during HCC surveillance and has been a potential cause for false positive diagnosis of HCC. Understanding of suggestive imaging findings of CC can minimize the false positive diagnosis of HCC.
This review presents typical imaging findings of the common mimickers of HCC in cirrhotic liver and appropriate diagnostic work-up for these lesions.
About 70% of hypervascular focal lesions in cirrhotic liver are benign rather than malignancy1 and nontumorous arterioportal shunts occupy the majority of hypervascular pseudolesions. Nontumorous arterioportal shunts imply locally disordered perfusion but the exact mechanism of development is not clearly identified. Nontumorous arterioportal shunts have typical imaging features including small, wedge-shaped, homogenous hypervascular lesion in the arterial phase, subcapsular or peripheral location, enhancing branching structure within the lesion representing early opacification of portal veins, and isointense to the liver without showing washout during the portal and delayed phases (Fig. 1) on CT or MR imaging.23
On contrast enhanced MR images using gadoxetic acid, hypervascular pseudolesions usually show isointensity compared to surrounding liver in the hepatobiliary phase4 whereas HCCs usually show hypointensity.56 Therefore the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid enhanced MR imaging can be helpful to differentiate between arterioportal shunts and HCCs.
Usually, nontumorous arterioportal shunts are not perceivable on unenhanced CT/MR or grayscale US imaging. On contrast-enhanced US (CEUS), a nontumorous arterioportal shunt is seldom visualized as a wedge-shaped enhancing area as it is transiently seen in the arterial phase and isoechoic to the liver in the portal vein and delayed phase.
Imaging findings are nearly diagnostic if all the typical imaging features of arterioportal shunt are shown. Follow-up imaging is often needed when the imaging findings are not entirely typical. Sometimes, small HCCs with associated transtumoral arterioportal shunt may show a similar appearance, but they are not common. In fact, arterioportal shunt associated with tumor is more frequently accompanied by small hemangiomas (Fig. 2) than small HCCs.78
Hemangiomas are detected frequently during HCC surveillance9 and potentially mimic HCC especially when the lesion is small. On gray-scale US, hemangiomas are usually hyperechoic. But hemangiomas are occasionally hypoechoic, especially when the liver is fatty (Fig. 3), or shows mixed echogenicity. Most hemangiomas are accurately diagnosed on dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging by demonstrating peripheral nodular enhancement with gradual central fill-in and sustained enhancement.101112
Fast-filling hemangiomas often show complete homogeneous enhancement in the arterial phase without central fill-in pattern on CT and MR imaging and the diagnosis of hemangioma can be uncertain (Fig. 2).13 CEUS with real-time evaluation of the arterialphase filling pattern is useful to confidently diagnose fast-filling hemangiomas with demonstration of a very early peripheral nodular enhancement with rapid central fill-in (Fig. 3).14151617 Disruption-replenishment technique is particularly helpful to show characteristic arterial phase enhancement pattern of rapid-filling hemangioma (Fig. 3).1718 Although washout feature in the delayed phase is highly suggestive of malignancy, hemangiomas infrequently show slight washout in the delayed phase on CEUS due to microbubble destruction by continuous ultrasound scanning which preferentially destroy microbubbles in hemangioma with extremely slow flow.19
The degree of enhancement of hemangiomas are usually equivalent to that of aorta in the arterial phase and that of blood pool in the portal venous phase or later phase on multiphasic contrast-enhanced CT (Fig. 3) and MRI using gadoxetic acid (Fig. 4).2021 However, hemangiomas occasionally show an attenuation lower than the portal vein in the portal venous phase (Fig. 2).22 This fading feature is more commonly seen in fast-filling hemangiomas and may cause a challenge in differentiating fast-filling hemangiomas from HCCs. MR imaging is helpful for the differentiation by demonstrating bright hyperintensity on T2-weighted images in hemangiomas.
On dynamic contrast-enhanced MR images using gadoxetic acid, most hemangiomas show hyperintensity in the arterial phase, and hypointensity in the equilibrium phase (typically at 5 minutes) and the hepatobiliary phase (typically at 20 minutes) compared with surrounding liver parenchyma (Fig. 4).23 This dynamic enhancement feature is identical to that of hypervascular malignancy and can result in difficulty in differentiating hemangiomas from HCCs. Bright hyperintensity on T2-weighted images is helpful for confident diagnosis of hemangiomas.2024
Hemangiomas that undergo degeneration and fibrous replacement are called sclerosed hemangiomas.25 The imaging findings of sclerosed hemangiomas are nonspecific, so it may not be possible to prospectively differentiate sclerosed hemangiomas from malignant tumors26 and they are mostly diagnosed only after biopsy. Previous studies reported several frequent findings of sclerosed hemangioma cases; lack of early enhancement, gradual and persistent mild peripheral enhancement,25262728 and mild hyperintensity much lower than typical hemangiomas on T2-weighted images (Fig. 5).25 Other helpful imaging features include a geographic margin (Fig. 5), capsular retraction, decrease in size over time, presence of transient hepatic attenuation difference, and loss of previously seen regions of enhancement at follow up.29
When the liver is affected by diffuse fatty infiltration, the degree of fatty infiltration may differ from site to site causing focal fat sparing areas. Focal fat sparing typically occurs around the gallbladder and the hepatic hilum. These areas are related to direct splanchnic venous supply to the liver other than the portal vein, resulting in localized reduction of the lipid-rich portal venous flow. For example, focal fat sparing at the posterior edge of segment 4 is related to aberrant gastric venous drainage to the region.30 On US, focal fat sparing is seen as a wedge or geographic shaped homogeneous hypoechoic lesion (Fig. 6). Color Doppler US may demonstrate an aberrant splanchnic venous drainage showing hepatopetal flow within the lesion. On CEUS, focal fat sparing shows normal arterial and portal perfusion compared to normal liver, confirming the benign nature of the lesion.31 Splanchnic venous supply might be demonstrated as early opacification of small venous branches within the lesion in the arterial phase.
The location of focal fat deposit can vary widely. The most common sites are the anteromedial side of the segment 4 and posteromedial side of segment 4.3032 The etiologies of focal fat deposit have not been clearly understood although focal fat deposit is also closely related to aberrant portal venous supply. These lesions are homogeneously hyperechoic on US and show normal arterial and portal perfusion on CEUS.
When focal fat deposit or sparing involves atypical sites of liver parenchyma and shows a nodular appearance, it can mimic the appearance of hepatic tumor (Fig. 7). Suggestive imaging findings of fatty pseudolesions rather than true masses include fat content, typical locations, absence of a mass effect on vessels and other liver structures, a geographic configuration rather than a round or oval shape, and contrast enhancement that is similar to that of the normal liver. T1-weighted chemical shift gradient-echo MR images are accurate to diagnose focal fat deposit by demonstrating a marked decrease in the signal intensity of the lesion on the opposed-phase images compared with the in-phase images (Fig. 8).33 Focal fat sparing is isointense on in-phase images and is hyperintense to the fatty liver which loses signal on the opposed-phase images (Fig. 7). Involved areas are usually small, but are occasionally large with confluent heterogeneous regions of focal fat deposit (Fig. 9) or sparing.33
A perivascular pattern of fat deposit in the liver is seen as fatty halos that surround the hepatic veins, the portal veins, or both hepatic and portal veins (Fig. 8). It is shown as tram-like or ring-like fatty lesions surrounding the vessels depending on the imaging plain,3334 potentially mimicking metastases or HCCs. The absence of mass effect, the presence of multiple similar lesions surrounding vessels, and the tubular appearance on multiplanar images can be clues for accurate diagnosis.34 Like other fat deposit lesions, signal intensity drop on opposed-phase images compared to in-phase images MR is confirmatory for the diagnosis.
Inflammatory masses such as pyogenic liver abscesses and inflammatory pseudotumors are also one of the most common causes of false-positive diagnosis for malignancy on imaging.
Pyogenic abscesses demonstrate variable imaging manifestations on ultrasound depending on the stage of the disease, ranging from hypoechoic solid-looking lesions in the initial stage to anechoic change of internal liquefied central portion in organized, mature stage. Mature abscesses show an ill-defined, round- or oval-shaped, thick-walled hypoechoic mass with posterior acoustic enhancement and often contain septae, debris, or bright punctate echoes representing air. On CEUS, they typically show heterogeneous or rim enhancement in the arterial phase followed by rapid washout.35 Frequently there are internal non-enhancing liquefied areas that can be a distinctive feature from HCC.1436 Other typical features include a coalescent appearance and a sharp boundary of the necrotic cavity, which is similar to the "cluster" sign at CT scan. It is a highly suggestive feature of an abscess since this feature is infrequently seen in liver tumors.36 On CT scan, abscesses most commonly show a rim-like enhancement with central non-enhancing areas. Some lesions can be heterogeneous with no internal non-enhancing areas, mimicking solid tumors. These lesions occasionally show transient perilesional hyperemia on the arterial phase imaging or less commonly a regional hypoattenuation secondary to a small hepatic or portal venous thrombosis (Fig. 10).37 Clinical signs and laboratory findings of infection are critical to lead a correct diagnosis. Chronic inflammatory mass can show no enhancement which is a differentiating feature from malignancy (Fig. 11).
Inflammatory pseudotumor is a rare benign mass of fibroblastic proliferation and chronic inflammation, which is frequently misdiagnosed as aggressive malignancy.38 As it can regress spontaneously and can be managed conservatively, the recognition of the suggestive imaging findings is critical to avoid invasive surgery.3940 Inflammatory pseudotumor usually presents as an ill-defined hypoechoic mass with internal heterogeneity on US. CEUS can show arterial-phase hypervascularity and subsequent washout, mimicking the appearance of malignant tumor. On CT or MR, inflammatory pseudotumors often show heterogeneous arterial phase enhancement and sustained enhancement on the portal venous phase which would reflect internal fibrotic components (Fig. 12, 13). Some of inflammatory pseudotumors regress on follow up imaging related to dynamic inflammatory changes. Ultimately it needs to be confirmed by biopsy. Previous literature also reported frequent development of inflammatory pseudotumors in patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis.40
When the main portal vein is obstructed by thrombosis, many collaterals gradually develop as cavernous transformation.41 Under this circumference, the central zone of the liver parenchyma close to the hepatic hilum preferentially receives portal venous flow by collaterals more than the peripheral zone of the liver which is distant from the hepatic hilum,42 thus relatively ischemic peripheral zone has compensatory hyperenhancement in the arterial phase. Central zone, including the caudate lobe and hepatic parenchyma near the hilum, gradually becomes relatively hypertrophic and may be seen as a mass-like lesion. These hemodynamic and morphologic changes in chronic portal vein thrombosis are reflected to imaging features on contrast-enhanced CT. In the arterial phase, the peripheral region with relative atrophy shows arterial-phase hyperenhancement whereas the enlarged central zone shows hypoenhancement mimicking a large mass. In the delayed phase, the central zone shows isoenhancement to the liver (Fig. 14).4143
Confluent fibrosis is a focal fibrotic mass as a result of hepatic parenchymal destruction in advanced cirrhosis44 and may mimic the appearance of HCC.444546 In most advanced cirrhotic patients who need liver transplantation, the differential diagnosis between confluent fibrosis and HCC is crucial to properly assign the eligibility and priority for a transplant.47
Confluent fibrosis is usually seen as a focal, irregular, often wedge-shaped mass radiating from the porta hepatis with segmental or lobar distribution and associated capsular retraction on imaging.444648 The most commonly involved areas are the anterior segment of right lobe and medial segment of left lobe, and less frequently the posterior segment of right lobe.47 Capsular retraction is the most useful finding to suggest confluent fibrosis and may progress as cirrhosis progresses (Fig. 15).4748 On dynamic contrast-enhanced CT or MR imaging, confluent fibrosis mostly shows hypo- or isoenhancement relative to the liver in the arterial phase, but may show hyperenhancement (Fig. 16). Hyperenhancement in the delayed phase (> 5 minutes) due to fibrosis (Fig. 16) is an important differentiating feature from HCC which mostly shows hypoenhancement in the delayed phase.4449 Confluent fibrosis is hypointense on T1-weighted image, mildly hyperintense on T2-weighted image, and hypointense in the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI (Fig. 15, 17). diffusion-weighted MR imaging might be helpful in differentiating confluent fibrosis from HCC by demonstrating relatively higher apparent diffusion coefficient.50
Liver cirrhosis and chronic viral hepatitis is a well-known risk factor for development of CC. For this reason, intrahepatic mass-forming CC is occasionally detected during HCC surveillance although the incidence of CC is much lower than HCC. Large intrahepatic CC have distinctive imaging features from HCC, including large hypoattenuating mass with peripheral enhancement, progressive enhancement in dynamic contrast imaging, capsular retraction, and frequent biliary dilatation.5152 However, small intrahepatic CC can mimic the appearance of HCC. Because HCCs and CCs have different biological features and prognoses, accurate differentiation between them is crucial for treatment planning.53
CCs are mostly hypovascular, but small CCs are often hypervascular (Fig. 18). Peripheral rim-like enhancement and the absence of washout are important differentiating features from HCC on CT or MRI (Fig. 18). Capsular retraction, if it is seen, is a highly suggestive finding for CC as it is rarely seen in HCC. On CEUS, most CCs are hypervascular. Arterial-phase enhancement features and the timing of washout are important differentiating features between CCs and HCCs on CEUS. Peripheral rim-like enhancement in the arterial phase is common in CC (Fig. 19), but is rare in HCC. CCs show rapid washout mostly begins earlier than 60 seconds (Fig. 19), while washout in HCC tends to be later, often beginning later than 90 seconds after contrast injection.19 The reason for the difference of washout features in CC between CT/MRI and CEUS is the different property of the contrast agent: purely intravascular contrast in CEUS and nonspecific contrast agent in CT/MRI.54
Mixed HCC and CC is an uncommon variant of malignancy in cirrhotic liver. The imaging findings are determined by the dominant tumor component and imaging diagnosis is often challenging (Fig. 20).55 Mixed HCC/CC most commonly has an imaging appearance similar to CC and the diagnosis requires biopsy.
Recent practice guidelines allow that the diagnosis of HCC is mostly made by typical imaging findings without biopsy. Therefore, high specificity of the diagnostic imaging test for HCC diagnosis is critical. Biopsy is needed when there are any suggestive features of CCs.
AML is a benign mesenchymal tumor composed of blood vessels, smooth muscle cells, and a varying amount of fat. AML with a high amount of fat can be easily diagnosed on imaging; however, the imaging diagnosis is challenging in AML with relatively smaller amount of fat. AML is often hypervascular in the arterial phase (Fig. 21) and shows washout, mimicking HCC.56 AML shows marked hypointensity in the hepatobiliary phase on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI as the lesion does not contain normal hepatocytes. Marked homogeneous hypointensity in the hepatobiliary phase might be a differentiating finding from HCC which usually shows mild hypointensity in the hepatobiliary phase.57 The presence of early draining vein and the absence of tumor capsule are other useful imaging findings for differentiating AML from HCC.58
Large regenerative nodules are associated with abnormal perfusion of the liver and commonly seen in cirrhotic livers related to Budd-Chiari syndrome.59 Because many of such nodules have fibrous scars at the center of the nodules resembling the typical stellate scars of FNH, these nodules are called FNH-like nodules.
On noncontrast CT, large regenerative nodules are hardly perceivable due to isoattenuation compared to the adjacent liver parenchyma. On contrast-enhanced CT and MR, large regenerative nodules are usually multiple, homogenous hyperenhancement in the arterial and portal venous phase,59 and isoenhancement in the delayed phase (Fig. 17, 22).60 Hypointense ring surrounding the hypervascular nodule is occasionally seen in the arterial phase and may be explained by atrophic tissue in the periphery.60 They are typically hyperintense on precontrast T1-weighted images and iso- or hypointense on T2-weighted images.61 MRI using gadoxetic acid is very useful for differentiating FNH-like nodules from HCC as FNH-like nodules show iso- or hyperintensity, due to their equal or stronger expression of organic anion-transporting polypeptides 8 (OATP8) (Fig. 17).62
On CEUS, FNH-like nodules show strong arterial enhancement which starts from the center of the lesions and then propagates to the peripheral area suggesting centrifugal enhancement pattern (Fig. 22).61 In the portal venous and the delayed liver phase, FNH-like nodules become isoenhancement compared to the surrounding liver parenchyma. FNH-like nodules are often small and multiple. Multiplicity might be a differentiating imaging feature from HCC.60
Large confluent vascular masses in HHT are often misdiagnosed as diffuse disseminated HCCs. They are defined as large enhancing areas more than 10 mm of visible conglomerated multiple telangiectasia or large shunts.63 These lesions show hyperenhancement in the arterial phase (Fig. 23) and, unlike HCCs, show persistent enhancement in the delayed phase.
Hepatic perfusion abnormalities in HHT are shown as inhomogeneous attenuation of hepatic parenchyma and best seen in the arterial phase, but almost always become isoattenuating in the portal venous or delayed phase.64 In contrast to the focal, peripherally located, and homogenous feature of the perfusion abnormalities in liver cirrhosis,65 the perfusion abnormalities of HHT are usually more diffuse and inhomogeneous.266
Focal hepatic lesions in HHT are often associated with arteriovenous, arterioportal, or portovenous shunts. Arteriovenous shunts are most common and are seen as early opacification of the hepatic veins in the arterial phase63 and enlargement of both hepatic arteries and hepatic veins (Fig. 23). Markedly enlarged hepatic arteries are an important clue to the diagnosis of HHT. Arterioportal shunts related to HHT show wedge-shaped hyperattenuating areas in the arterial phase, like arterioportal shunts in other condition. In addition, there are other typical imaging features including early opacification of the portal vein and visualization of the enlarged portal vein branches and paired hepatic artery in the arterial phase.6467 Portovenous shunts are rarely seen on imaging.63
It is important to be aware of various conditions in the liver that can mimic the imaging appearance of HCC. The recognition of the potential HCC mimickers and their typical or suggestive findings is crucial to avoid false-positive diagnosis of HCC and subsequent invasive managements. A multimodality imaging approach along with a careful review of clinical and laboratory findings can be helpful when in doubt for these potential tumor mimicking lesions.
REFERENCES
1. O'Malley ME, Takayama Y, Sherman M. Outcome of small (10-20 mm) arterial phase-enhancing nodules seen on triphasic liver CT in patients with cirrhosis or chronic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100:1523-1528. 15984975.


2. Kim TK, Choi BI, Han JK, Chung JW, Park JH, Han MC. Nontumorous arterioportal shunt mimicking hypervascular tumor in cirrhotic liver: two-phase spiral CT findings. Radiology 1998;208:597-603. 9722834.


3. Yu JS, Kim KW, Jeong MG, Lee JT, Yoo HS. Nontumorous Hepatic Arterial-Portal Venous Shunts: MR Imaging Findings. Radiology 2000;217:750-756. 11110939.


4. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, Sano K, Tominaga L, Muhi A, et al. Distinguishing Hypervascular Pseudolesions of the Liver from Hypervascular Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced MR Imaging. Radiology 2010;256:151-158. 20574092.


5. Sun HY, Lee JM, Shin CI, Lee DH, Moon SK, Kim KW, et al. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating small hepatocellular carcinomas (Ōēż 2 cm in diameter) from arterial enhancing pseudolesions: special emphasis on hepatobiliary phase imaging. Invest Radiol 2010;45:96-103. 20057319.


6. Frericks BB, Loddenkemper C, Huppertz A, Valdeig S, Stroux A, Seja M, et al. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhotic liver enhancement using Gd-EOB-DTPA. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;193:1053-1060. 19770329.


7. Byun JH, Kim TK, Lee CW, Lee JK, Kim AY, Kim PN, et al. Arterioportal shunt: prevalence in small hemangiomas versus that in hepatocellular carcinomas 3 cm or smaller at two-phase helical CT. Radiology 2004;232:354-360. 15215556.


8. Kim KW, Kim TK, Han JK, Kim AY, Lee HJ, Choi BI. Hepatic hemangiomas with arterioportal shunt: findings at two-phase CT. Radiology 2001;219:707-711. 11376258.


9. Kim TK, Lee KH, Jang HJ, Haider MA, Jacks LM, Menezes RJ, et al. Analysis of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR findings for characterizing small (1-2-cm) hepatic nodules in patients at high risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 2011;259:730-738. 21364083.


10. Kim TK, Choi BI, Han JK, Hong HS, Park SH, Moon SG. Hepatic tumors: contrast agent-enhancement patterns with pulse-inversion harmonic US. Radiology 2000;216:411-417. 10924562.


11. Kim JH, Kim TK, Kim BS, Eun HW, Kim PN, Lee MG, et al. Enhancement of hepatic hemangiomas with levovist on coded harmonic angiographic ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med 2002;21:141-148. 11833870.


12. Brannigan M, Burns PN, Wilson SR. Blood flow patterns in focal liver lesions at microbubble-enhanced US. Radiographics 2004;24:921-935. 15256618.


13. Jang HJ, Kim TK, Lim HK, Park SJ, Sim JS, Kim HY, et al. Hepatic hemangioma: atypical appearances on CT, MR imaging, and sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003;180:135-141. 12490492.


14. Kim TK, Jang HJ, Wilson SR. Benign liver masses: imaging with microbubble contrast agents. Ultrasound Q 2006;22:31-39. 16641791.

15. Jang HJ, Yu H, Kim TK. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the detection and characterization of liver tumors. Cancer Imaging 2009;9:96-103. 19933022.


16. Jang HJ, Yu H, Kim TK. Imaging of focal liver lesions. Semin Roentgenol 2009;44:266-282. 19715792.


17. Wilson SR, Jang HJ, Kim TK, Iijima H, Kamiyama N, Burns PN. Realtime temporal maximum-intensity-projection imaging of hepatic lesions with contrast-enhanced sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008;190:691-695. 18287440.


18. Kim TK, Jang HJ. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of nodules in liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:3590-3596. 24707142.



19. Bhayana D, Kim TK, Jang HJ, Burns PN, Wilson SR. Hypervascular liver masses on contrast-enhanced ultrasound: the importance of washout. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010;194:977-983. 20308500.


20. Tamada T, Ito K, Yamamoto A, Sone T, Kanki A, Tanaka F, et al. Hepatic hemangiomas: evaluation of enhancement patterns at dynamic MRI with gadoxetate disodium. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;196:824-830. 21427331.


21. Heiken JP. Distinguishing benign from malignant liver tumours. Cancer Imaging 2007;7(Spec No A):S1-S14. 17921080.



22. Alturkistany S, Jang HJ, Yu H, Lee KH, Kim TK. Fading hepatic hemangiomas on multiphasic CT. Abdom Imaging 2012;37:775-780. 22143263.



23. Doo KW, Lee CH, Choi JW, Lee J, Kim KA, Park CM. "Pseudo washout" sign in high-flow hepatic hemangioma on gadoxetic acid contrast-enhanced MRI mimicking hypervascular tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;193:W490-W496. 19933623.


24. Zech CJ, Herrmann KA, Reiser MF, Schoenberg SO. MR imaging apected liver metastases: value of liver-specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA. Magn Reson Med Sci 2007;6:43-52. 17510541.


25. Cheng HC, Tsai SH, Chiang JH, Chang CY. Hyalinized liver hemangioma mimicking malignant tumor at MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995;165:1016-1017. 7676959.


26. Haratake J, Horie A, Nagafuchi Y. Hyalinized hemangioma of the liver. Am J Gastroenterol 1992;87:234-236. 1370873.

27. Takayasu K, Moriyama N, Shima Y, Muramatsu Y, Yamada T, Makuuchi M, et al. Atypical radiographic findings in hepatic cavernous hemangioma: correlation with histologic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1986;146:1149-1153. 3518366.


28. Yamashita Y, Shimada M, Taguchi K, Gion T, Hasegawa H, Utsunomiya T, et al. Hepatic sclerosing hemangioma mimicking a metastatic liver tumor: report of a case. Surg Today 2000;30:849-852. 11039718.


29. Doyle DJ, Khalili K, Guindi M, Atri M. Imaging features of sclerosed hemangioma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;189:67-72. 17579154.


30. Matsui O, Kadoya M, Takahashi S, Yoshikawa J, Gabata T, Takashima T, et al. Focal sparing of segment IV in fatty livers shown by sonography and CT: correlation with aberrant gastric venous drainage. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995;164:1137-1140. 7717220.


31. Nicolau C, Br├║ C. Focal liver lesions: evaluation with contrastenhanced ultrasonography. Abdom Imaging 2004;29:348-359. 15354344.


32. Itai Y, Matsui O. 'Nonportal'splanchnic venous supply to the liver: abnormal findings on CT, US and MRI. Eur Radiol 1999;9:237-243. 10101644.


33. Hamer OW, Aguirre DA, Casola G, Lavine JE, Woenckhaus M, Sirlin CB. Fatty Liver: Imaging Patterns and Pitfalls. Radiographics 2006;26:1637-1653. 17102041.


34. Hamer OW, Aguirre DA, Casola G, Sirlin CB. Imaging Features of Perivascular Fatty Infiltration of the Liver: Initial Observations. Radiology 2005;237:159-169. 16100085.


35. Liu GJ, Lu MD, Xie XY, Xu HX, Xu ZF, Zheng YL, et al. Real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of infected focal liver lesions. J Ultrasound Med 2008;27:657-666. 18359914.


36. Kim KW, Choi BI, Park SH, Kim AY, Koh YH, Lee HJ, et al. Pyogenic hepatic abscesses: distinctive features from hypovascular hepatic malignancies on contrast-enhanced ultrasound with SH U 508A; early experience. Ultrasound Med Biol 2004;30:725-733. 15219952.


37. Syed MA, Kim TK, Jang HJ. Portal and hepatic vein thrombosis in liver abscess: CT findings. Eur J Radiol 2007;61:513-519. 17161932.


38. Menias CO, Surabhi VR, Prasad SR, Wang HL, Narra VR, Chintapalli KN. Mimics of cholangiocarcinoma: spectrum of disease. Radiographics 2008;28:1115-1129. 18635632.


39. Gollapudi P, Chejfec G, Zarling EJ. Spontaneous regression of hepatic pseudotumor. Am J Gastroenterol 1992;87:214-217. 1734701.

40. Yoon KH, Ha HK, Lee JS, Suh JH, Kim MH, Kim PN, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver in patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis: CT-histopathologic correlation. Radiology 1999;211:373-379. 10228516.


42. Itai Y, Murata S, Saida Y, Minami M. Central zone and peripheral zone of the liver based on portal and hepatic arterial blood supply: imaging approach to deformity of cirrhotic liver. Jpn J Clin Radiol 1994;39:1553-1559.
43. Mathieu D, Vasile N, Dibie C, Grenier P. Portal cavernoma: dynamic CT features and transient differences in hepatic attenuation. Radiology 1985;154:743-748. 3881794.


44. Ohtomo K, Baron RL, Dodd GD 3rd, Federle MP, Miller WJ, Campbell WL, et al. Confluent hepatic fibrosis in advanced cirrhosis: appearance at CT. Radiology 1993;188:31-35. 8511316.


45. Hussain HK, Syed I, Nghiem HV, Johnson TD, Carlos RC, Weadock WJ, et al. T2-weighted MR Imaging in the Assessment of Cirrhotic Liver. Radiology 2004;230:637-644. 14739306.


46. Ohtomo K, Baron RL, Dodd GD 3rd, Federle MP, Ohtomo Y, Confer SR. Confluent hepatic fibrosis in advanced cirrhosis: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 1993;189:871-874. 8234718.


47. Brancatelli G, Baron RL, Federle MP, Sparacia G, Pealer K. Focal con fluent fibrosis in cirrhotic liver: natural history studied with serial CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;192:1341-1347. 19380559.


48. Kelekis NL, Makri E, Vassiou A, Patsiaoura K, Spiridakis M, Dalekos GN. Confluent hepatic fibrosis as the presenting imaging sign in nonadvanced alcoholic cirrhosis. Clin Imaging 2004;28:124-127. 15050225.


49. Ooi CG, Chan KL, Peh WC, Saing H, Ngan H. Confluent hepatic fibrosis in monozygotic twins. Pediatr Radiol 1999;29:53-55. 9880618.


50. Park YS, Lee CH, Kim BH, Lee J, Choi JW, Kim KA, et al. Using Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced 3-T MRI for the differentiation of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma and focal confluent fibrosis in liver cirrhosis. Magn Reson Imaging 2013;31:1137-1142. 23688409.


51. Kim TK, Choi BI, Han JK, Jang HJ, Cho SG, Han MC. Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma of the liver: two-phase spiral CT findings. Radiology 1997;204:539-543. 9240550.


52. Choi BI, Kin TK, Han JK. MRI of Clonorchiasis and Cholagiocarcinoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 1998;8:359-366. 9562062.


53. Guo LH, Xu HX. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Controversy over the ASSLD Guideline. Biomed Res Int 2015;349172. 26090401.




54. Wilson SR, Kim TK, Jang HJ, Burns PN. Enhancement patterns of focal liver masses: discordance between contrast-enhanced sonography and contrast-enhanced CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007;189:W7-W12. 17579140.


55. Fowler KJ, Sheybani A, Parker RA 3rd, Doherty S, M Brunt E, et al. Combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma (biphenotypic) tumors: imaging features and diagnostic accuracy of contrastenhanced CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;201:332-339. 23883213.


56. Lee SJ, Kim SY, Kim KW, Shin YM, Kim HJ, Lee JS, et al. Hepatic angiomyolipoma with minimal fat, mimicking hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol 2012;18:330-335. 23091816.



57. Kim R, Lee JM, Joo I, Lee DH, Woo S, Han JK, et al. Differentiation of lipid poor angiomyolipoma from hepatocellular carcinoma on gadoxetic acid-enhanced liver MR imaging. Abdom Imaging 2015;40:531-541. 25231411.


58. Jeon TY, Kim SH, Lim HK, Lee WJ. Assessment of triple-phase CT findings for the differentiation of fat-deficient hepatic angiomyolipoma from hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver. Eur J Radiol 2010;73:601-606. 19200676.


59. Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Grazioli L, Golfieri R, Lencioni R. Large regenerative nodules in Budd-Chiari syndrome and other vascular disorders of the liver: CT and MR imaging findings with clinicopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002;178:877-883. 11906867.


60. Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Grazioli L, Golfieri R, Lencioni R. Benign Regenerative Nodules in Budd-Chiari Syndrome and Other Vascular Disorders of the Liver: Radiologic-Pathologic and Clinical Correlation. Radiographics 2002;22:847-862. 12110714.


61. Newerla C, Schaeffer F, Terracciano L, Hohmann J. Multiple FNHLike lesions in a patient with chronic Budd-Chiari syndrome: Gd-EOB-enhanced MRI and BR1 CEUS findings. Case Rep Radiol 2012;685486. 22606569.




62. Yoneda N, Matsui O, Kitao A, Kita R, Kozaka K, Koda W, et al. Hepatocyte transporter expression in FNH and FNH-like nodule: correlation with signal intensity on gadoxetic acid enhanced magnetic resonance images. Jpn J Radiol 2012;30:499-508. 22618456.


63. Memeo M, Stabile Ianora AA, Scardapane A, Buonamico P, Sabb├Ī C, Angelelli G. Hepatic involvement in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: CT findings. Abdom Imaging 2004;29:211-220. 15290948.


64. Siddiki H, Doherty MG, Fletcher JG, Stanson AW, Vrtiska TJ, Hough DM, et al. Abdominal Findings in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Pictorial Essay on 2D and 3D Findings with Isotropic Multiphase CT. Radiographics 2008;28:171-184. 18203937.


65. Oliver JH 3rd, Baron RL. Helical biphasic contrast-enhanced CT of the liver: technique, indications, interpretation, and pitfalls. Radiology 1996;201:1-14. 8816509.

Figure┬Ā1
Arterioportal shunt in 70-year-old man with hepatitis B. (A) There is a wedge shaped subcapsular hyperattenuating lesion in the liver. There is a tubular hyperattenuating structure (arrow) representing early opacification of the branching portal vein due to arterioportal shunt. (B) In the portal venous phase, the lesion is not visible due to isoattenuation.
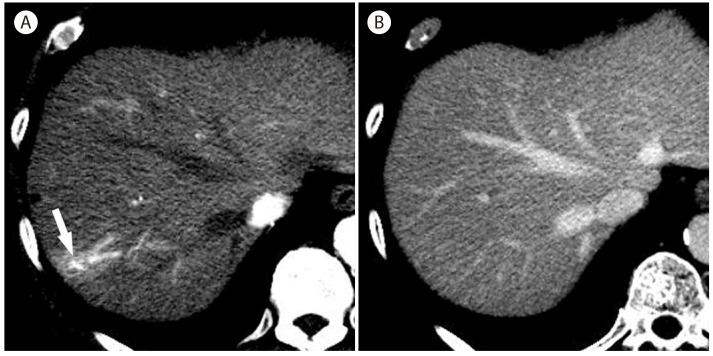
Figure┬Ā2
Fast filling and fading hemangioma with ar teriopor tal shunt in 75-year-old woman. (A) CT scan in the arterial phase shows a homogenously enhancing nodule (arrow) associated with a wedge shaped hyperenhancement representing a hemangioma with arterioportal shunt. (B) In the portal venous phase, the hemangioma (arrow) is homogenously enhancing but with a lesser degree than portal vein. The arterioportal shunt which was shown in the arterial phase is not seen due to isoattenuation.
Figure┬Ā3
Hemangioma in 45-year-old woman with hepatitis B. (A) CT in the arterial phase shows hypervascular mass (arrow) with heterogeneous enhancement. (B) CT in the delayed phase shows homogenous hypervascular mass (arrow) in the liver. (C) On gray scale US, the mass shows hypoechogenicity (arrow). The mass shows peripheral nodular enhancement with rapid central filling in two consecutive images (D, E; arrows) of CEUS after microbubble disruption using high mechanical-index frames. The mass shows strong homogenous enhancement in the late phase (F; arrows), which is diagnostic of hemangioma.
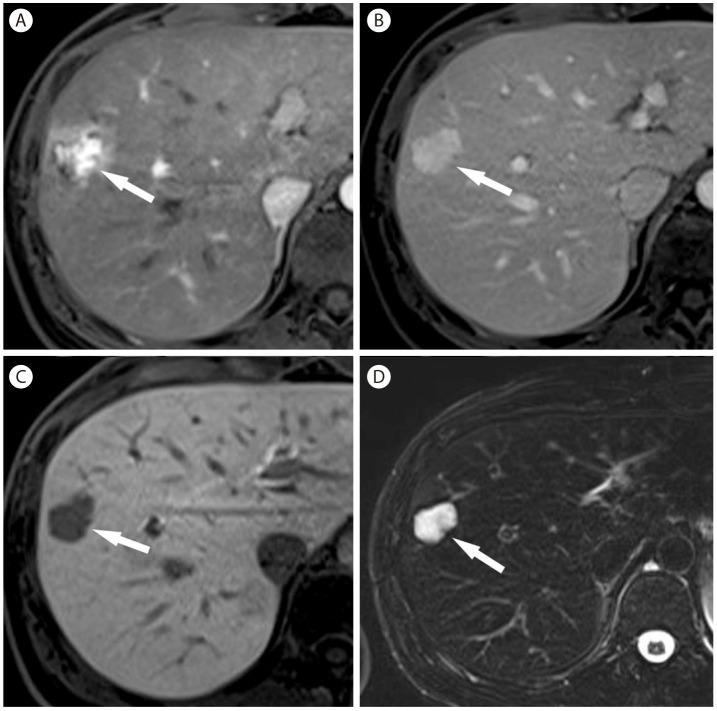
Figure┬Ā4
Hemangioma in 40-year-old woman with hepatitis B. (A) Arterial phase of T1-weighed postcontrast image with gadoxetic acid shows heterogeneous hypervascular nodule (arrow) in the liver. (B) In portal venous phase the nodule (arrow) shows hyperenhancement. (C) In hepatobiliary phase, the nodule (arrow) shows marked hypointensity. (D) On T2-weighted image, the nodule (arrow) is markedly hyperintense.
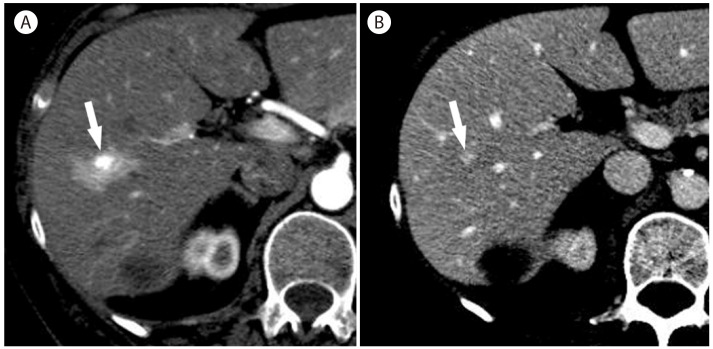
Figure┬Ā5
Sclerosed hemangioma in 69-year-old woman. (A) Unenhanced T1-weighted MR image shows a hypointense mass (arrow) in the liver. There is mild peripheral enhancement of the mass (arrow) in the arterial phase (B) which progresses in the late phase (C, arrow). However, there is no typical enhancement pattern for hemangioma. (D) On T2-weighted image, the mass (arrow) is mildly hyperintense.
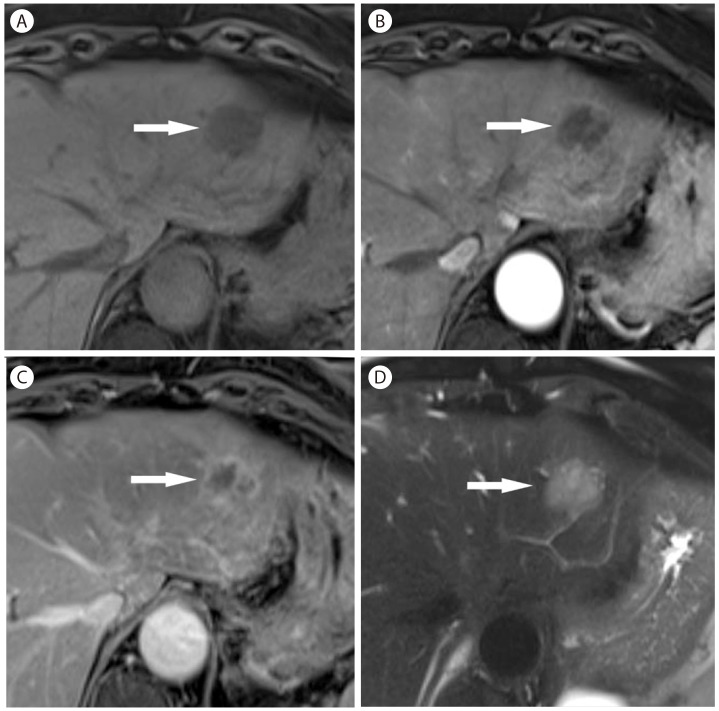
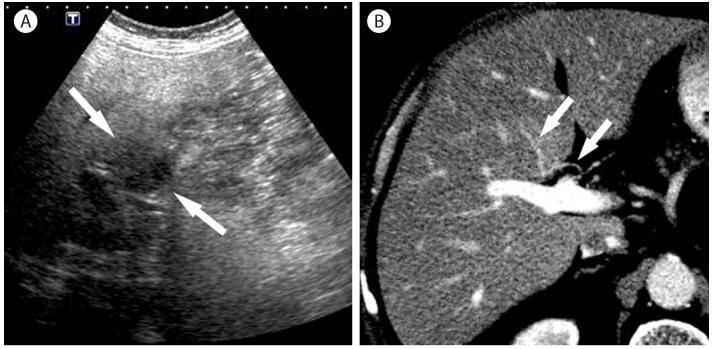
Figure┬Ā6
Focal fat sparing in 69-year-old man with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. (A) Oblique ultrasound scan shows a hypoechoic mass like lesion (arrows) in the liver. (B) CT scan in the portal venous phase shows an aberrant drainage of the right gastric vein (arrows) into the segment 4b of the liver, which shows slight hyperattenuation.
Figure┬Ā7
Focal fat sparing in 59-year-old woman with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. (A) US scan shows a hypoechoic nodule (arrow) in the fatty liver. (B) Noncontrast CT shows fatty infiltration more severely involving the right lobe of the liver with a small hyperattenuating nodule (arrows). (C) In the arterial phase, the nodule (arrows) is slightly hyperattenuating compared to the surrounding liver with fatty infiltration. In phase (D) and out of phase (E) T1-weighted MR images show a diffuse reduction of liver signal intensity in the out of phase representing diffuse fatty liver, more severely involving the right liver. There is a hyperintense nodule (arrow) only visualized in the out of phase (E) representing nodular focal fat sparing.
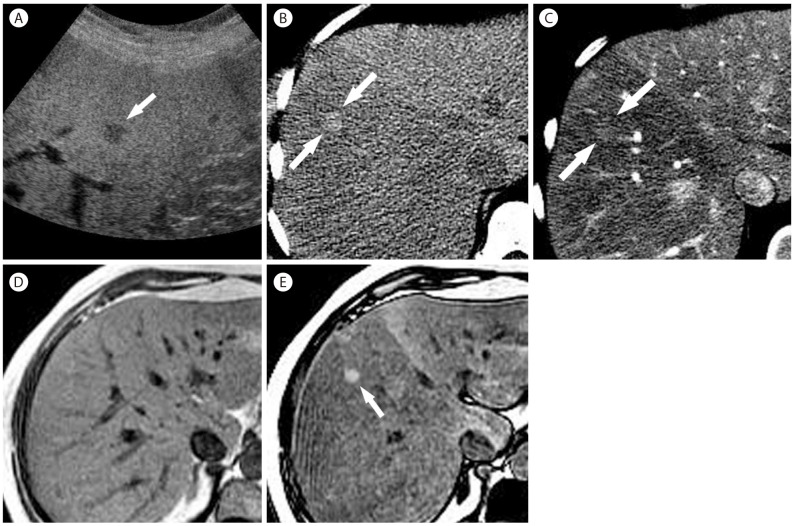
Figure┬Ā8
Multifocal fat deposit in 40-year-old woman with hepatitis B cirrhosis. (A) CT in venous shows multifocal ill-defined hypoattenuating lesions throughout the liver. In phase (B) T1-weighted MR image shows multifocal hepatic lesions which show signal-drop in the out of phase (C), confirming multifocal fat deposit.
Figure┬Ā9
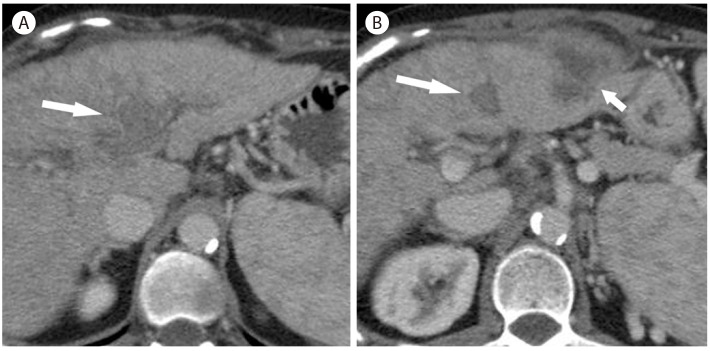
Perivascular fat deposition in 63-year-old woman with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. (A) On noncontrast image, there is marked hypoattenuating subcapuslar lesion (arrows) in the left lobe. The lesion (arrows) shows heterogeneous enhancement in the arterial phase (B) and shows marked hypoenhancement in the delayed phase (C).
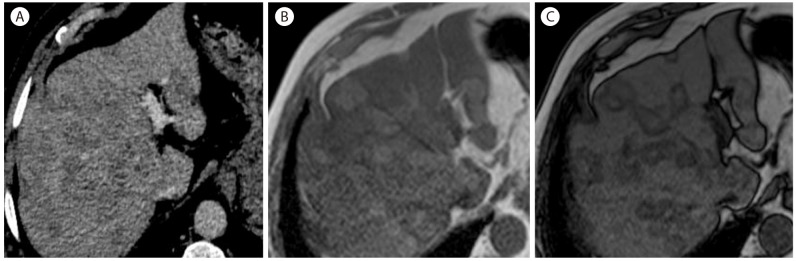
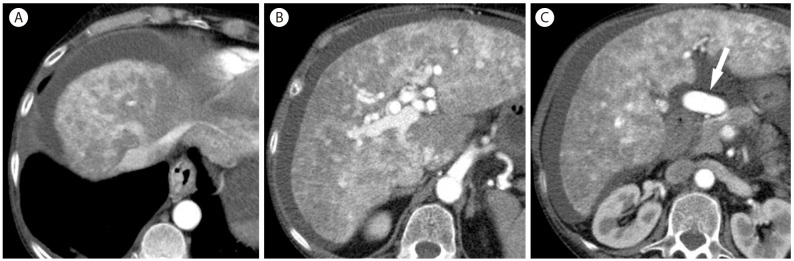
Figure┬Ā10
Abscess with portal vein thrombosis in 54-year-old woman in hepatitis C cirrhosis. On CT scan in the portal vein phase (A, B), there is thrombosis (arrow) within the portal vein. There is an exophytic heterogeneous hypoattenuating mass (B, short arrow) in the left lobe of the liver. Biopsy revealed a pyogenic abscess
Figure┬Ā11
Inf lammatory mass in 66-year-old man with hepatitis C cirrhosis. (A) CT in the arterial phase show a heterogeneous hypoattenuating mass (arrow) in the right lobe of the liver. (B) Oblique gray scale ultrasound shows a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass (arrow) in the liver. CEUS in the arterial (C) and venous (D) phase shows no enhancement in the lesion, confirming the diagnosis of avascular non-tumorous lesion (arrow).

Figure┬Ā12
Inflammatory pseudotumor in 39-year-old man. (A) T2-weighted MR image shows a mildly hyperintense mass (arrow) in the liver. (B) Gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted image in the arterial phase shows ill-defined rim-like enhancement (arrow). (C) Delayed-phase gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR image demonstrates retention of contrast agent within the mass (arrow) reflecting internal fibrosis. Biopsy revealed an inflammatory pseudotumor.
Figure┬Ā13
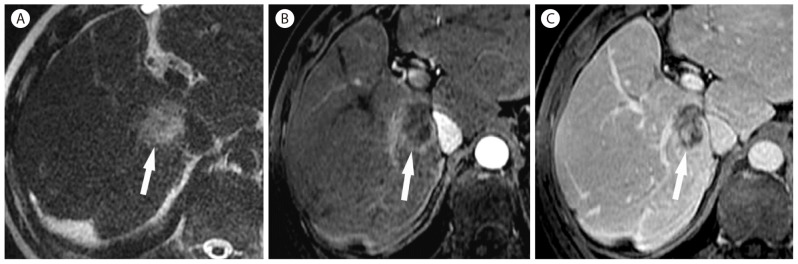
Inflammatory pseudotumor in 50-year-old woman. (A) Arterial phase CT scan shows a large mass (arrow) with heterogeneous enhancement and irregular intralesional arteries. (B) In the delayed phase, the mass (arrow) is heterogeneously hypoattenuating. Surgery revealed an inflammatory pseudotumor.
Figure┬Ā14
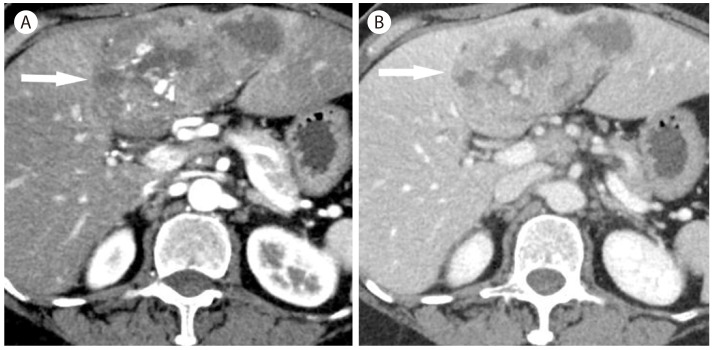
Portal vein thrombosis zones in 46-year-old woman with hepatitis B cirrhosis. (A) In the arterial phase, there is a large hypoattenuating mass like lesion surrounding the hepatic vessels. (B) In the portal venous phase scan shows extensive chronic portal vein thrombosis. The perivascular lesion remains hypoattenuating. (C) In the delayed phase, the lesion shows isoenhancement to the liver.
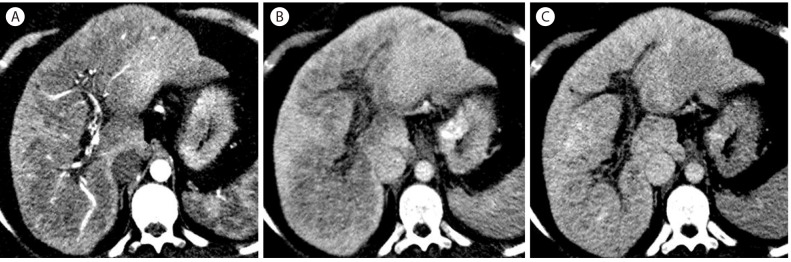
Figure┬Ā15
Confluent fibrosis in 63-year-old man with hepatitis B cirrhosis. (A) On T2-weighted image, there is an irregular hyperintense lesion (arrows) in the right lobe of the liver. (B) The lesion is slightly hypervascular in the arterial phase (arrows). There is slight capsular retraction of the liver (short arrow). (C) In 3 minutes delay, the lesion (arrows) is slightly hypointense. (D) In the hepatobiliary phase, the lesion (arrows) in markedly hypointense.
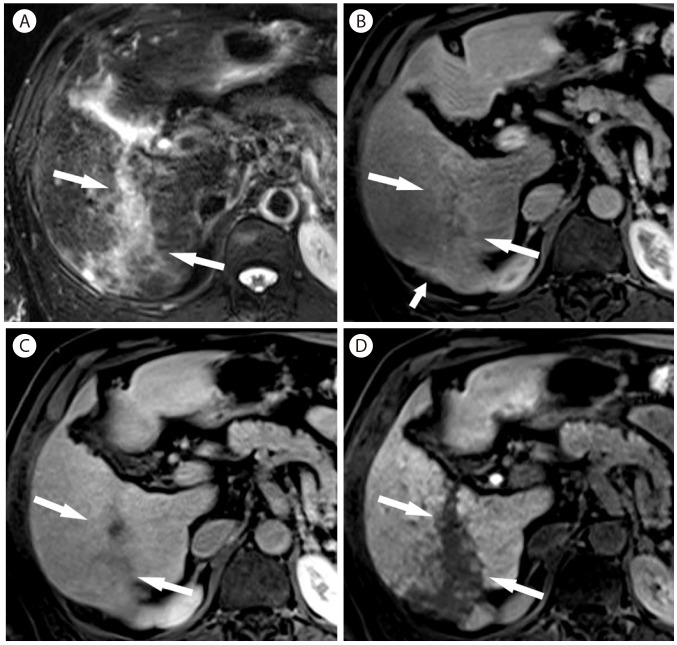
Figure┬Ā16
Confluent fibrosis in 46-year-old woman with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. (A) On T1-weighted MR image, the liver shows heterogeneous signal intensity. (B) In the arterial phase, there is a heterogeneous hypervascular lesion in the subcapsular portion (arrows) with mild capsular retraction. (C) In delayed phase, the lesion (arrows) shows mild hyperenhancement relative to the liver. (D) On diffusion-weighted image, the lesion is hyperintense.

Figure┬Ā17
Large regenerative nodules and confluent fibrosis in 41-year-old woman with Budd-Chiari syndrome. (A) On T2-weighted image, there are multiple hypointense nodules (arrows). There are irregular hyperintense lesions (short arrows) representing confluent fibrosis associated with Budd-Chiari syndrome. (B) In the arterial phase of gadoxetic acid enhanced T1-weighted imaging, the nodules (arrows) are homogenously hypervascular. (C) The nodules (arrows) remain hyperenhancing at 3 minutes delay. (D) The nodules (arrows) are strongly hyperintense in the hepatobiliary phase. There are irregular hypoenhancing lesions representing confluent fibrosis (short arrows).
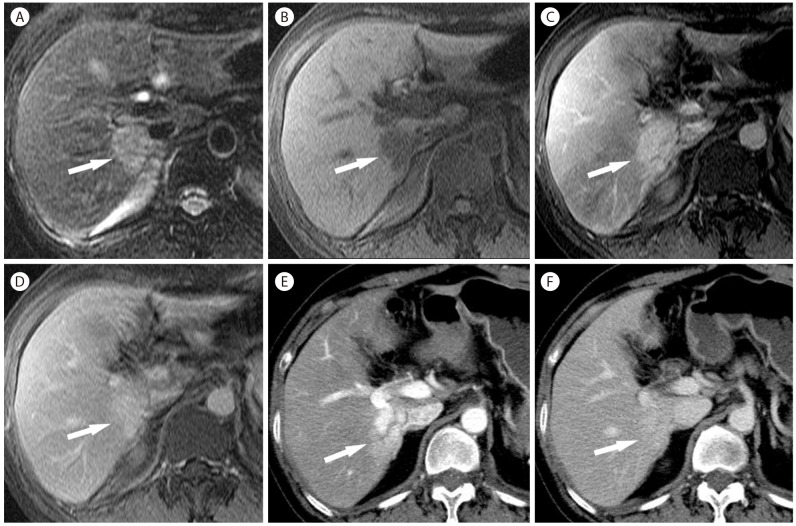
Figure┬Ā18
Intrahepatic mass-forming CC in 56-year-old woman with hepatitis B. (A) CT scan in the arterial phase shows mass (arrow) with heterogeneous hypervascularity. (B) The mass (arrow) shows persistent hyperattenuation in the delayed phase. (C) The mass (arrow) is hyperintense on T2-weighted MR image. (D) On T1-weighted image, the mass (arrow) is hypointense. The mass (arrow) is hyperintense in the arterial phase (E) and delayed phase (F).
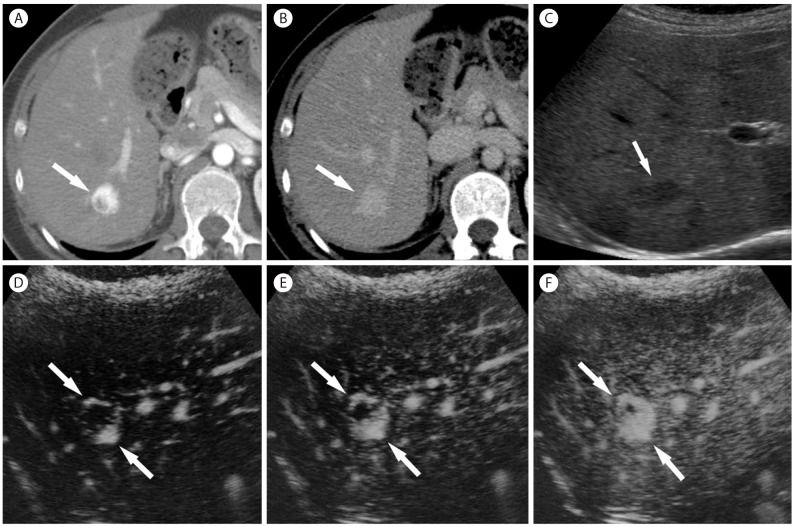
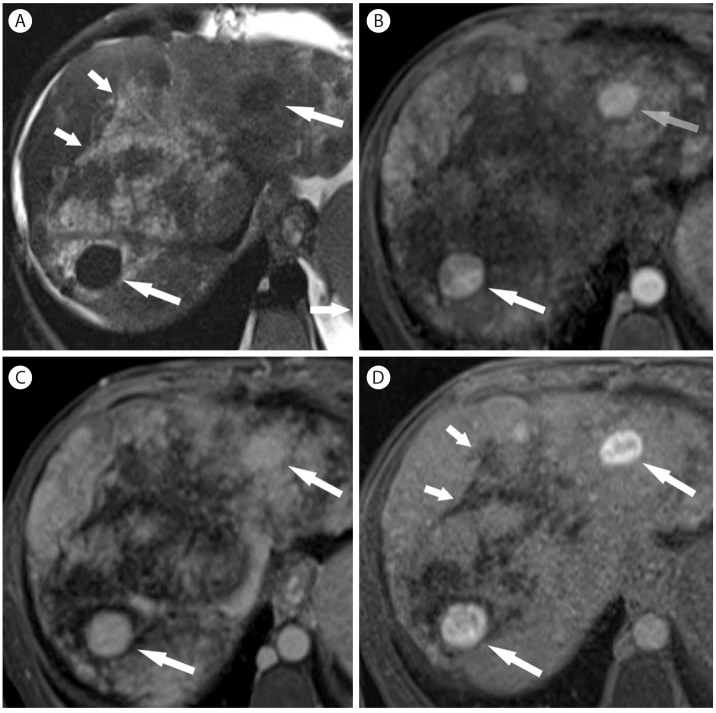
Figure┬Ā19
Intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma in 56-year-old woman with hepatitis B cirrhosis. (A) CT in the arterial phase show subcapsular hypoattenuating mass (arrow) with peripheral enhancement. (B) In the portal venous phase, the mass (arrow) is hypoattenuating. (C) Contrast enhanced ultrasound at 14 seconds show a mass (arrow) with mild peripheral hypervascularity. (D) At 15 seconds the tumor (arrow) shows diffuse heterogeneous hypervascularity. (E) At 28 seconds, tumor shows rapid wash-out. (F) At 108 seconds, the mass (arrow) shows marked wash out and is seen as punched out lesion.
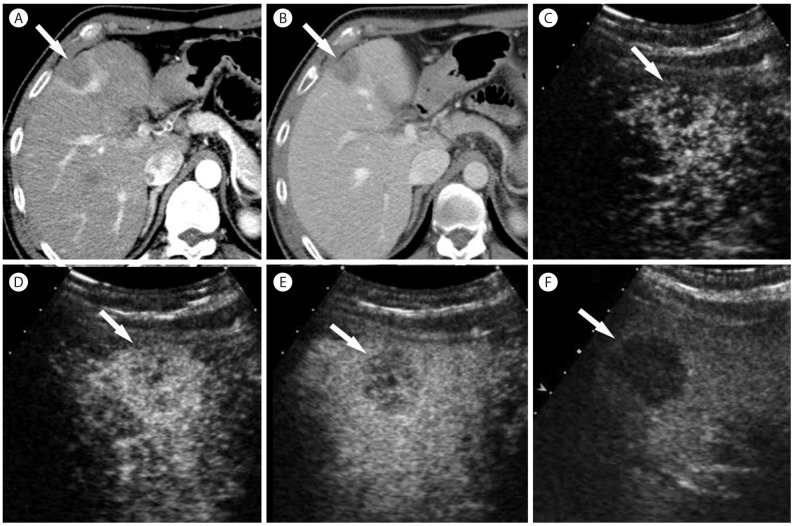
Figure┬Ā20
Mixed hepatocellular carcinoma/cholangiocarcinoma in 61-year-old woman. (A) In the arterial phase, there is hypoattenuating mass (arrow) with peripheral enhancement. There is a hypervascular mass (short arrow) in the left lobe, representing focal nodular hyperplasia. The mass (arrow) is hypoattenuating in portal venous phase (B) and delayed phase (C). There is central hyperenhancing area in the delayed phase (C).
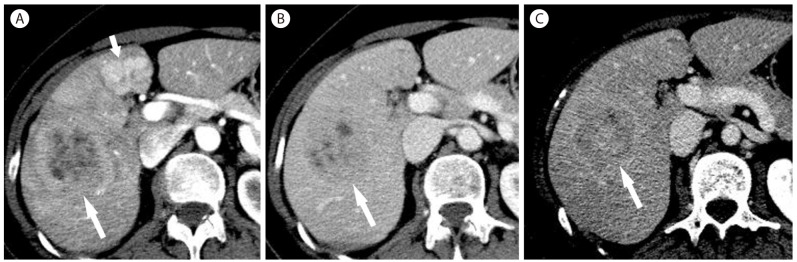
Figure┬Ā21
Fat-deficit angiomyolipoma in 43-year-old woman. (A) T1-weighted image shows mass (arrow) with multiple hyperintense foci representing hemorrhagic necrosis in the left lobe. There are two typical hemangiomas (short arrows). Arterial (B) and venous (C) phase postcontrast T1-weighted images show heterogeneous enhancement with areas of nonenhancing necrosis. (D) On T2-weighted image, the mass shows hyperintensity with small areas of hemorrhagic necrosis showing fluid-fluid levels.
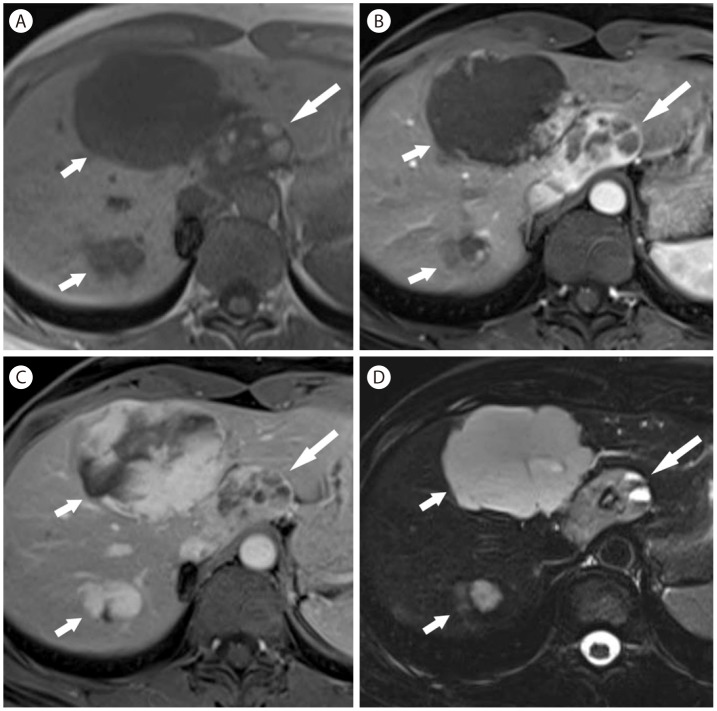
Figure┬Ā22
Regenerative nodule in 53-year-old woman with Budd-Chiari syndrome. (A) CT in the arterial phase shows heterogeneous enhancement of the liver, central hypertrophy with hyperenhancement which is characteristic findings of Budd-Chiari syndrome. There is a subcapsular hypervascular nodule (arrow). The nodule (arrow) remains hyperattenuating at 3 minutes delay (B). Three consecutive CEUS in the arterial phase (C, D, and E) show hypervascularity with centrifugal enhancement of the nodule (arrow). (F) At 3 minutes delay, the nodule (arrow) shows sustained hyperenhancement.

Figure┬Ā23
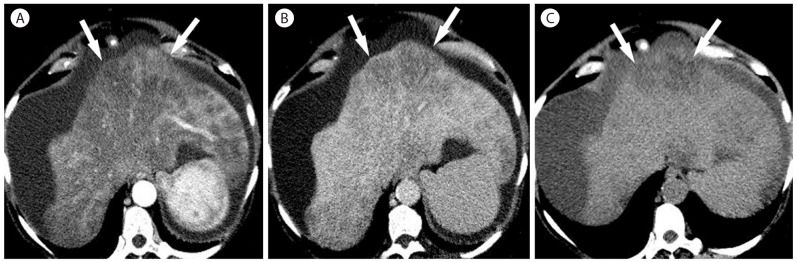
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in 65-year-old woman. Three CT images in the arterial phase (A, B, and C) show early opacification of the hepatic vein due to arteriovenous shunt (A) and marked heterogeneous enhancement with ill-defined hypervascular focal abnormalities throughout the liver. Common hepatic artery (arrow) is markedly enlarged (C).



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print




